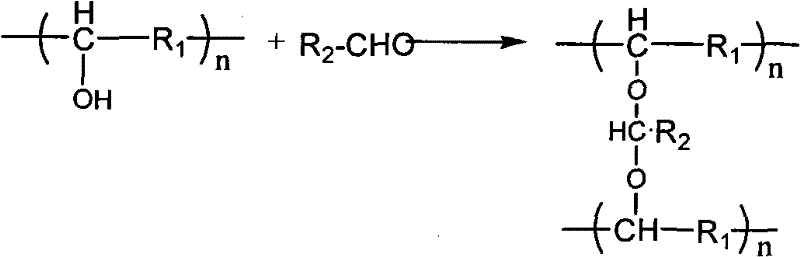
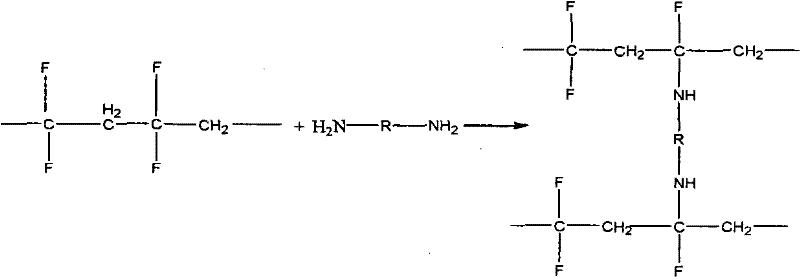Method for modifying interpenetrating polymer network on surface of polyvinylidene fluoride porous membrane
A polyvinylidene fluoride and interpenetrating polymer technology, applied in the field of separation membrane technology and membrane materials, can solve the problems of separation index decline, large driving force, and restricted application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] The polyvinylidene fluoride / N,N-dimethylacetamide solution with a polymer weight percentage of 25% is cast on a glass plate, and water is used as a coagulant, and a polyvinylidene fluoride porous flat film is prepared by a dry-wet method. Pure water flux is 600~700L / m 2 · h · 0.1MPa.
[0053] Soak the polyvinylidene fluoride flat film in an aqueous solution containing 1% polyvinyl alcohol and 0.2% glutaraldehyde for 10 minutes; then the polyvinylidene fluoride adsorbed polyvinyl alcohol and glutaraldehyde The ethylene porous membrane is immersed in an aqueous solution containing amine compounds, wherein the aqueous solution containing amine compounds contains ethylenediamine with a mass concentration of 50% and phosphoric acid with a mass concentration of 1%. The water temperature is controlled at 40°C. After reacting for 10 hours, soak in deionized water at 30°C for 12 hours to obtain a polyvinylidene fluoride porous membrane modified by a surface interpenetrating pol...
Embodiment 2
[0056] In Example 1, the N,N-dimethylformamide solution of the used polyvinylidene fluoride was spun through an annular spinneret, and this was all using water as the core liquid and the coagulation liquid. A hollow fiber membrane with an outer diameter of 1.6mm and an inner diameter of 0.9mm was obtained, and the pure water flux of the hollow fiber membrane was 600-700L / m 2 · h · 0.1MPa.
[0057] Then, the hollow fiber membrane was cross-linked in the same manner as in Example 1, wherein the aqueous solution containing amine compounds contained 90% ethylenediamine and 2% phosphoric acid. The pure water flux of the cross-linked hollow fiber membrane is 650-750L / m 2 · h · 0.1MPa, after 120 hours of continuous operation, the measured flux remains at 650-750L / m 2 · h · 0.1MPa. The prepared membrane was dried in an oven at 50°C for 24 hours, and then rehydrated directly after taking it out. The measured pure water flux was 550-600L / m 2 · h · 0.1MPa.
[0058] The cross-linked ...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Put the polyvinylidene fluoride resin and benzophenone into a high-temperature stirring tank and heat up It becomes a polymer homogeneous solution at 200°C, and then it is spun through a ring-shaped spinneret. The core liquid is glycerol, and water is used as a coagulation bath. A hollow fiber membrane with an outer diameter of 1.6mm and an inner diameter of 0.9mm was obtained, and the pure water flux of the hollow fiber was 800-1000L / m 2 · h · 0.1MPa.
[0061] Then, the hollow fiber membrane is carried out cross-linking reaction in the same manner as in Example 1, wherein the aqueous solution containing the amine compound contains 50% hexamethylenediamine, 40% methylamine and 1.5% phosphoric acid . The pure water flux of the cross-linked hollow fiber membrane is 850-1100L / m 2 · h · 0.1MPa, after 120 hours of continuous operation, the measured flux remains at 850-1100L / m 2 · h · 0.1MPa. The prepared membrane was dried in an oven at 50°C for 24 hours, and then rehyd...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com