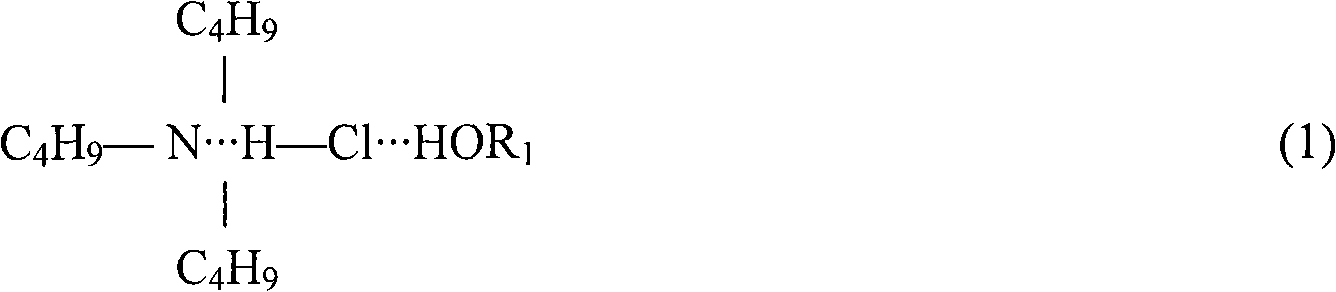Method for removing chlorine from solution of zinc sulfate
A zinc sulfate solution and chlorine removal technology, applied in the field of chlorine removal from zinc sulfate solution, can solve problems such as affecting the quality of zinc electrowinning electrolytic zinc products, destroying acidity balance, deteriorating production workshop environment, etc. Electrolysis operating environment, satisfying volume balance, and significant comprehensive benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
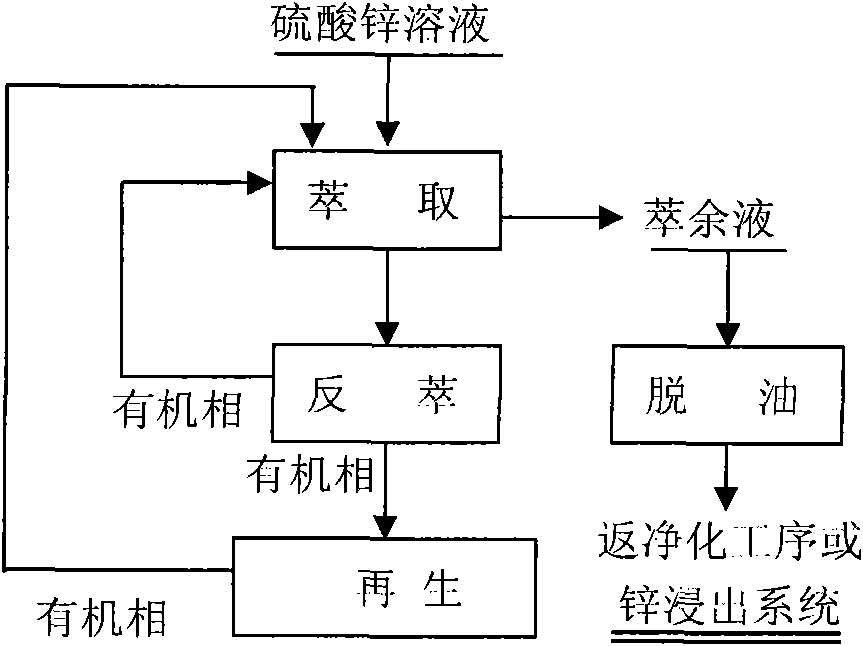
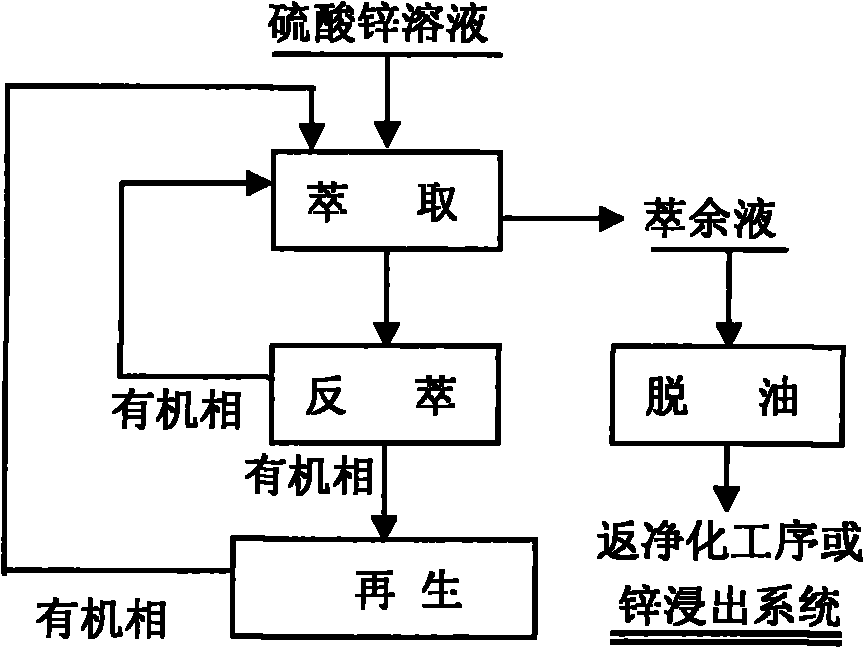
[0025] Example 1: Using the present invention to treat zinc sulfate solution, the components of the zinc sulfate solution are the following mass percentage concentrations: Zn135g / L, Cl0.85g / L, H 2 SO 4 1g / L, adjust the pH to 3.0 with NaOH, and then perform extraction dechlorination. The specific extraction conditions are: tri-n-butylamine as the extractant, 200# kerosene as the diluent, and the volume ratio of the two is tri-n-butylamine: kerosene = 40%:60%, extraction ratio 1:2, extraction temperature 25°C, mixing time 3min, clarification time 5min, extraction level 3, extraction dechlorination rate 85.82%.
[0026] The raffinate contains 0.12g / L Cl. After 5g / L activated carbon is used for adsorption and deoiling, the concentration of organic matter in the water phase is less than 5ppm, and the purification process is returned.
[0027] The organic phase contains about 1.46g / L of chlorine. It is back-extracted with 5% sodium hydroxide solution. The back-extraction conditions are as...