Salbutamol molecularly imprinted polymer and preparation method thereof
A salbutamol and molecularly imprinted technology, applied in the preparation of albuterol molecularly imprinted polymers, in the field of salbutamol molecularly imprinted polymers, can solve the problems of inability to identify specific molecules, non-specific stationary phases, and no reports on preparation methods, etc. Achieve good recognition ability and selection characteristics, good binding ability and separation ability, and controllable particle size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
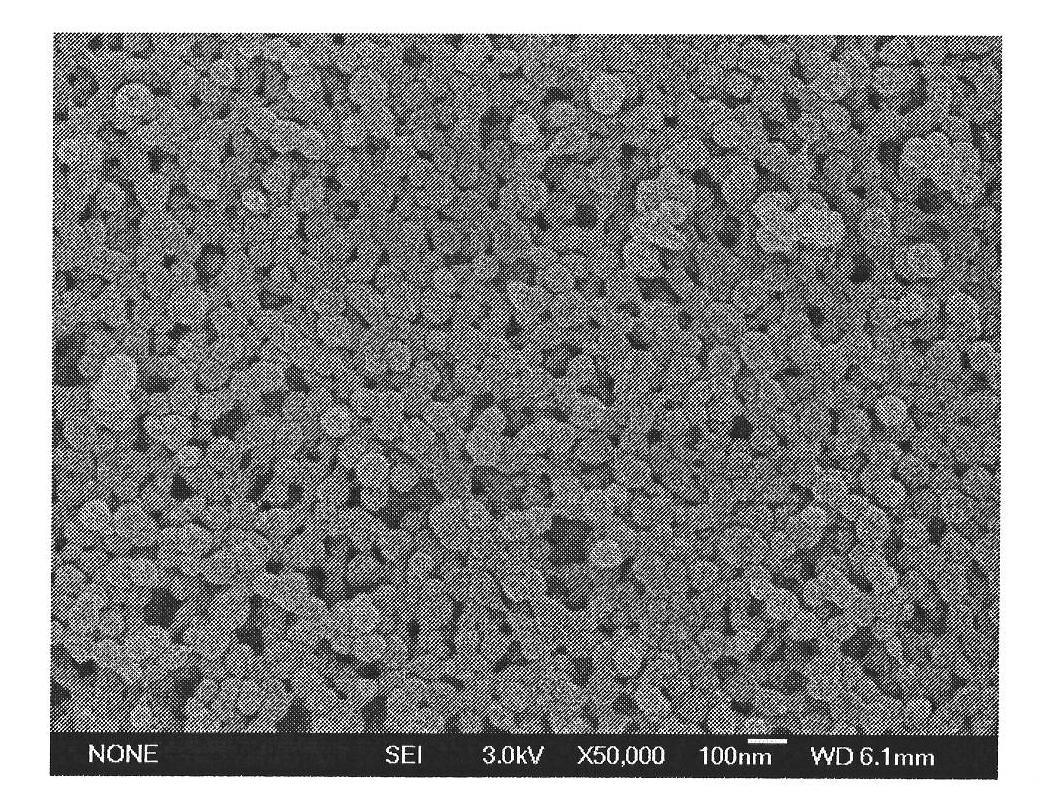
[0044] A salbutamol molecularly imprinted polymer, such as figure 1 As shown, the particle size is about 50nm-100nm, measured by BET nitrogen adsorption method, the pore size is 24.6nm, and the specific surface area is 88.7m 2 / g, the total pore volume is 0.519cm 3 / g.
[0045] Weigh 20 mg of albuterol molecularly imprinted polymer into a polytetrafluoroethylene centrifuge tube, add 5 ml of albuterol in acetonitrile solution, put it in a shaker at room temperature for 12 h, centrifuge at 10000 r / min for 20 min, take the supernatant, and pass through 0.45 Filter with a μm filter membrane, measure the content of salbutamol in the obtained solution by HPLC, and calculate the maximum adsorption capacity Q of the molecularly imprinted polymer according to the change of the solution concentration before and after adsorption max and the equilibrium dissociation constant K d They are 641.33mg / g and 414.94mg / L respectively.
[0046] The molecularly imprinted polymer was placed in a...
