Plant development associated protein, encoding gene and application thereof
A technology for encoding genes and plant development, which is applied in the field of plant development-related proteins and their encoding genes and applications, can solve problems such as increasing yield, and achieve the effects of increasing plant yield and improving plant type
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Example 1, the discovery of OsILI1
[0063] 1. Obtaining and Morphological Observation of Mutant Plant ili1-D
[0064] 1. Obtaining of mutant plants ili1-D
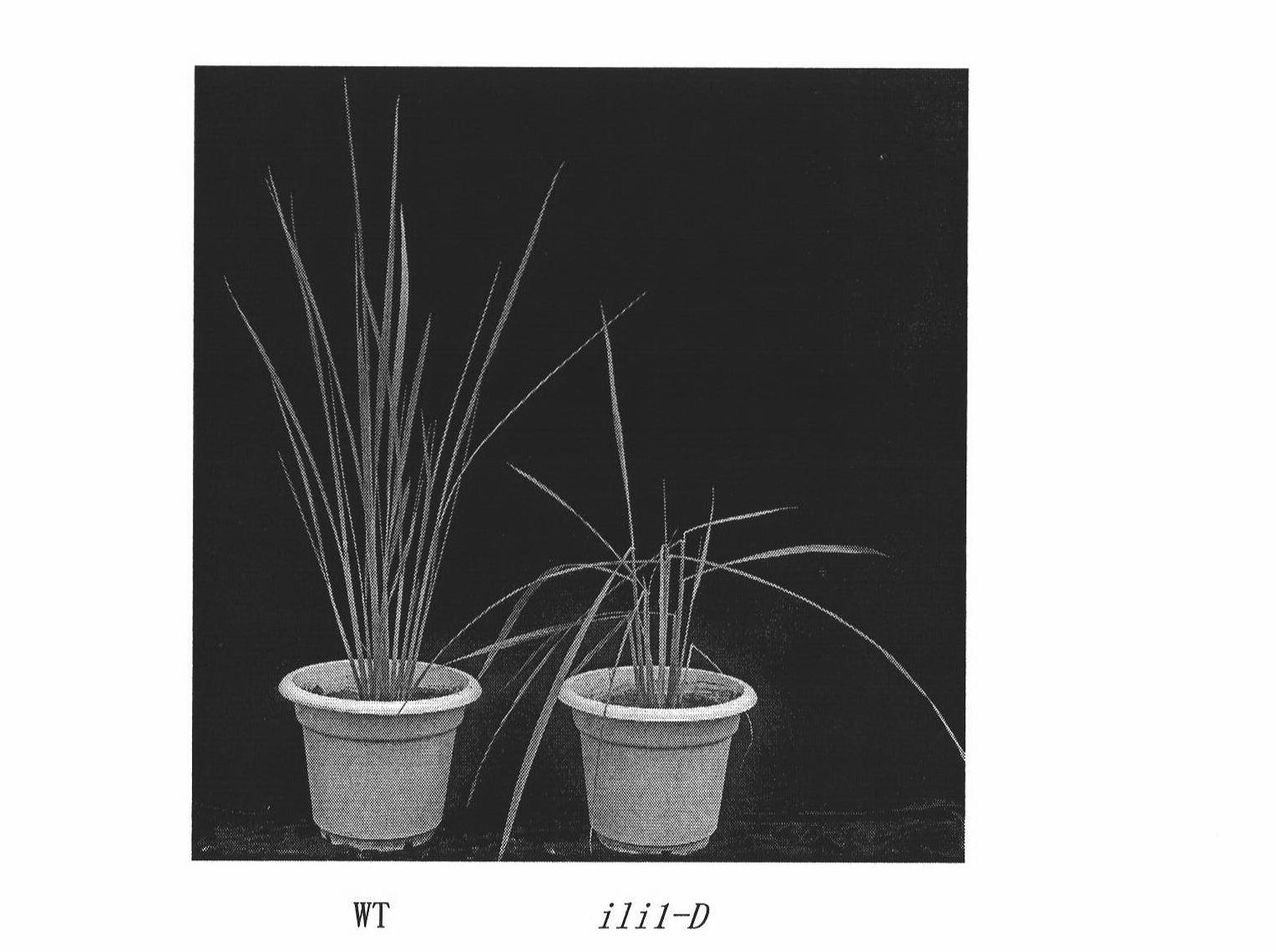
[0065] A Nipponbare rice T-DNA insertion mutant library was constructed, and a mutant plant ili1-D with a significantly increased leaf angle was found.
