Method for preparing bacterial cellulose by using wheat straw
A technology of bacterial cellulose and wheat straw, which is applied in the field of bacterial cellulose preparation, can solve the problems of straw dissolution that have not been reported in detail, and achieve the effect of improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] (1) Pretreatment of wheat straw
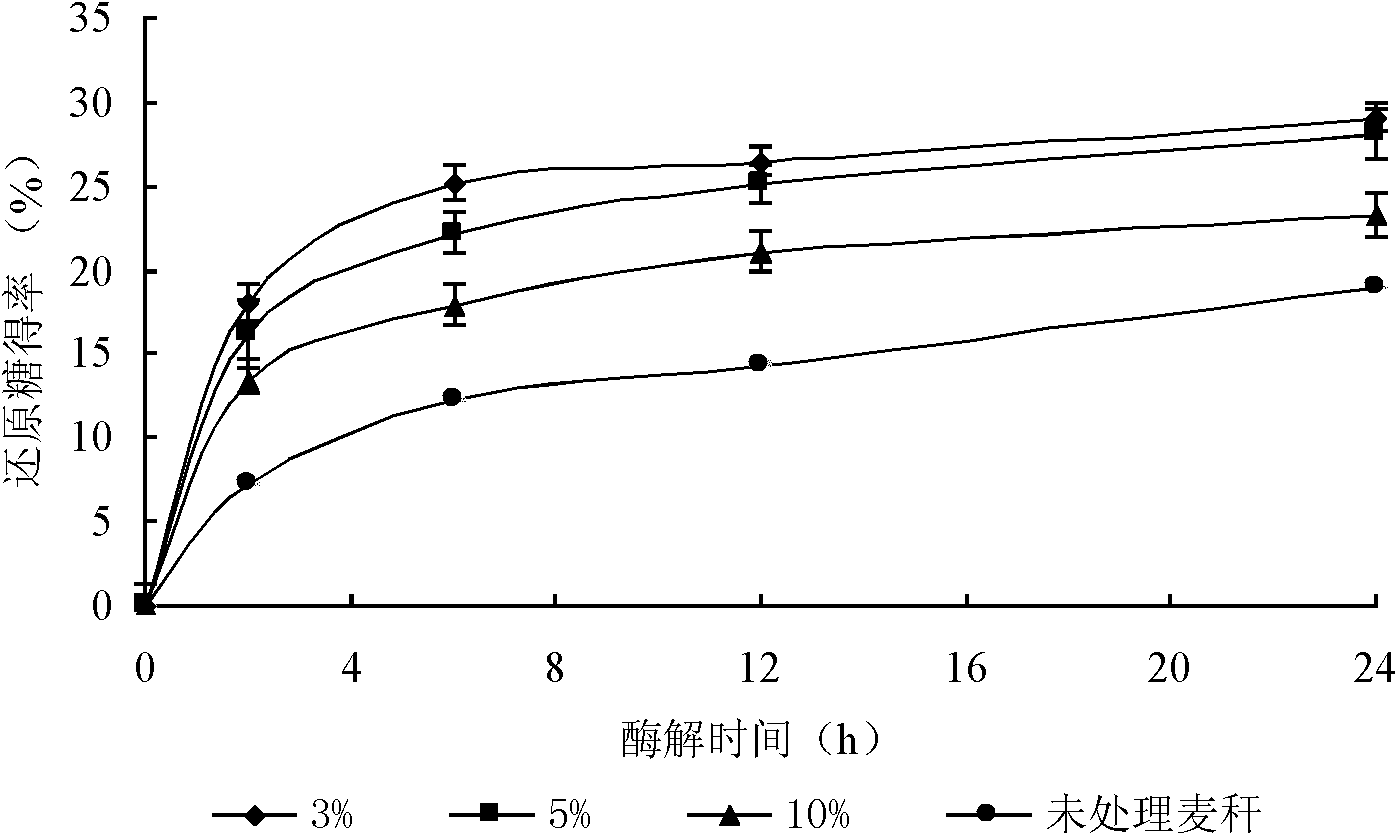
[0040] At 100°C and 500 rpm magnetic stirring speed, 150 mg of 40-60 mesh wheat straw was placed in 1.5 g, 3 g, and 5 g ionic liquid (AMIM) Cl, respectively, and pretreated for 2 h.
[0041] (2) Regeneration of wheat straw
[0042] Add 5 times the volume of deionized water to the ionic liquid mixture after the above treatment, stir for 30 min, centrifuge the mixture at 4000 rpm for 10 min, and wash the precipitate repeatedly until the supernatant is colorless and transparent.
