Reagents and methods for the determination of pk/adme-tox characteristics of new chemical entities and of drug candidates
A technology for optical properties and candidate compounds, which can be used in biological testing, measurement devices, scientific instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as low performance and timeliness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
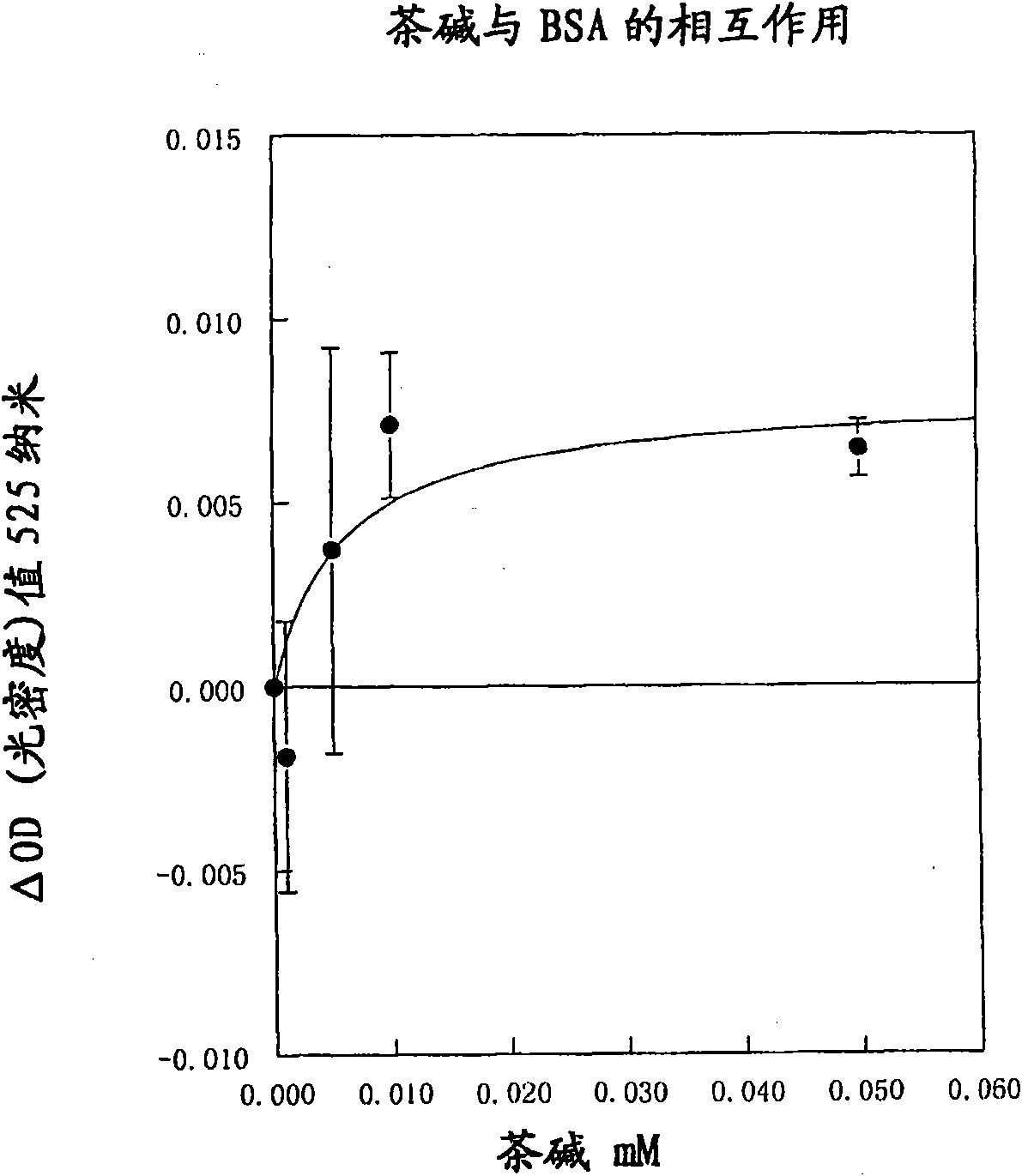
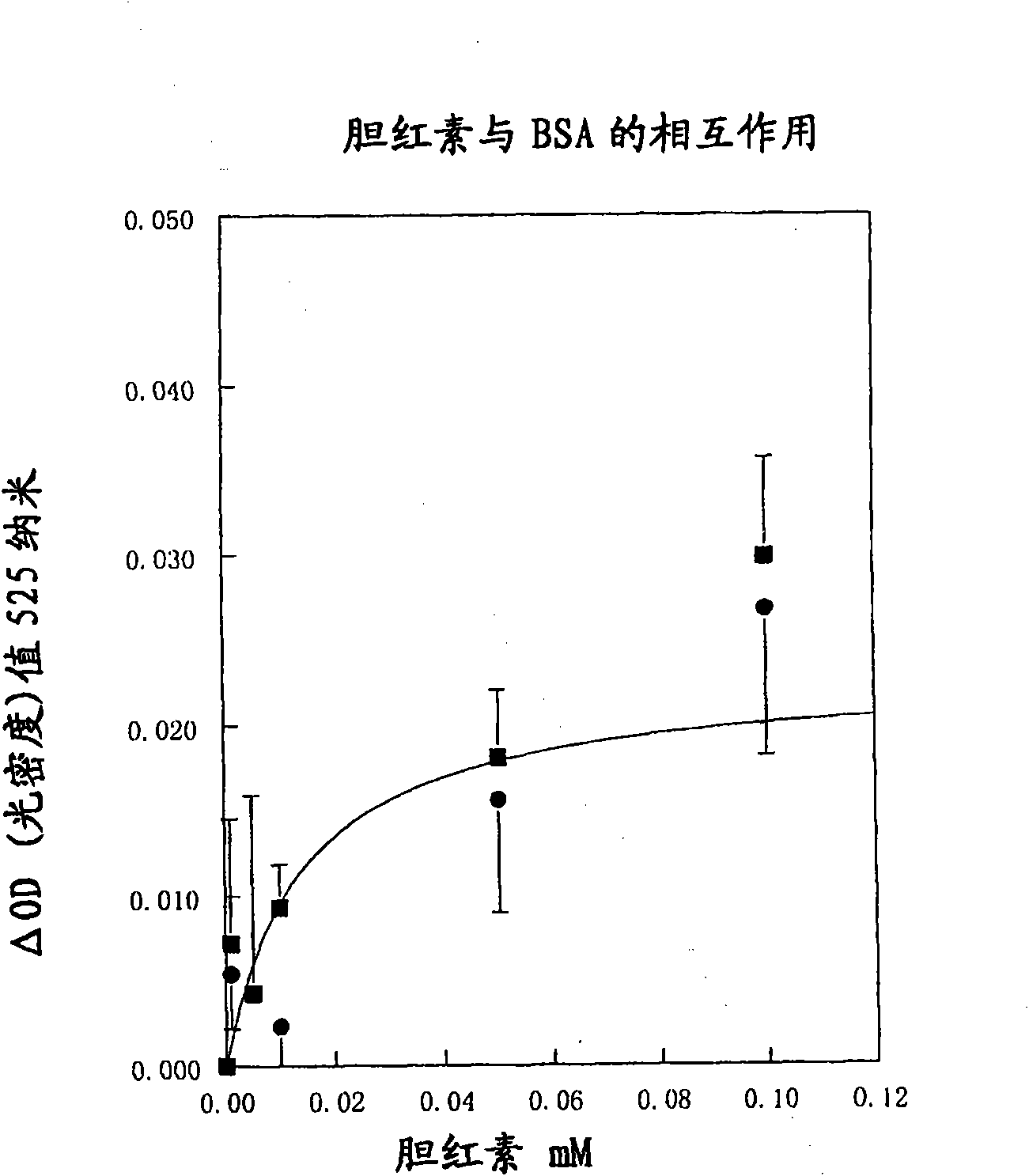
[0146] A solution of gold nanoparticles with an average diameter of 40 nm was prepared by dissolving 200 mg of tetrachloroauric acid (III) (Acros 22362-0010) in 500 ml of distilled water in a 1 liter Erlenmeyer flask. Add a magnetic bar and place the container on a magnetic stirrer. The solution was heated to boiling with vigorous stirring. When boiling, 30 ml of 1% sodium citrate (prepared by neutralizing 1% anhydrous citric acid (Sigma C-0759),) was quickly poured into the vessel. Boiling and stirring continued until the solution gradually turned black and then dark red, indicating the formation of nanoparticles. The solution was then cooled to room temperature. The resulting sol was characterized by an absorption band at 524 nm and an optical density value of 4 (of 1 cm).
[0147] A 10 ml amount of the colloidal gold solution was then poured into a beaker with a magnetic stirring bar and gradually neutralized to pH 6.5 using 10 mM sodium hydroxide under magnetic stirring...
