Doxorubicin hydrochloride-carrying natural polymer-poly(3-benzene acid acrylamide) composite nanospheres, manufacturing method and application thereof
A technology of acrylamidophenylboronic acid and natural polymers, which is applied in the direction of non-active ingredients of polymer compounds, preparation of microspheres, medical preparations of non-effective ingredients, etc., to achieve stable chemical properties, strong drug sustained release function, and biophase good capacitive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1: Preparation of dextran-poly(3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid) composite nanospheres
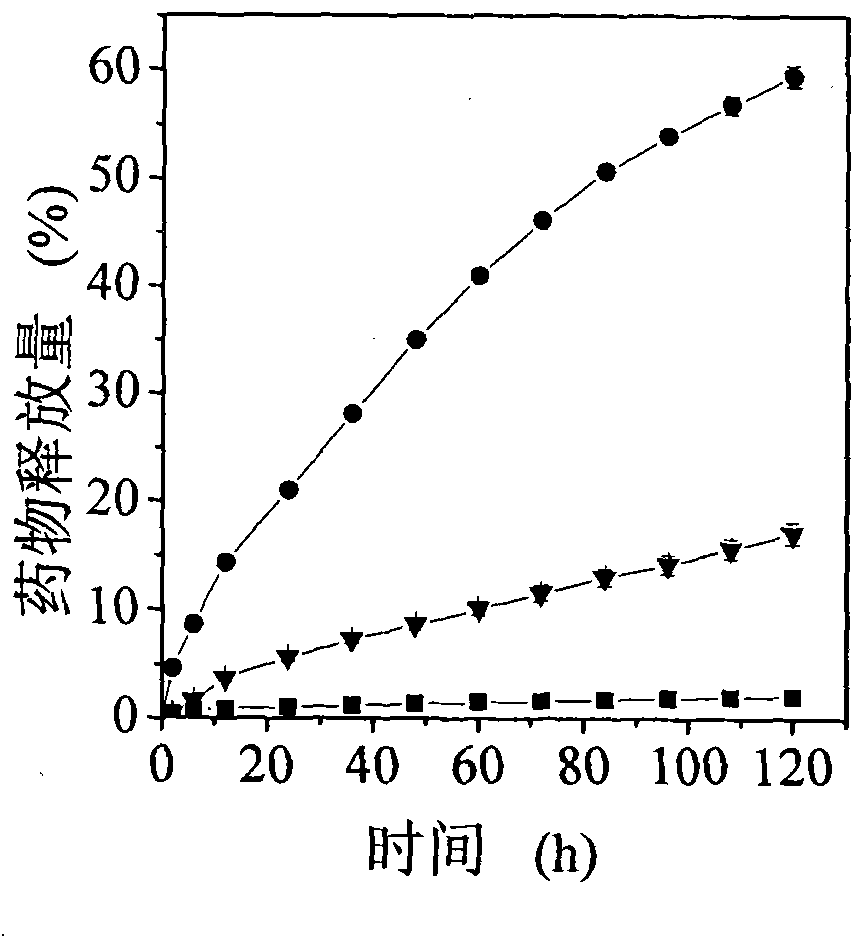
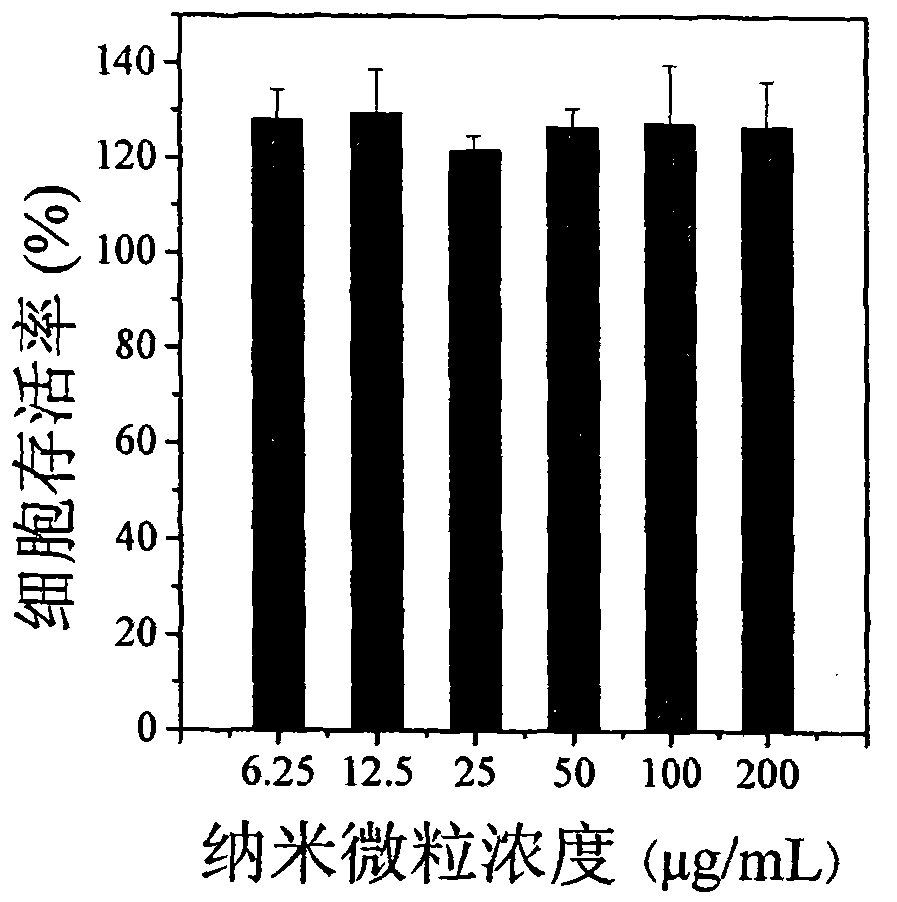
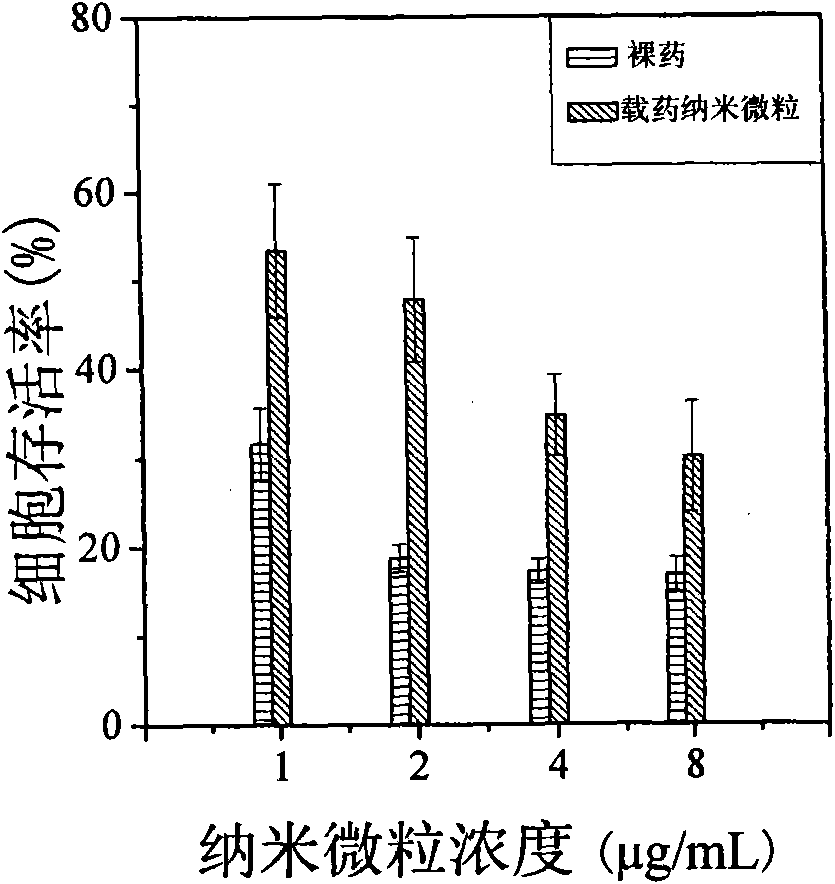
[0030] In a 25 ml stirred reactor, 90 mg of 3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid and 152 mg of dextran with a number average molecular weight of 3000 were dissolved in 12 ml of distilled water. After cooling to room temperature, 9.4 mg of 4,4'-azo (4-cyanovaleric acid) initiator was added. The temperature was raised to 80°C, and the polymerization reaction was initiated for 2 hours to obtain an aqueous solution of dextran-poly(3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid) composite nano-microspheres. The reaction was stopped, the temperature of the system was lowered to room temperature, and the aqueous dispersion was put into a dialysis bag (Cut-off molecular weight is 12000) and dialyzed for 24 hours to remove unreacted monomers in the system. The average particle size of the nanospheres measured by dynamic light scattering is 72.5±2.0 nm. Among them, natural polymers accounted for 9.1%, and pol...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2: Preparation of dextran-poly(3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid) composite nanospheres
