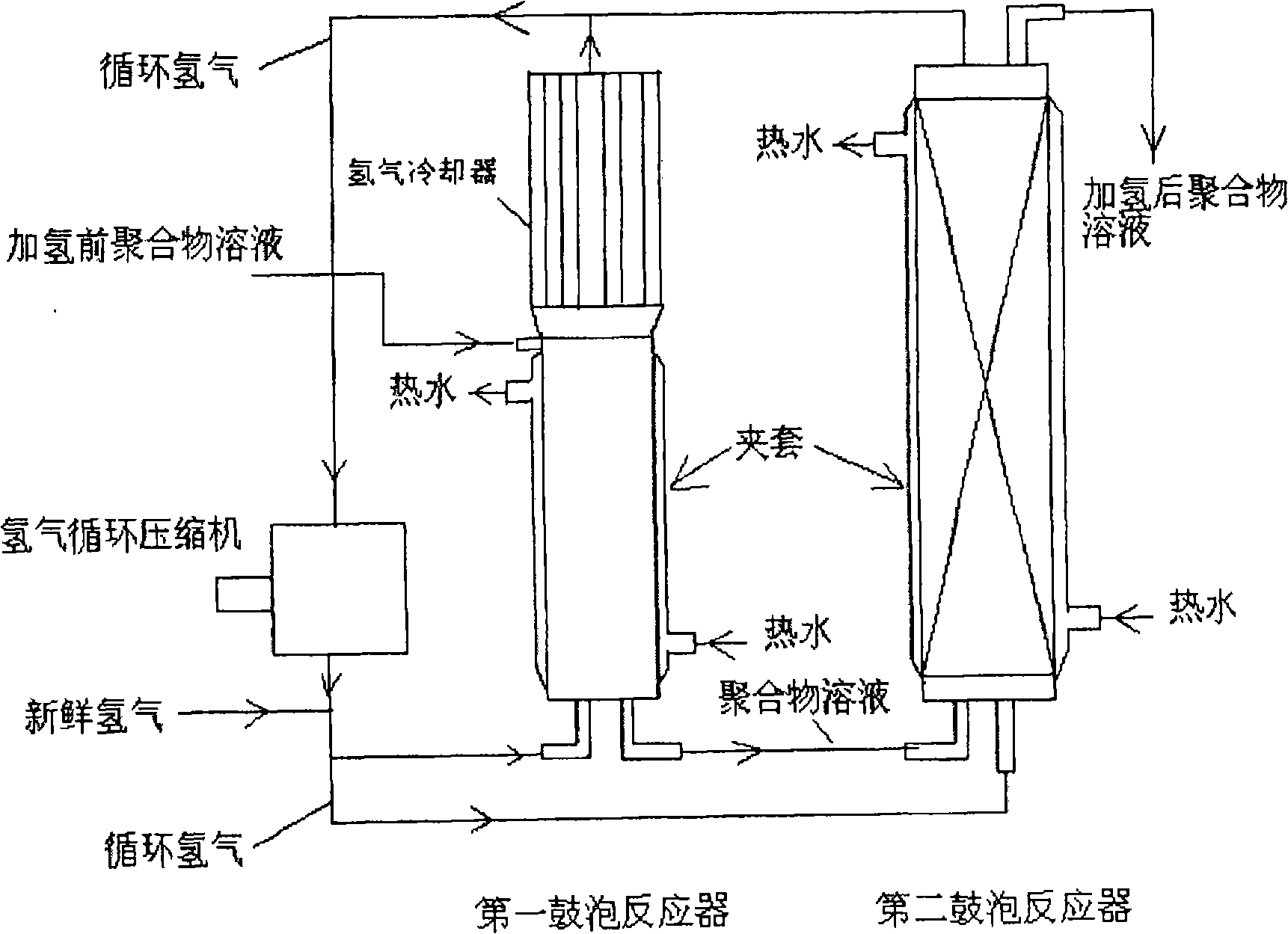
Hydrogenator and polymer hydrogenation method
A hydrogenation reactor and a hydrogenation reaction technology are applied in the field of combined hydrogenation reactors, which can solve the problems affecting the efficiency of the hydrogenation reaction, energy consumption, and high manufacturing costs, and improve the activity of the hydrogenation catalyst and the efficiency of the hydrogenation reaction. , Low manufacturing and maintenance costs, and the effect of reducing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] The 500L jacketed stirred reactor was replaced with refined nitrogen, and after the replacement, 250L of refined mixed solvent of cyclohexane and hexane (the weight percentage of cyclohexane was 87wt%) and 3.6L of refined styrene were added, and n-butyllithium and Tetrahydrofuran was reacted at 50-60°C for 30 minutes, 24.6L of refined butadiene was added to react for 30 minutes, and then 3.6L of refined styrene was added to react for 30 minutes. After the reaction was completed, 30mL of isopropanol was added to terminate the reaction. Butadiene-styrene block copolymer concentration is 10wt% based on the whole polymerization system, the molar ratio of tetrahydrofuran and n-butyl lithium is 37:1, the number average molecular weight of this block copolymer is 55,000, styrene and butadiene The weight ratio of the diene monomer units is 3:7, and the vinyl content of the butadiene segment in the polymer is 38 wt%. Nickel naphthenate (Beijing Yanshan Synthetic Rubber Factory, ...
