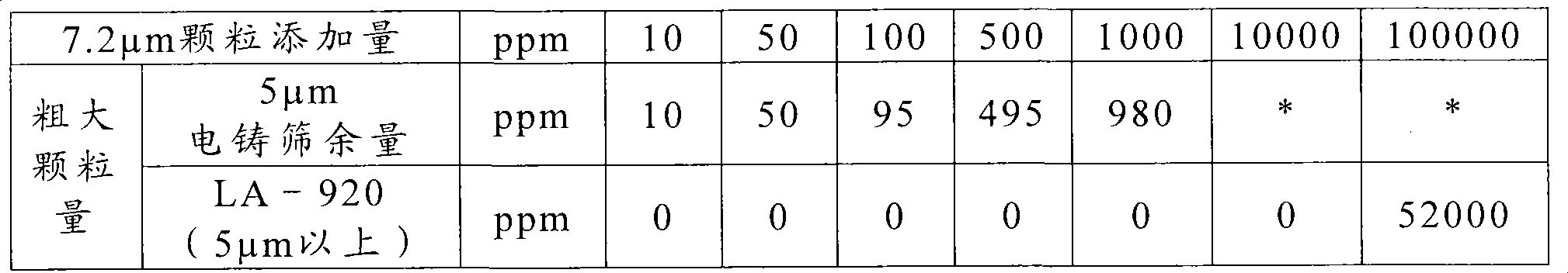Dry-process fine silica particle
A dry silica and particle technology, applied in the directions of silica, silica, electrography, etc., can solve the problems of poor interstitial permeability, reduced machine reliability, inability to control particle size distribution, etc., and achieve sharp particle size distribution, Excellent effect of suppressing abrasion and fluidity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
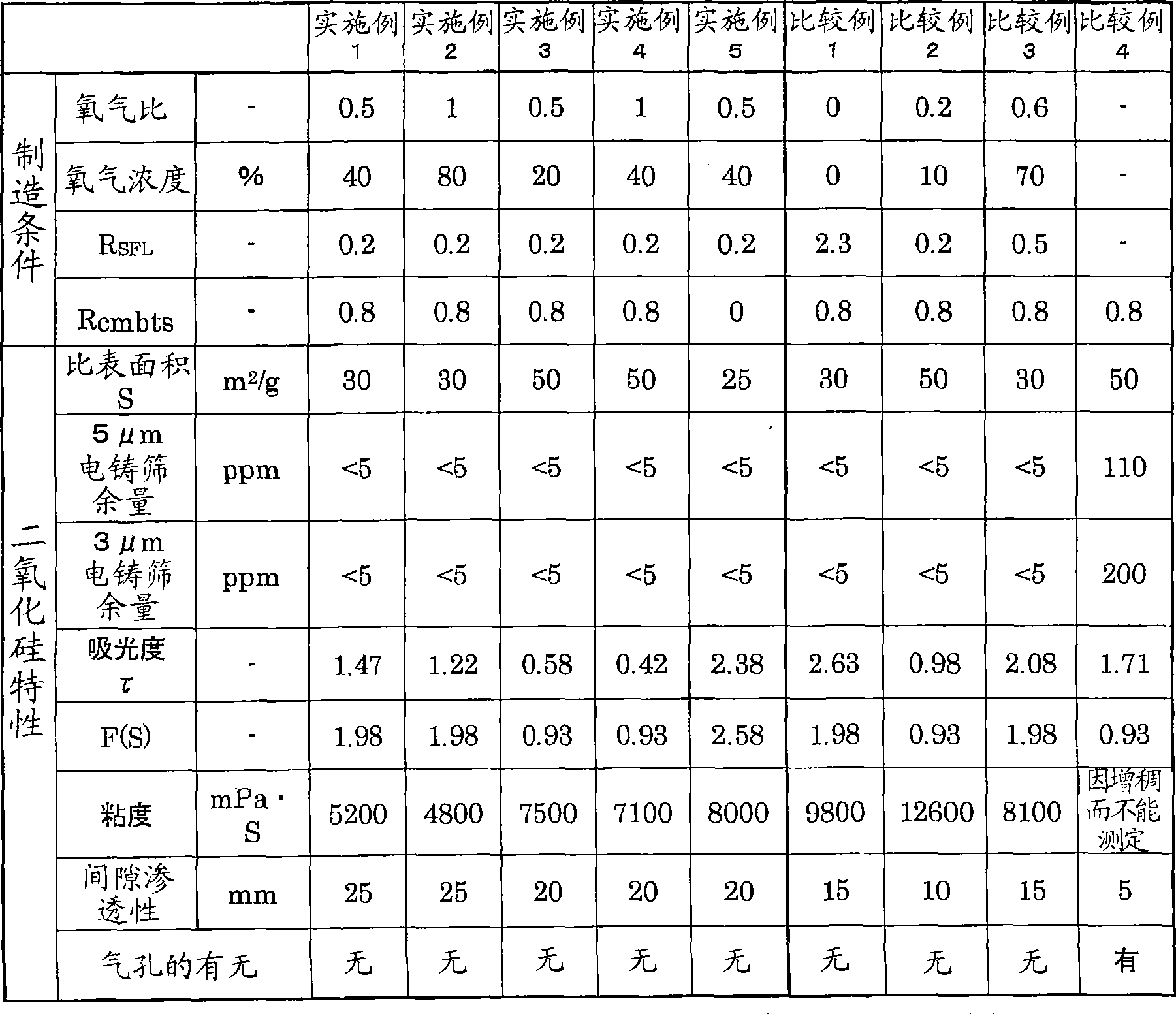
Embodiment 1~5、 comparative example 1-3
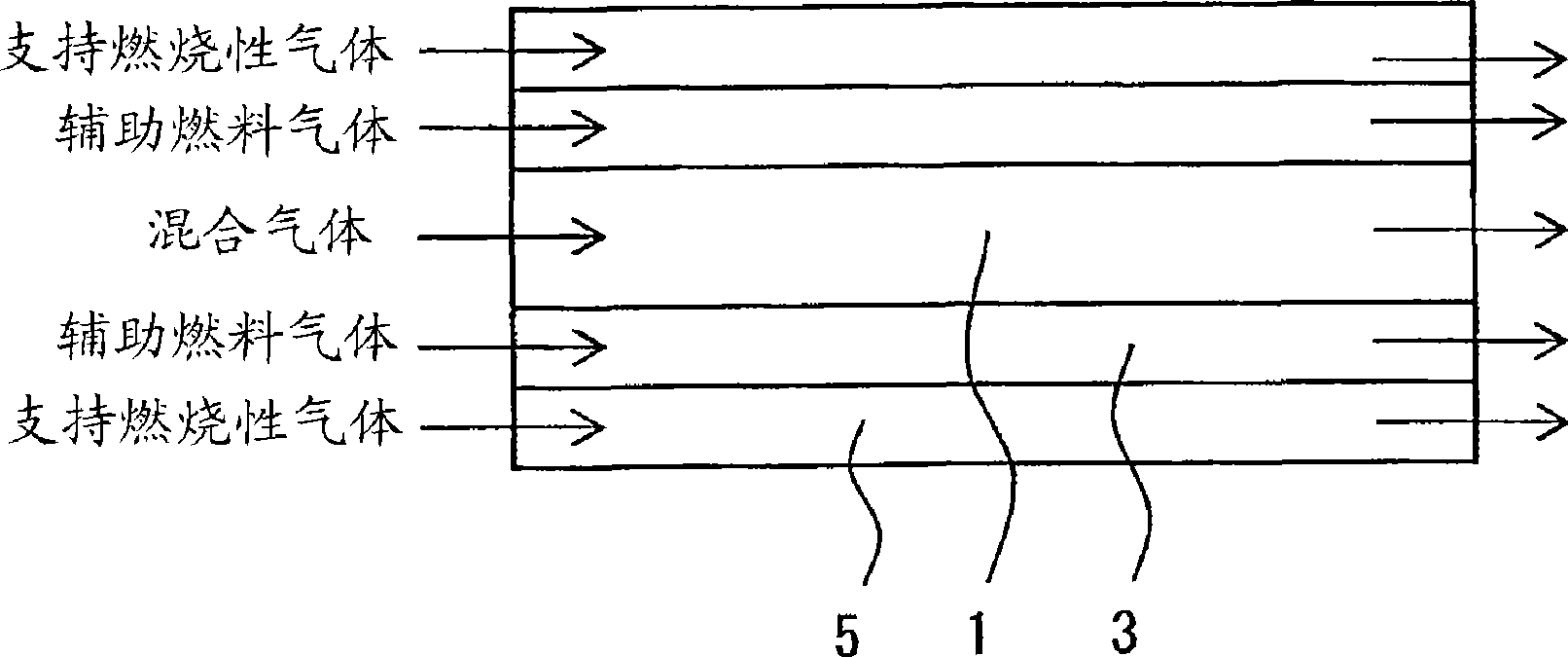
[0161] Octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane was burned in a three-layer tube burner as follows to produce silica fine particles.
[0162] After heating and vaporizing octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane, oxygen and nitrogen are mixed, they are introduced into the center tube of the burner. In addition, hydrogen as an auxiliary fuel gas is introduced into the first annular tube adjacent to the center tube, and oxygen as a supporting combustible gas is introduced into the second annular tube adjacent to the outside of the first annular tube. middle. The manufacturing conditions are as described in Table 2. (Also, in Example 5, silica fine particles were produced under exactly the same conditions as in Example 1, except that the supporting combustible gas was not introduced into the second annular pipe.)
[0163] The specific surface area S of the obtained silica fine particles, the sieve residue in electroformed sieves with openings of 5 μm and 3 μm, the absorbance τ of the aqueous suspensio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com