Method for preparing selective emission area of crystalline silicon solar cell
A solar cell and selective technology, applied in the direction of circuits, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in mass production, rising costs, and screen printing pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
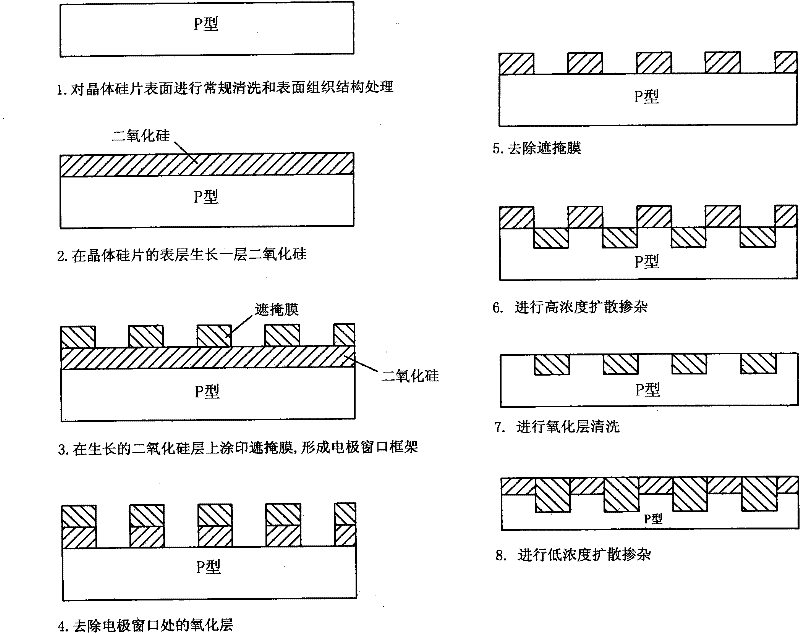
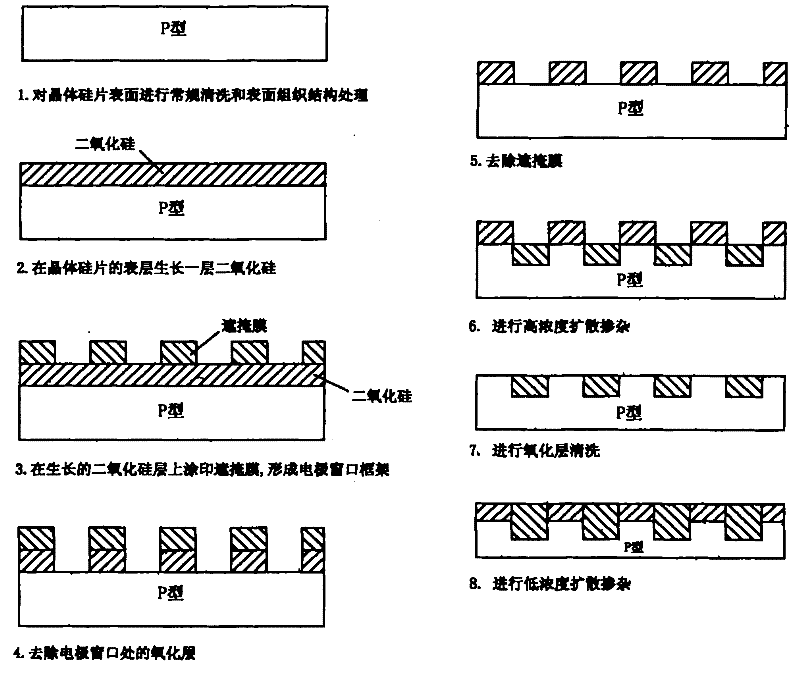
[0030] 1. Perform routine cleaning and surface structure treatment on the surface of crystalline silicon wafers.
[0031] 2. A layer of silicon dioxide is grown on the surface of the crystalline silicon wafer, and the thickness is controlled at 5nm.
[0032] 3. Applying a masking film on the grown silicon dioxide layer by screen printing to form an electrode window frame.
[0033] 4. Removing the oxide layer at the electrode window, that is, removing the silicon dioxide layer not covered by the masking film. A 10% hydrofluoric acid solution is selected to remove the silicon dioxide layer not covered by the masking film.
[0034] 5. Use 5% sodium hydroxide solution to remove the masking film.
[0035] 6. The liquid source of phosphorus oxychloride is converted into a gaseous state, and high-concentration diffusion doping is carried out at a high temperature of 870°C for 55 minutes.
[0036] 7. Cleaning the oxide layer, that is, removing the silicon dioxide layer originally c...
Embodiment 2
[0043] 1. Perform routine cleaning and surface structure treatment on the surface of crystalline silicon wafers.
[0044] 3. A layer of silicon dioxide is grown on the surface of the crystalline silicon wafer, and the thickness is controlled at 6nm.
[0045] 3. Applying a masking film on the grown silicon dioxide layer by screen printing to form an electrode window frame.
[0046] 4. Removing the oxide layer at the electrode window, that is, removing the silicon dioxide layer not covered by the masking film. A 12% hydrofluoric acid solution is selected to remove the silicon dioxide layer not covered by the masking film.
[0047] 5. Use 5% sodium hydroxide solution to remove the masking film.
[0048] 6. The phosphorus oxychloride liquid source is converted into a gaseous state, and high-concentration diffusion doping is carried out at a high temperature of 880°C for 53 minutes.
[0049] 7. Cleaning the oxide layer, that is, removing the silicon dioxide layer originally cove...
Embodiment 3
[0056] 1. Perform routine cleaning and surface structure treatment on the surface of crystalline silicon wafers.
[0057] 4. A layer of silicon dioxide is grown on the surface of the crystalline silicon wafer, and the thickness is controlled at 6.5nm.
[0058] 3. Applying a masking film on the grown silicon dioxide layer by screen printing to form an electrode window frame.
[0059] 4. Removing the oxide layer at the electrode window, that is, removing the silicon dioxide layer not covered by the masking film. A 15% hydrofluoric acid solution is selected to remove the silicon dioxide layer not covered by the masking film.
[0060] 5. Use 5% sodium hydroxide solution to remove the masking film.
[0061] 6. The phosphorus oxychloride liquid source is converted into a gaseous state, and high-concentration diffusion doping is carried out at a high temperature of 885°C for 50 minutes.
[0062] 7. Cleaning the oxide layer, that is, removing the silicon dioxide layer originally co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com