Hybrid protein rapid enzymolysis method
A protein and enzymatic hydrolysis technology, applied in instruments, analytical materials, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems that cannot meet the high-throughput analysis requirements of proteomics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
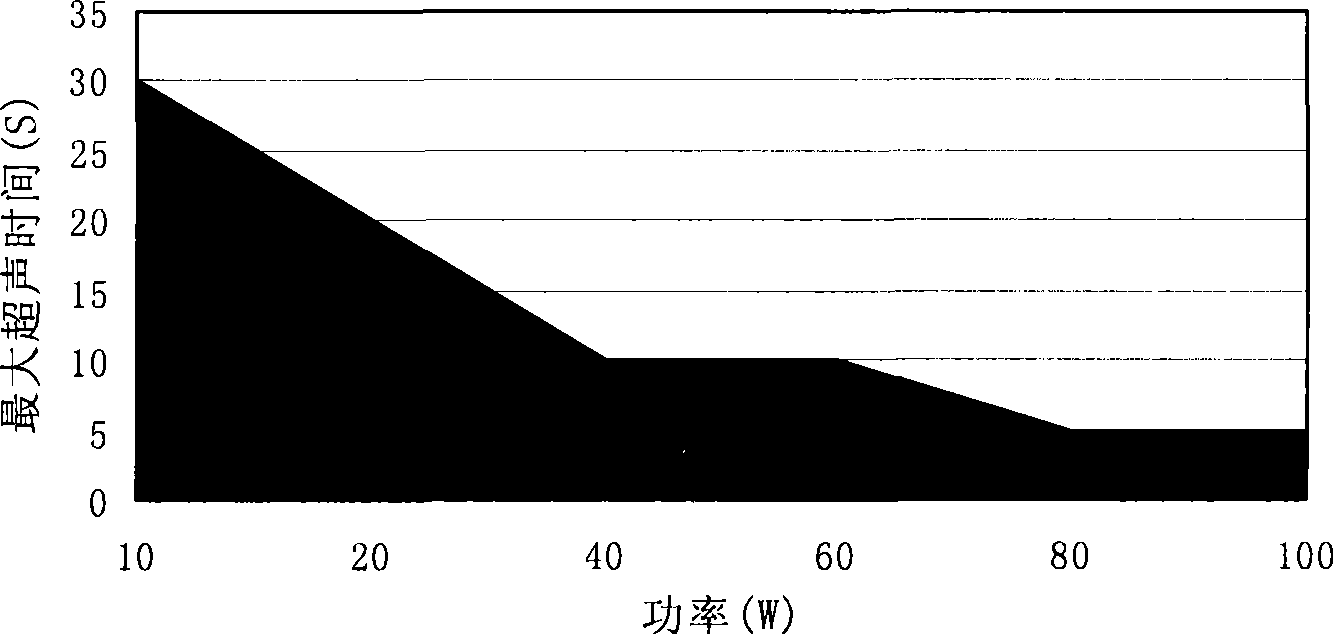
[0105] Example 1. Establishment of ultrasound power and ultrasound time safety zone
[0106] Mixed sample of 9 proteins (myosin 200KD, β-galactosidase 116KD, phosphatase b 97.2KD, bovine serum albumin 66.4KD, ovalbumin 44.287KD, carbonic acid 29KD, trypsin inhibitor 20.1KD , lysozyme 14.3KD and aprotinin 6.5KD) take 1μL (18μg / μL) after denaturation by traditional reagents, ultrasonic in the environment without the action of trypsin, the samples are detected by SDS-PAGE, analyzed by Total lab 2.0, according to Equation (1) calculates the relative percentage of protein remaining after sonication.
[0107] As a result, safe regions for ultrasound power and time were established see figure 1 , in the safe area, the protein molecules are basically not broken after being ultrasonicated, and the protein content in the sample is basically unchanged. When the total time of ultrasound is the same as the interval time, the effect of changing the continuous ultrasound time on the protei...
Embodiment 2
[0108] Embodiment 2. Determination of optimal conditions for ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis
[0109] In order to optimize the enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency, the two variables of ultrasonic power and ultrasonic time were selected, and a two-level response surface design (Response Surface Design) was carried out in the safe area. The response surface design is shown in Table 1 (according to the accuracy of the ultrasonic instrument power setting, the The design value of each variable was rounded up before the experiment). 1 μL (18 μg / μL) of the mixed sample of 9 proteins was denatured by traditional reagents, and then ultrasonic-assisted digestion was performed according to the response surface design table. The degree of digestion was detected by SDS-PAGE, analyzed by Total lab 2.0, and calculated according to formula (3) Relative percentage of protein digestion.