Embodiment 2
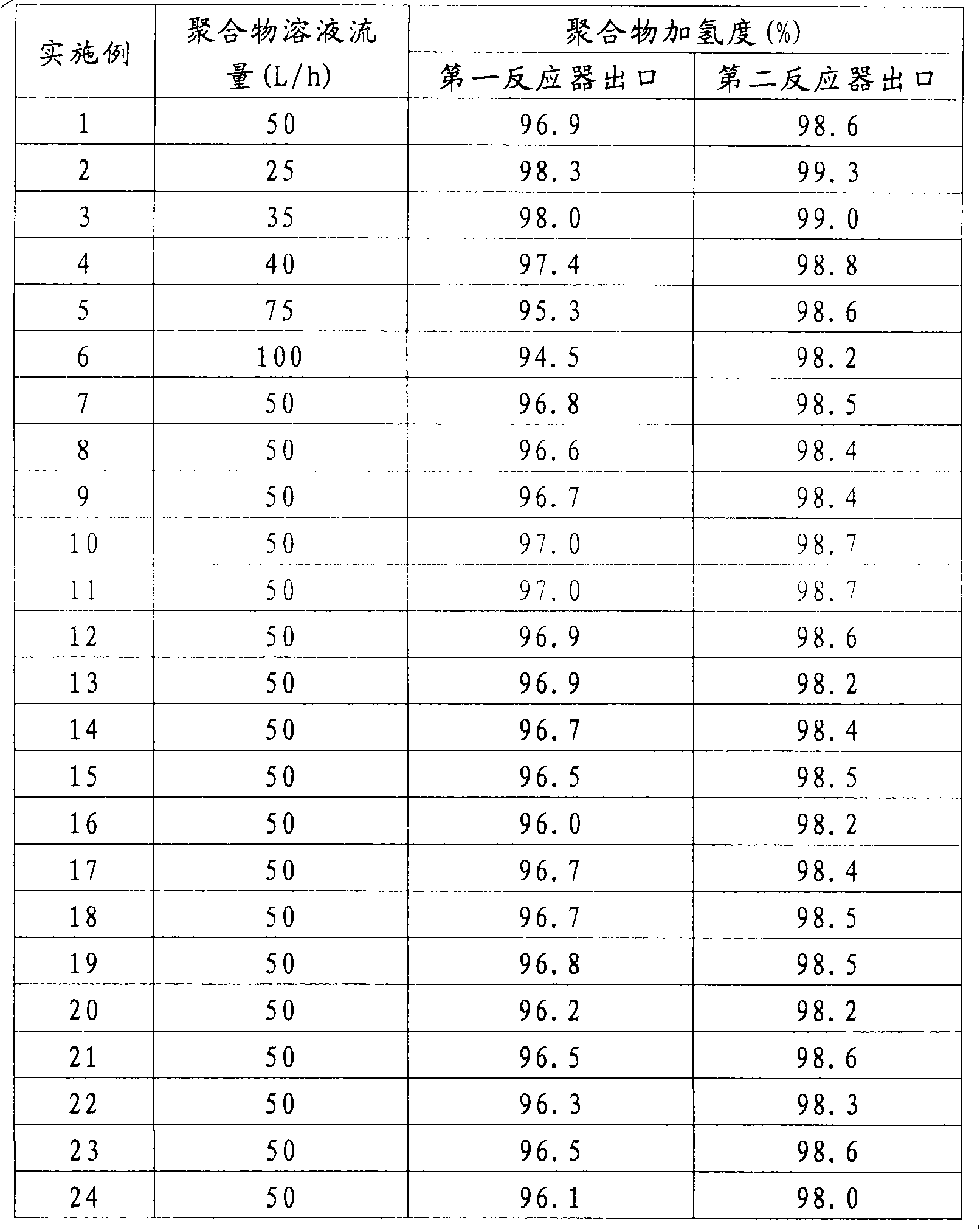
[0031] Repeat Example 1, but the polymer solution flow rate is 25L / h, and the hydrogenation reaction results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Repeat Example 1, but polymer solution flow rate is 35L / h, hydrogenation reaction result is shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com