Embodiment 2
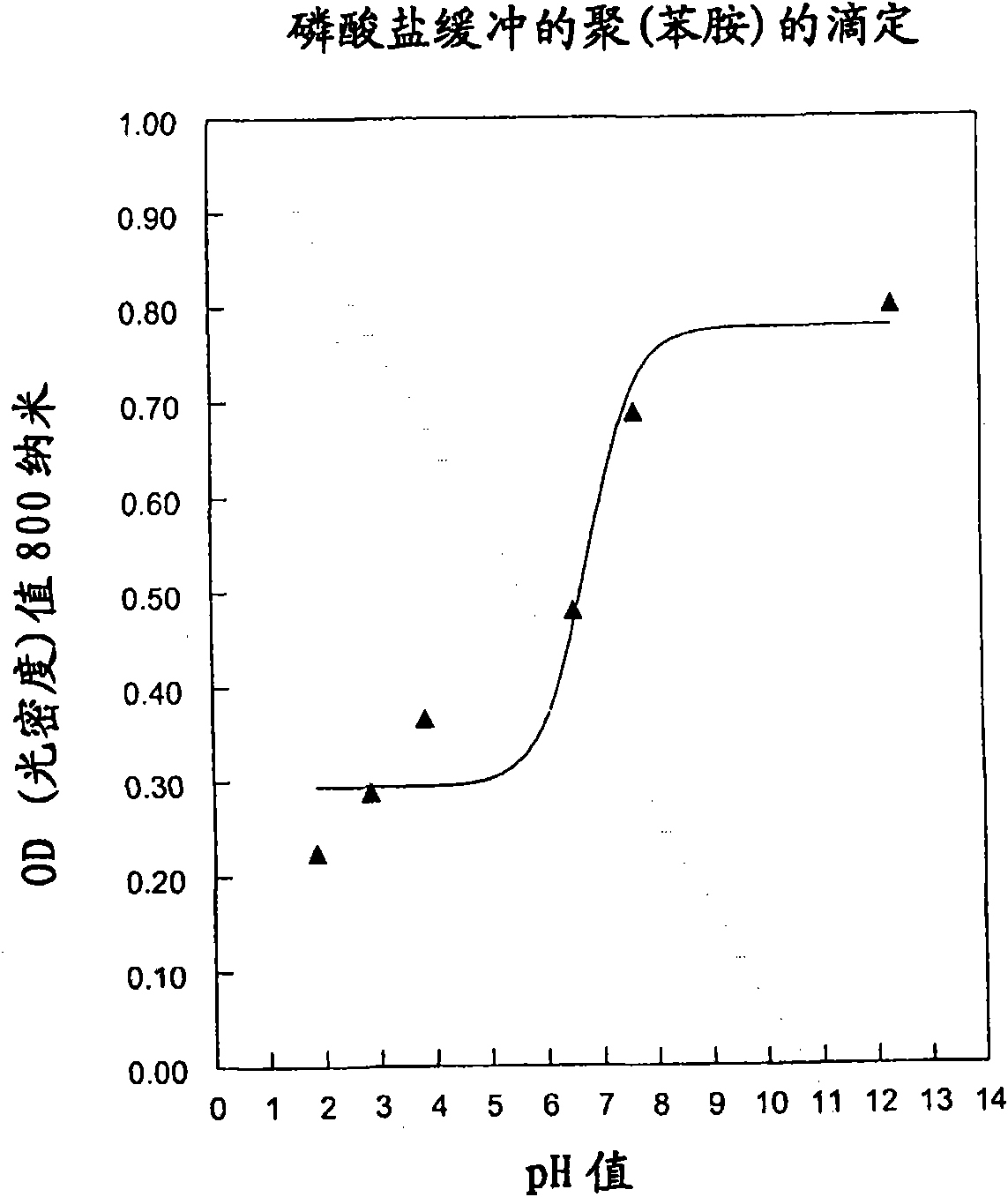
[0152] Colloidal poly(aniline) was obtained as follows: up to 10 g of poly(vinyl alcohol) was dissolved in 200 ml of boiling water. The hot solution was then filtered and cooled to room temperature. The solution was then acidified by adding 16.8 ml of 12N hydrochloric acid. A portion (100 ml) of this solution was transferred to a clean beaker with a magnetic bar placed on a magnetic stirrer at 4°C. The solution was stirred and 0.25 ml of aniline (Aldrich 24, 861-4) was injected. Immediately after the infusion, 658 mg of ammonium peroxodisulfate (Aldrich 24, 861-4) just dissolved in 5 ml of water was added. The solution remained stirring at 4°C for 48 hours. The colloid was then purified by chromatography on a Sephacryl S-1000 column, eluting with 0.1 M phosphate buffer, pH 8, containing 0.5% Tween 20.
[0153] The buffer was then titrated with hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide and the spectra at each pH value recorded during the titration were obtained (Ultrospec 2000,...
Embodiment 3
[0156] Colloidal gold sol is prepared according to the above-mentioned Example 1. The colloids were then coated with human serum albumin (HSA, Sigma A-1653) as described above, except that the colloidal gold was set at pH 5.5. The reagent was then buffered with 50 mM borate as above and further stabilized by the addition of 150 mM sodium chloride, Tween 20 (0.2%) and fish gelatin (0.1%), respectively.
[0157] Digoxigenin (Fluka 37100) was dissolved in methanol (100 mg / l, 128 μΜ) and further diluted in PBS to generate sample solutions containing 256, 128, 64, 25.8 and 12.8 nm, respectively. These samples (30 μl) were mixed with acceleration buffer (120 μl; 200 mM Tris-HCl pH 8 containing 250 mM magnesium chloride, 70 g / l polyethylene glycol 6000, 15 g / l polyethylene glycol 35,000 and Triton X-100 ( Triton X-100) 10ml / l) mixed. Mixing and reactions were carried out in a clinical chemistry analyzer (Cobas Mira Plus Analyzer, ABX Diagnostics, Montpellier, France) and in disposa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com