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: The present invention is used to treat zinc sulfate solution. The components of the zinc sulfate solution are the following mass percentage concentrations: the zinc sulfate solution contains 128 g / L of Zn, 0.88 g / L of Cl, and H 2 SO 4 1g / L, adjust the pH to 1.0 with sulfuric acid, and then perform extraction dechlorination. The specific extraction conditions are: tri-n-butylamine as the extractant, 260 kerosene as the diluent, the volume ratio of the two is tri-n-butylamine: kerosene = 40%:60%, extraction ratio 1:2.5, extraction temperature 25°C, mixing time 3min, clarification time 5min, extraction stages 3, extraction dechlorination rate 86.09%.
[0030] The raffinate contains 0.12g / L Cl. After 5g / L activated carbon is used for adsorption and deoiling, the concentration of organic matter in the water phase is less than 5ppm, and the purification process is returned.
[0031] The organic phase contains about 1.90g / L of chlorine, and it is back-extracted with 5% so...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Example 3: Using the present invention to treat zinc sulfate solution, the components of the zinc sulfate solution are the following mass percentage concentrations: the zinc sulfate solution contains 95 g / L of Zn, 1.03 g / L of Cl, and H 2 SO 4 5g / L, adjust the pH to 1.0 with sulfuric acid, and then carry out extraction and dechlorination. The specific extraction conditions are: tri-n-butylamine as extractant, sec-octanol as diluent, and the volume ratio of the two is tri-n-butylamine: sec-octane Alcohol=30%:70%, extraction ratio 1:2.5, extraction temperature 25°C, mixing time 3min, clarification time 5min, extraction level 3, extraction dechlorination rate 87.38%.
[0034] The raffinate contains 0.13g / L Cl. After 5g / L activated carbon is used for adsorption and deoiling, the concentration of organic matter in the water phase is less than 5ppm, and it returns to the purification process.
[0035] The organic phase contains about 2.24g / L of chlorine, and it is back-extracted wit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com