[0066] 2. Morphological observation of mutant plants ili1-D
[0067] The following morphological observations were performed on the mutant plant ili1-D.
[0068] (1) leaf angle
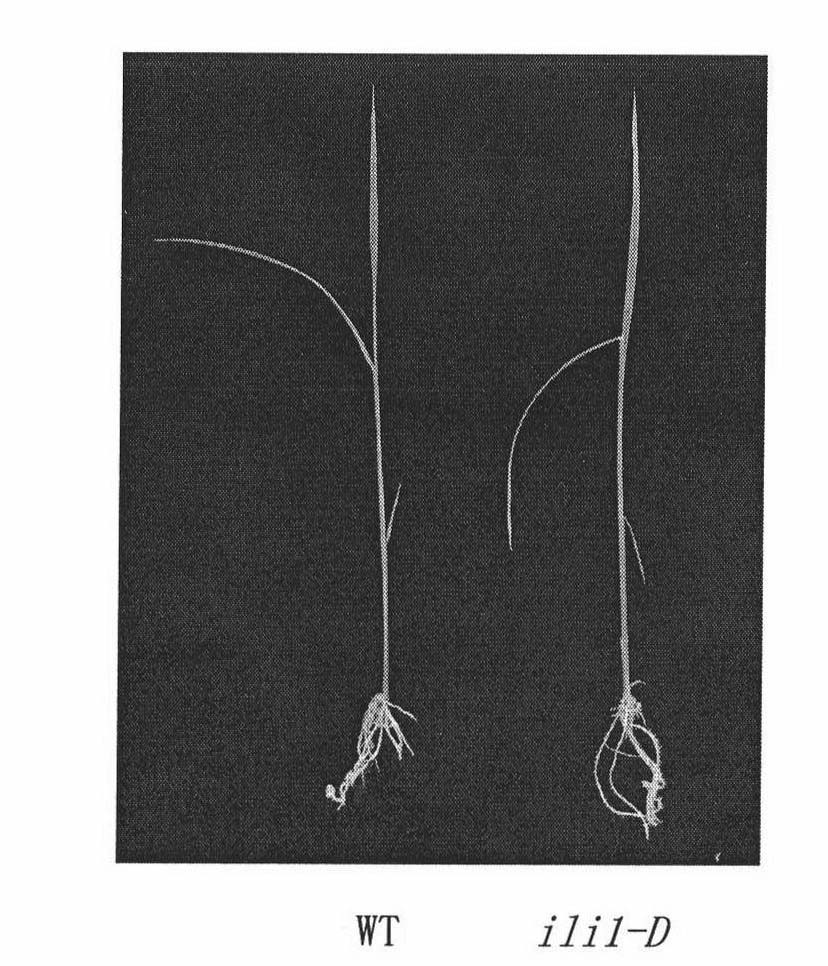
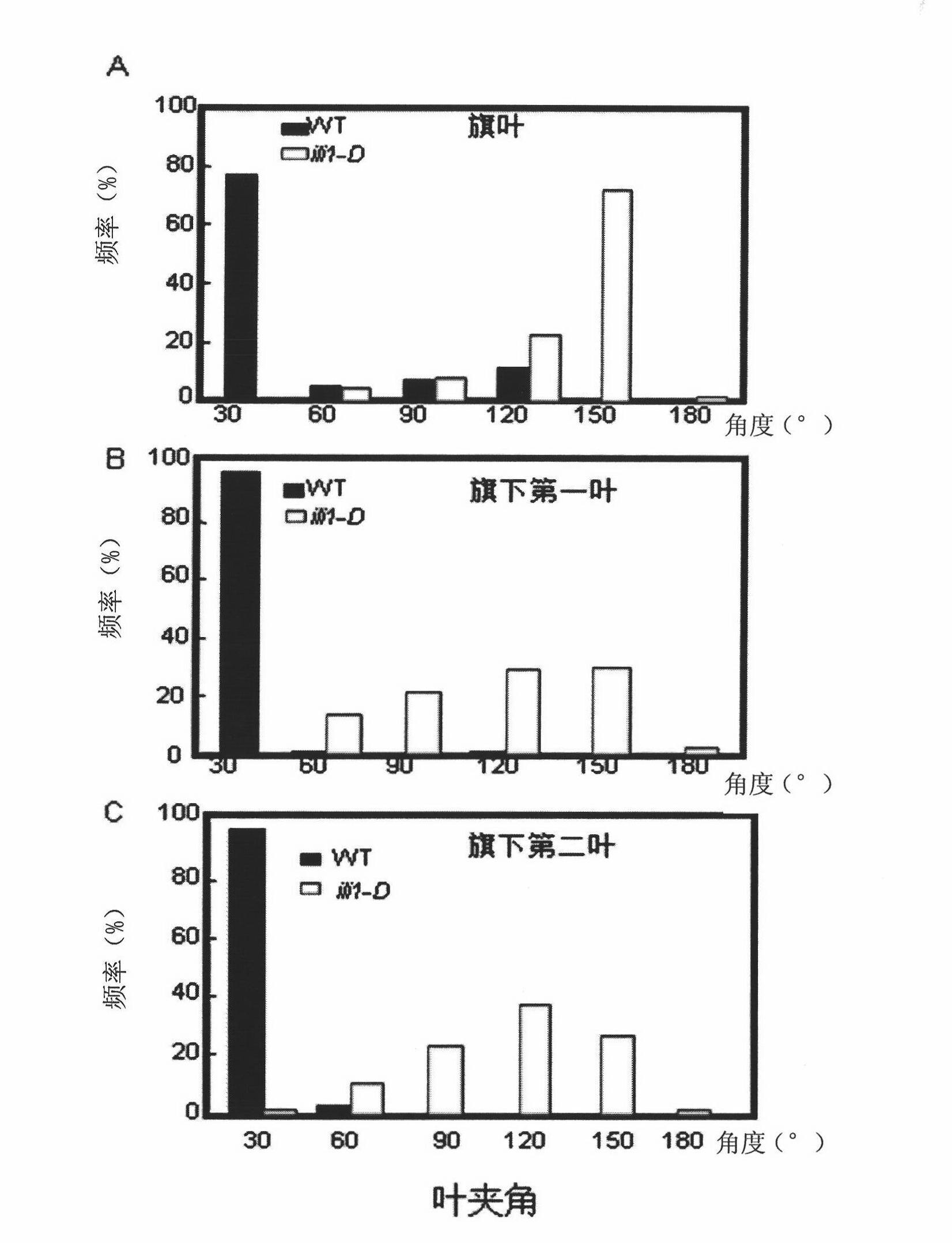
[0069] The most important phenotype of ili1-D was that the leaf angle increased significantly at each growth stage. At the seedling stage, the mutant grew for about 5 days after germination, and after the second leaf was fully developed, it could be observed that the angle between the second leaf and the leaf angle was bent more than 90 degrees (see figure 1 ). At the tillering stage, each new tiller of the mutant showed a significantly increased leaf angle (see figure 2 ).
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0094] Embodiment 2, the discovery of OsIBP1
[0095] 1. Discovery of OsIBP1
[0096] According to the analysis of OsILI1 protein sequence, OsILI1 belongs to the bHLH family of transcription factors, but it does not have a typical basic domain. Such bHLH proteins are classified as class D bHLH proteins, which cannot directly bind DNA and regulate their functions mainly by forming heterodimers with canonical bHLH transcription factors. Using the full-length OsILI1 protein as bait, yeast two-hybrid technology was used to screen for proteins interacting with OsILI1. After the coding sequence of OsILI1 was amplified from the