[0110] The results showed that the recommended values of each factor were power 22.53W (100μL syste...
Embodiment 3
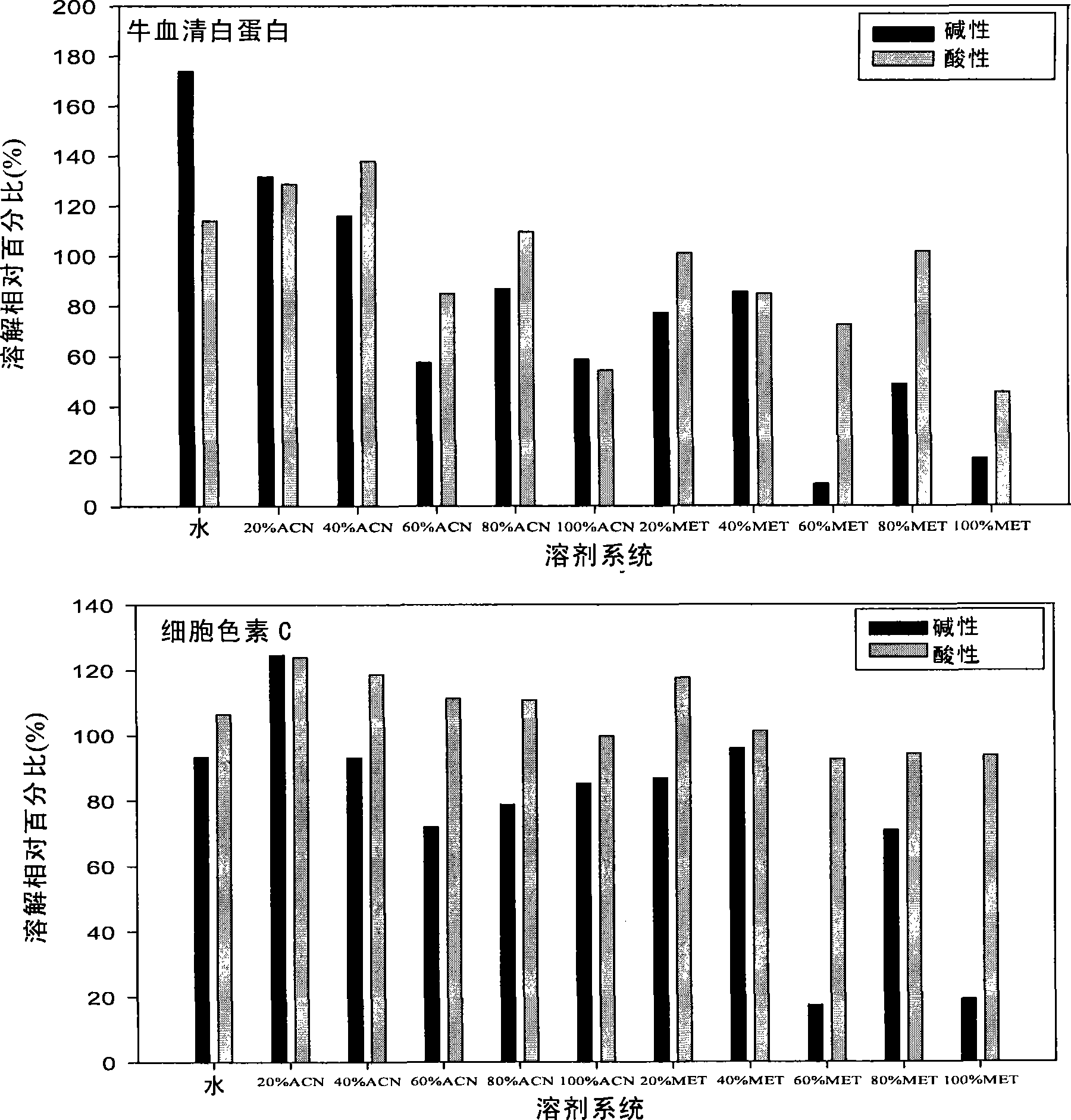
[0113] Example 3. System pH and organic phase ratio are adjusted to improve protein solubility during thermal denaturation
[0114] Take 0.5 μL (20 μg / μL) of bovine serum albumin (BSA) and cytochrome c and heat denature them in systems with different pH and organic phase ratios, then use SDS-PAGE to detect protein solubility, and use Total lab2.0 to analyze, according to Equation (2) calculates the relative percentage of protein solubilization.
[0115] The result is as figure 2 : When the pH of the system is acidic, the solubility of the protein after thermal denaturation is higher than when it is alkaline, especially the solubility difference of cytochrome c is more significant, and the solubility of BSA in the aqueous phase is higher after alkaline than acidic thermal denaturation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com