Method and device for measuring optical axis and gap of lens group by differential confocal internal focusing method
A differential confocal, measurement method technology, applied in the direction of measurement device, optical device, optical performance test, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing measurement error, increasing working distance, and fast measurement speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
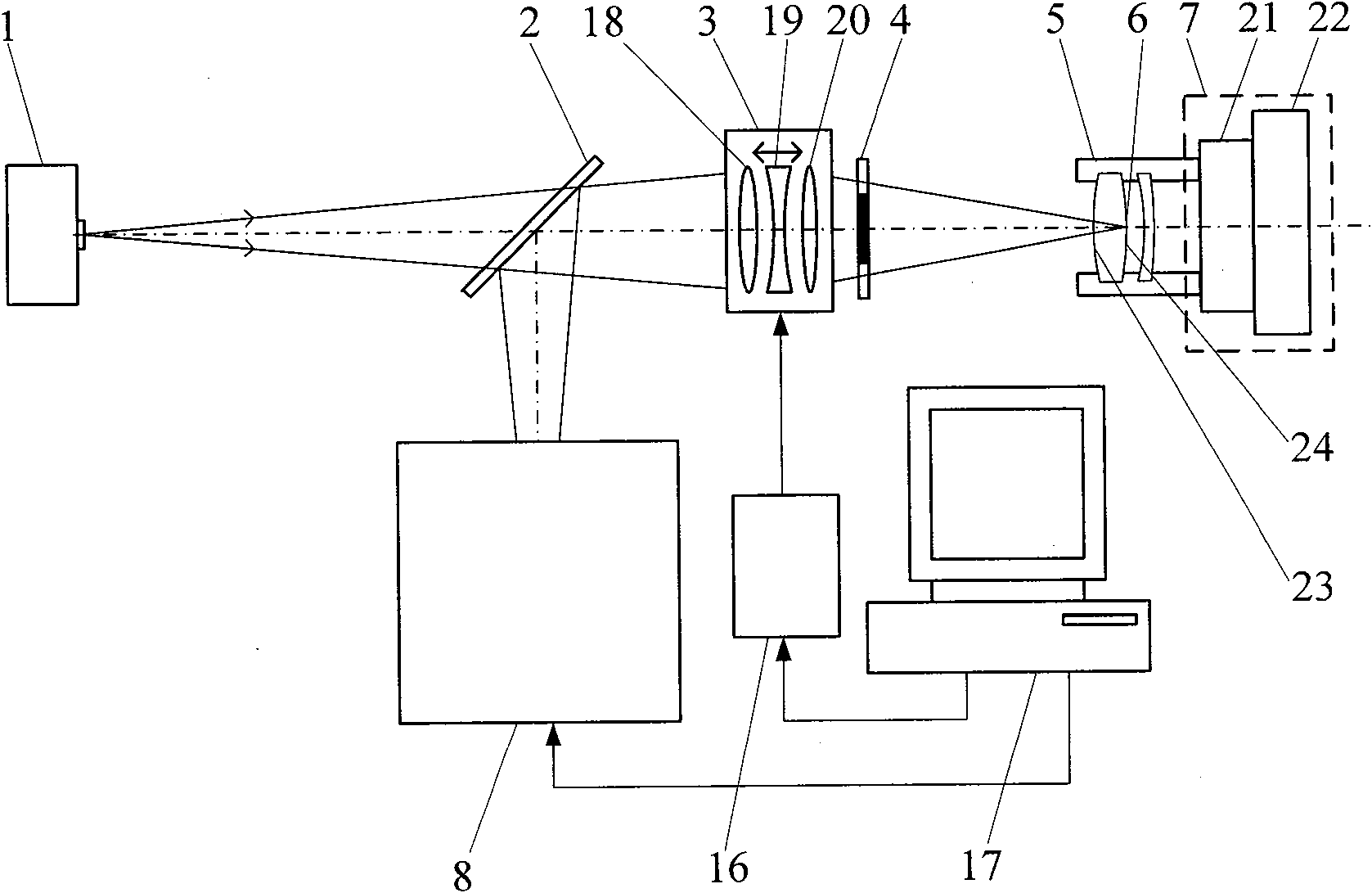
[0056] As shown in Figure 4 and Figure 7, the optical axis and gap measurement device of the differential confocal inner focusing method mirror group includes a point light source 1, which is sequentially placed in the first beam splitter 2 and the inner focusing The objective lens 3 and the annular pupil 4 also include a differential confocal system 8 placed in the reflection direction of the first beam splitter 2; the surface of the measured mirror group 5 and the first beam splitter 2 reflect the light beam to the differential confocal system 8, The second beam splitter 11 in the differential confocal system 8 divides the light into two paths, the reflected light illuminates the first light intensity sensor 9 located behind the focus, and the transmitted light illuminates the second light intensity sensor 10 located before the focus.
[0057] The device also includes an adjustment frame 7 , a main control computer 17 and an electromechanical control device 16 . The adjustme...
Embodiment 2
[0074] As shown in FIGS. 5 and 7 , the second embodiment can be formed by replacing the differential confocal system 8 in FIG. 7 of the first embodiment with the differential confocal system 8 of FIG. 5 . The difference from Embodiment 1 is that after the light enters the differential confocal system 8, the second beam splitter 11 divides the light into two paths, the reflected light illuminates the first light intensity sensor 9 after passing through the focused pinhole 12, and the transmitted light passes through The front pinhole 13 illuminates the second light intensity sensor 10 behind. All the other measuring methods and devices are the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0076] As shown in FIGS. 6 and 7 , the third embodiment can be formed by replacing the differential confocal system 8 in FIG. 7 of the first embodiment with the differential confocal system 8 of FIG. 6 . The difference from Embodiment 1 is that after the light enters the differential confocal system 8, the second beam splitter 11 divides the light into two paths, and the reflected light forms an image on the surface of the first light intensity sensor 9 after passing through the focused microscopic objective lens 14. The transmitted light is imaged on the surface of the second light intensity sensor 10 after passing through the pre-focus microscopic objective lens 15; wherein the object plane of the back-focus microscopic objective lens 14 is positioned after the focus, and the first light intensity sensor 9 is placed on its image plane, and the pre-focus microscopic The object plane of the objective lens 15 is located in front of the focus, and the second light intensity senso...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com