cDNA library, it was connected into the pBD-GAL4 vector, and then the constructed vector was transformed into yeast AH109, and after being made into competent cells, the yeast two-hybrid library at the three-leaf stage of rice was co-transformed. The efficiency of the sieve library is 3×10 5 Clones / g DNA, the total amount of screening library is 3×10 6 C...
Embodiment 3
[0107] Embodiment 3, the acquisition of OsIBP1 overexpression rice
[0108] 1. Construction of recombinant expression vector
[0109] 1. Obtaining the 35S promoter fragment
[0110] Plasmid vector pBI221 (Clontech) was double digested with restriction endonucleases HindIII and BamHI, and a 35S promoter fragment with a length of about 0.8 kb was recovered after detection by agarose gel electrophoresis.
[0111] 2. The Noster poly A termination sequence was excised from the plasmid vector pBI221 (Clontech) with restriction enzymes Sac I and EcoR I, and connected to the corresponding site of the vector pUC19 (TaKaRa Company) to obtain a recombinant vector named as pUC19-Noster. Restriction endonucleases HindIII and BamHI were used to double digest pUC19-Noster, and after detection by agarose gel electrophoresis, the large linearized vector fragment was recovered, and the recovered fragment was connected with the 35S promoter fragment obtained in step 1 to obtain recombinant ve...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com