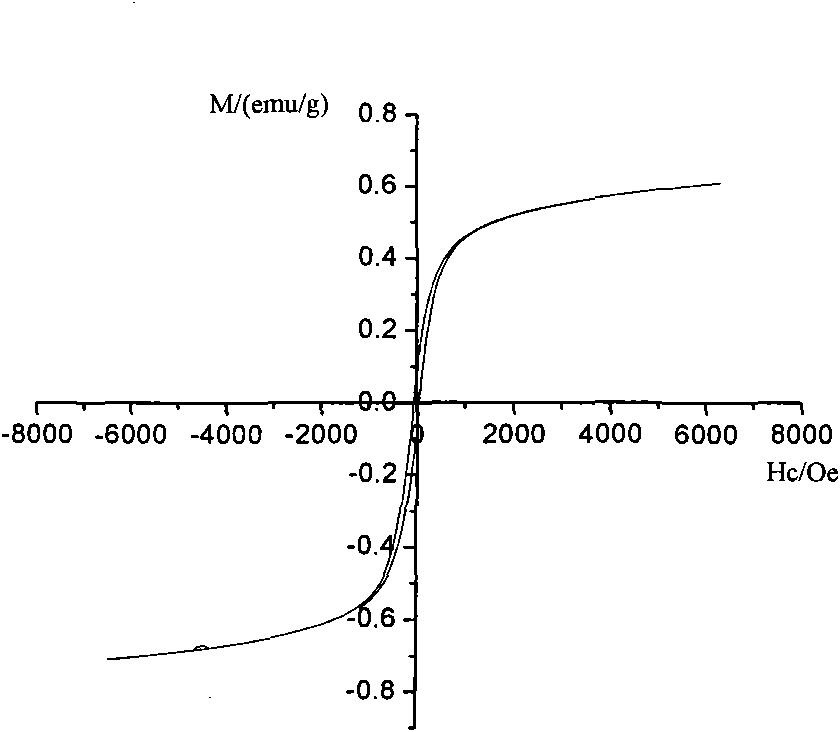Preparation of magnetic photocatalyst for absorption and photocatalytic degradation of dye waste water
A manganese chloride and mixed oxide technology, which is used in catalyst activation/preparation, adsorbed water/sewage treatment, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc. Good adsorption and photocatalytic degradation, realizing industrialization and uniform particle size distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Weigh a certain amount of lanthanum nitrate, ferric nitrate, manganese chloride and stearic acid respectively so that the molar ratio is 1:0.2:0.8:8. First, under the condition of constant temperature oil bath heating, dissolve stearic acid, under constant temperature magnetic stirring, dissolve lanthanum nitrate, ferric nitrate and manganese chloride solids in molten stearic acid, control the temperature at 115°C, and react for enough time to make it Become a stearic acid complex solution. Combust it at 500°C to obtain the precursor-mixed oxide, and its XRD diffraction pattern is shown in the attached Figure 2a . Take out the burned product and grind it into a muffle furnace, and calcinate it at 700°C for 1 hour to get LaFe 0.2 mn 0.8 o 3 Powder, its XRD diffraction pattern is shown in the attached Figure 2b .
Embodiment 2
[0028] Weigh a certain amount of lanthanum nitrate, ferric nitrate, manganese chloride, and stearic acid respectively so that the molar ratio is 1:0.4:0.6:7. First, under the condition of constant temperature oil bath heating, stearic acid is dissolved, and under constant temperature magnetic stirring, lanthanum nitrate, ferric nitrate, and manganese chloride solid are dissolved in molten stearic acid, and the temperature is controlled at 113°C, and the reaction time is sufficient to form Stearic acid complex solution, after it is burnt at 450 ℃, obtains precursor-mixed oxide, and its scanning electron microscope sees attached Figure 3a . Take out the burned product and grind it into a muffle furnace, and calcinate it at 650°C for 1 hour to get LaFe 0.4 mn 0.6 o 3 Powder, its scanning electron microscope SEM sees attached Figure 3b .
Embodiment 3
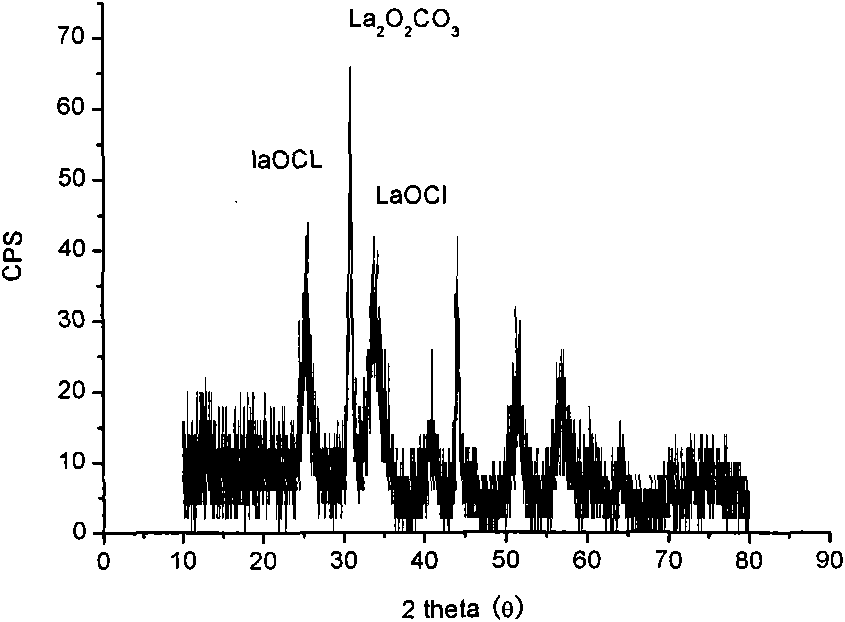
[0030] Weigh a certain amount of lanthanum nitrate, ferric nitrate, manganese chloride and stearic acid respectively so that the molar ratio is 1:0.6:0.4:8. First, under the condition of constant temperature oil bath heating, dissolve stearic acid, under constant temperature magnetic stirring, dissolve lanthanum nitrate, ferric nitrate and manganese chloride solids in molten stearic acid, control the temperature at 117°C, and react for enough time to make it Become a stearic acid complex solution. Combust it at 500°C to obtain the precursor-mixed oxide, which is LaOCl and La through XRD analysis 2 o 2 CO 3 And the mixture of amorphous powder. Take out the burned product and grind it into a muffle furnace, calcining it at 750°C for 1 hour to get the following Figure 4 LaFe shown 0.6 mn 0.4 o 3 Powder.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com