Method for constructing high-yield polyglutamic acid engineering strain
A technology of polyglutamic acid and engineering strains, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as limited oxygen utilization, complex synthetic metabolic pathways, and high viscosity of fermentation broth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
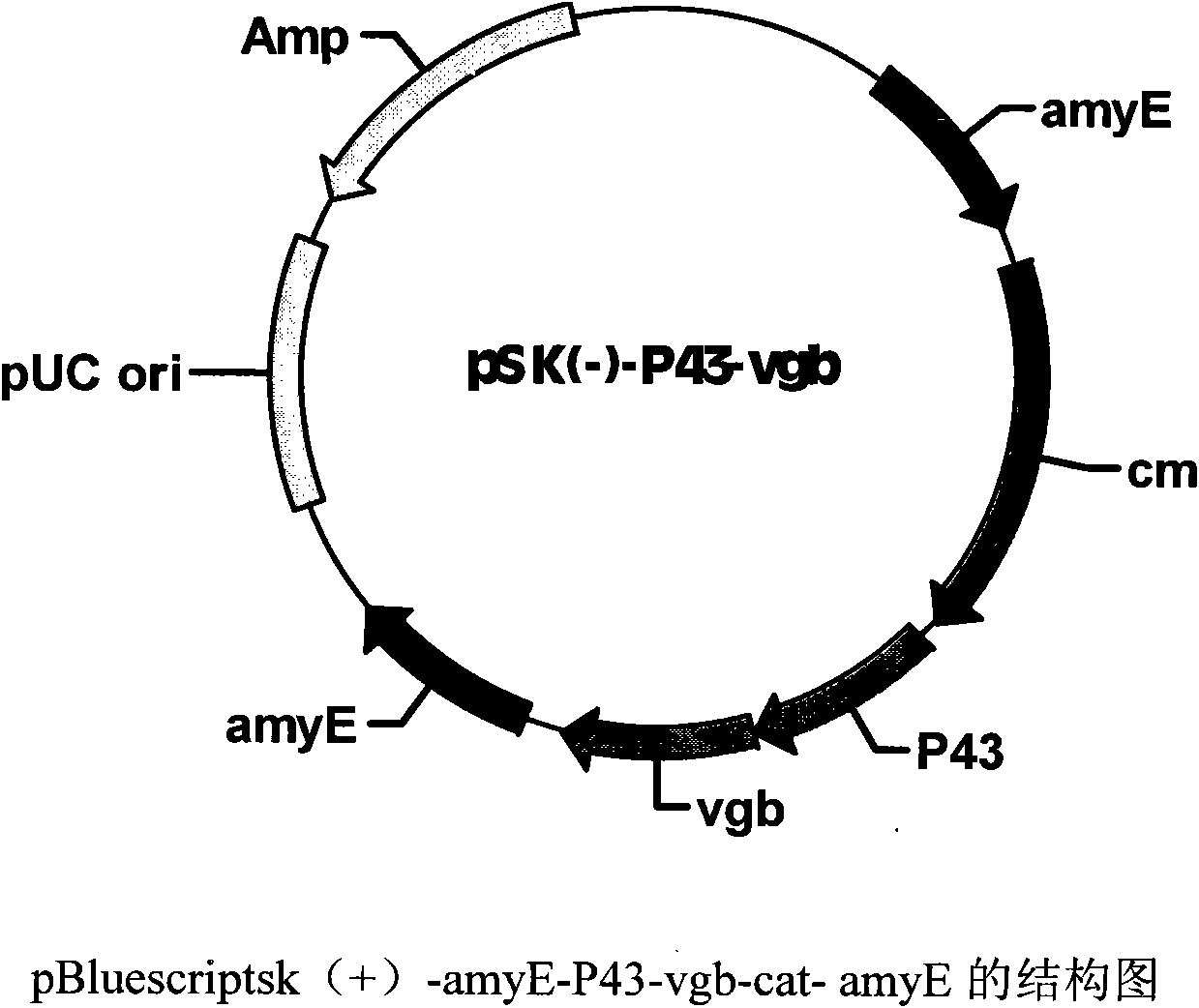
[0013] Example 1: Construction of Bacillus subtilis integration vector expressing hemoglobin gene
[0014] Using conventional molecular biology techniques, the nucleotide sequences at positions 1-500 and 1381-1984 at the 5' end of the Bacillus subtilis amylase gene were cloned into the Xho I, HindIII, Xba I, and SacII positions of the pBluescriptsk (-) plasmid, respectively. Between the points, the primers used are: AmyE15'ATTGCTCGAGATGT TTGCAAAACGATTCAAA3'; AmyE25'GGATAAGCTTTGTGTGTTTCC ATGT GTCCAGT3'; AmyE35'ATTGTCTAGAGCTGTGCTTTATCCTGATGATA3'; AmyE45'ATTACCGCGGTCAATGGGGAAGAGAACCGCT3';
[0015] Using the Bacillus subtilis genome as a template, using P15'ATTAGAATTCTGTCGACGT GCATGCAGGC3'; P25'TAGGATCCTATAATGGTACCGCTATCACT3' as primers to amplify the P43 promoter gene by PCR; insert it between the EcoR I and BamH I sites of the pBluescriptsk (-) plasmid;
[0016] Using pUC19-vgb as a template and using VGB15'ATTGGATCCGGAAGACCCTCATGT TAGA3'; VGB25'ATTATCTAGATTATTCAACCGCTTGAGCGTA3'...
Embodiment 2
[0018] Example 2: Construction of high-yield γ-polyglutamic acid engineered bacteria
[0019] The vector pSK(-)-P43-vgb constructed in Example 1 was linearized with restriction endonuclease Xho I or SacII; dephosphorylated with alkaline phosphatase, recovered and used for electrotransformation. The specific method is as follows:
[0020] (1) Inoculate B. subtilis in 3ml LB medium and culture overnight. (2) Take 2.6 mL of the overnight culture and inoculate into 40 mL (LB+0.5 mol / L sorbitol), and culture at 37°C and 200 r / min until OD600=0.85-0.95. (3) Bath the bacterial solution in ice water for 10 minutes, then centrifuge at 4°C for 5 minutes under a centrifugal force of 5000 g, and collect the bacterial cells. (4) Use 50mL pre-cooled electroporation medium (0.5mol / L sorbitol, 0.5mol / L mannitol, 10% glucose), re-suspend the bacteria, centrifuge at 5000g, 5min, 4°C to remove the supernatant, and rinse like this 4 times. (5) Suspend the washed cells in 1 mL electroporation ...
Embodiment 3
[0021] Example 3: Verification of high-yield γ-polyglutamic acid in genetically recombined Bacillus subtilis
[0022] Inoculate the original strain and the genetically recombined strain obtained in Example 2 into 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks containing 50 mL of seed medium, and culture overnight at 37° C., with a shaker speed of 210 r / min. The cultured seeds were inoculated into 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks containing 50 mL of fermentation medium at an inoculation amount of 2%, and cultured at 37° C. for 48 to 72 hours, with the shaker rotating at 210 r / min. After the fermentation, take 1mL of fermentation broth, dilute it 10 times, centrifuge at 12000r / min, 4°C for 10min, take the supernatant, filter it through a microporous membrane, and perform chromatographic analysis. The chromatographic analysis conditions are: chromatographic column: Hypersil BDS C18, 5μm , 4.6mm×250mm; mobile phase: disodium hydrogen phosphate-potassium dihydrogen phosphate, pH6.98; flow rate: 1mL / min; column ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com