[0032] In a 25 ml stirred reactor, 90 mg of 3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid and 76 mg of dextran with a number average molecular weight of 3000 were dissolved in 12 ml of distilled water. After cooling to room temperature, 9.4 mg of 4,4'-azo (4-cyanovaleric acid) initiator was added. The temperature was raised to 80°C, and the polymerization reaction was initiated for 2 hours to obtain an aqueous solution of dextran-poly(3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid) composite nano-microspheres. The reaction was stopped, the temperature of the system was lowered to room temperature, and the filtration was carried out. After filtration, the aqueous dispersion was put into a dialysis bag (Cut-off molecular weight is 12000) and dialyzed for 24 hours to remove unreacted monomers in the system. The average particle size of the nano-microspheres measured by dynamic light scattering is 77.4±2.1 nm, of...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Example 3: Preparation of dextran-poly(3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid) composite nanospheres
[0034] In a 25 ml stirred reactor, 90 mg of 3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid and 38 mg of dextran with a number average molecular weight of 3000 were dissolved in 12 ml of distilled water. After cooling to room temperature, 9.4 mg of 4,4'-azo (4-cyanovaleric acid) initiator was added. The temperature was raised to 80°C, and the polymerization reaction was initiated for 2 hours to obtain an aqueous solution of dextran-poly(3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid) composite nano-microspheres. The reaction was stopped, the temperature of the system was lowered to room temperature, and the filtration was carried out. After filtration, the aqueous dispersion was put into a dialysis bag (Cut-off molecular weight is 12000) and dialyzed for 24 hours to remove unreacted monomers in the system. The average particle size of the nano-microspheres measured by dynamic light scattering is 65.1±0.1 nm, of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com