Embodiment 2
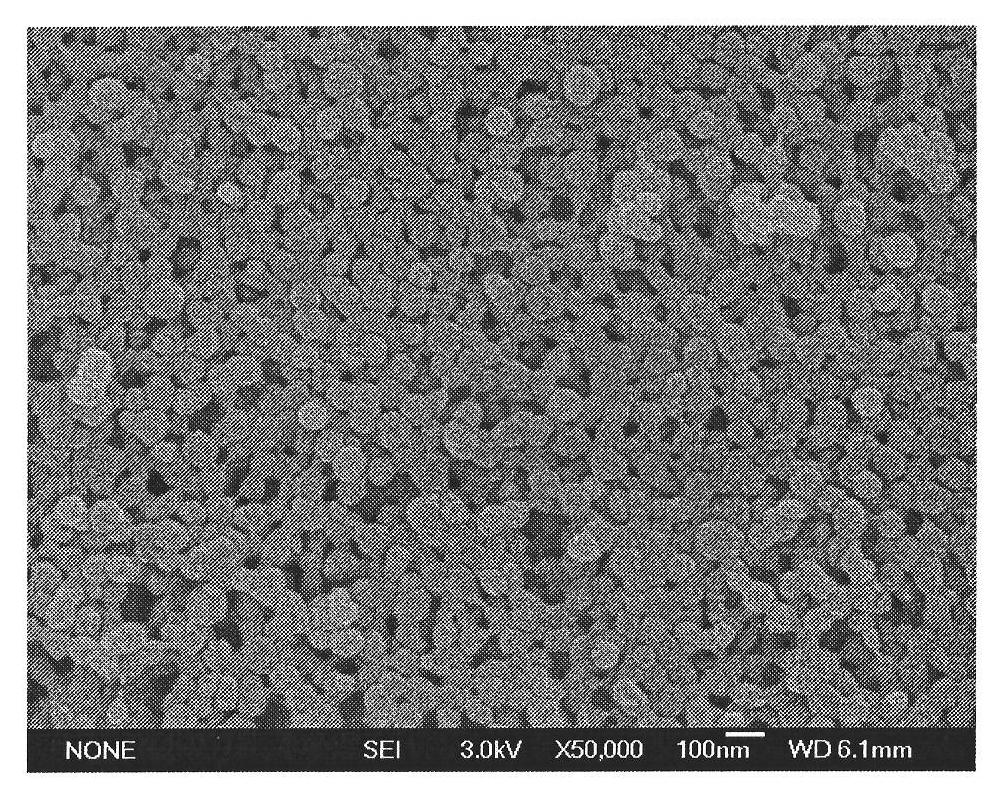
[0052] A salbutamol molecularly imprinted polymer, the particle size is about 30nm-100nm, measured by BET nitrogen adsorption method, the pore size is 15nm, and the specific surface area is 126m 2 / g.
[0053] The maximum adsorption capacity Q of molecularly imprinted polymers max and the equilibrium dissociation constant K d Be respectively 203mg / g and 71mg / L, measure and calculate method with embodiment 1.
[0054] The static adsorption partition coefficient K of the molecularly imprinted polymer is 0.5, and the recognition factor β is 5.2, and the measurement and calculation methods are the same as in Example 1.
[0055] Its preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0056] (1) Add the template molecule salbutamol and the polymerized monomer acrylamide in a ratio of 1:3 to the porogen methanol solution whose ratio to salbutamol is 300ml / mmol, and stir at 8°C for 0.5h;
[0057] (2) adding in the product of step (1) is that the crosslinking agent trimethoxypropan...
Embodiment 3
[0060] A salbutamol molecularly imprinted polymer, the particle size is about 80nm-150nm, measured by BET nitrogen adsorption method, the pore size is 30nm, and the specific surface area is 30.8m 2 / g.
[0061] The maximum adsorption capacity Q of molecularly imprinted polymers max and the equilibrium dissociation constant K d Be respectively 689mg / g and 507.9mg / L, measure and calculate method with embodiment 1.
[0062] The static adsorption distribution coefficient K of the molecularly imprinted polymer is 1.0, and the recognition factor β is 10, and the measurement and calculation methods are the same as in Example 1.
[0063] Its preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0064] (1) Add the template molecule salbutamol and the polymerized monomer trifluoromethacrylic acid in a ratio of 1:8 to the porogen acetone solution whose ratio to salbutamol is 70ml / mmol, and stir at 5°C for 2.5h;
[0065] (2) Add a cross-linking agent with a ratio of 1:30 to salbutamol a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com