[0043] (3) Enzymatic hydrolysis of regenerated wheat straw
[0044] Completely transfer 150mg of precipitate to a 50ml Erlenmeyer flask, add 30ml, 50mmol pH 4.8 acetate buffer, then add 90mg of cellulase (11000U / g), put it in a shaking water bath, 50℃, 100rpm for enzymatic hydrolysis For the reaction, suck the reaction solution at regular intervals (respectively 2, 6, 12, 24h), centrifuge at 4000-10000rpm for 5-20min to separate the undegraded wheat straw and the enzymati...
Embodiment 2
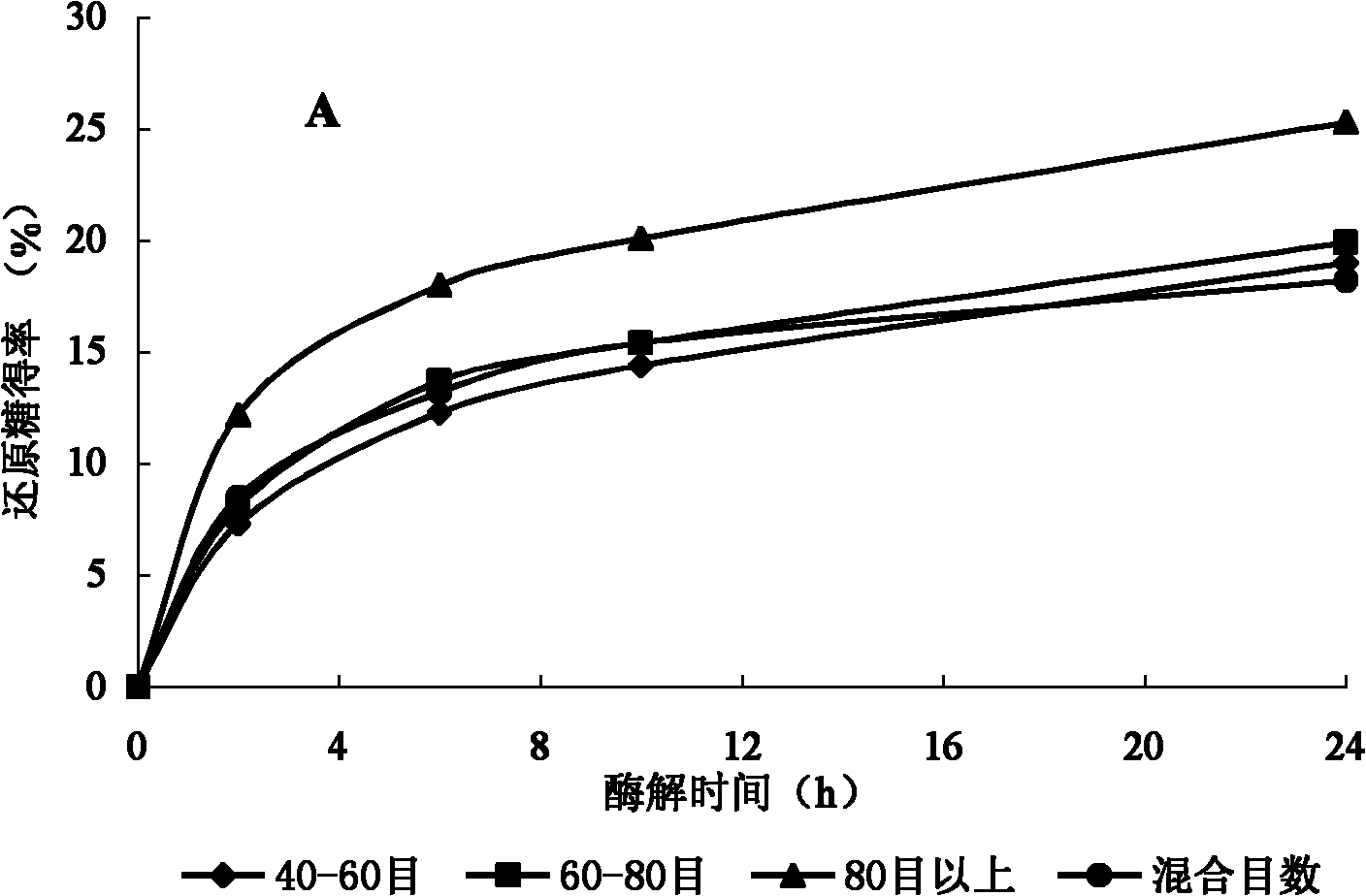
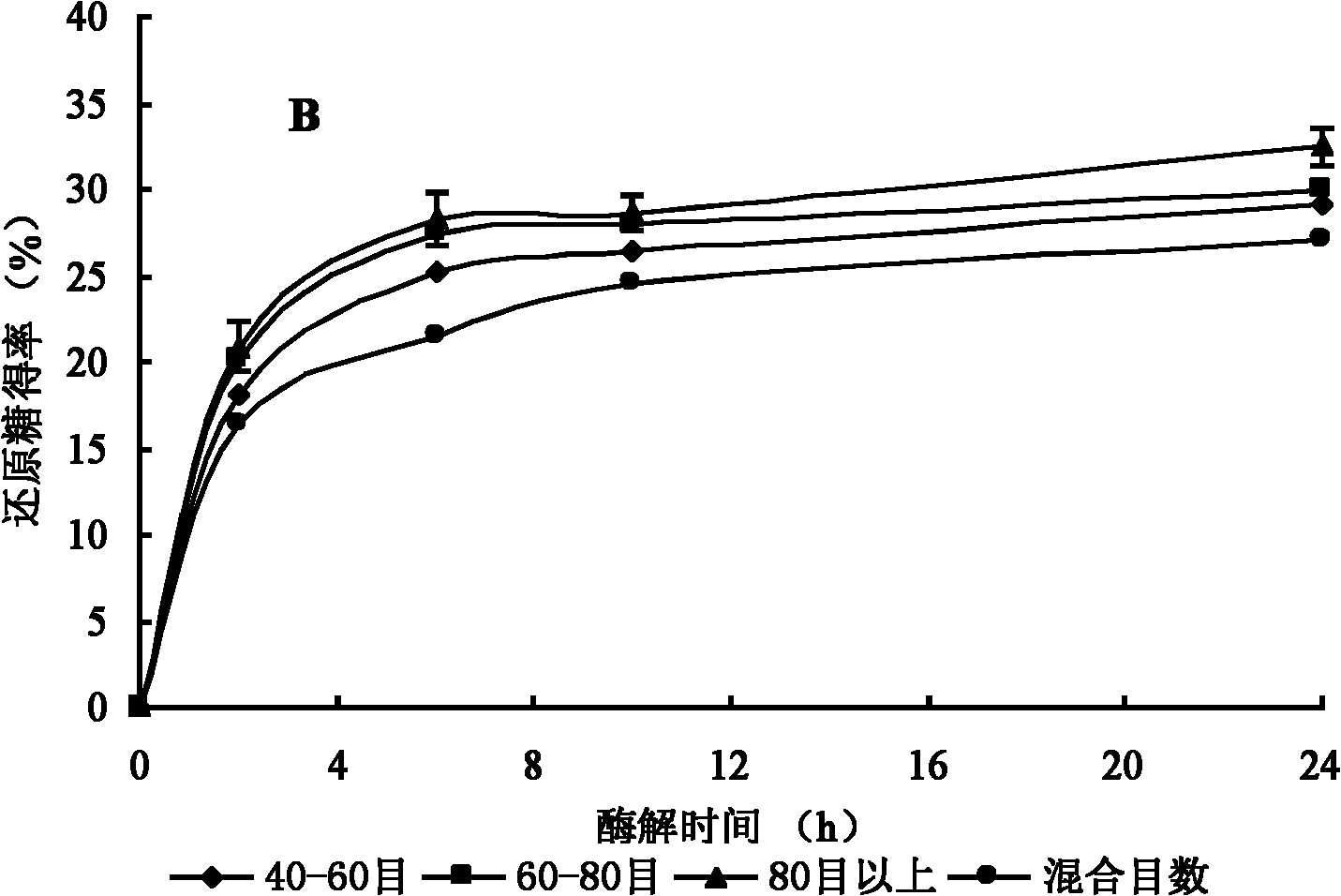
[0049] (1) Pretreatment of wheat straw
[0050] 100 ℃, 500 rpm magnetic stirring speed, put 150mg of wheat straw of different meshes (40-60 mesh, 60-80 mesh, 80 mesh and above, mixed mesh) in 50ml containing 5g of ionic liquid (AMIM) Cl Pretreatment for 2h in a triangular Erlenmeyer flask.
[0051] (2) Regeneration of wheat straw
[0052] Add 5 times the volume of deionized water to the ionic liquid mixture after the above treatment, stir for 30 min, pour the mixture into a Buchner funnel, and filter the filter residue repeatedly until the filtrate is colorless and transparent. Collect the residue And the filtrate for solution.
[0053] (3) Distillation recovery of ionic liquid
[0054] Place the collected filtrate in a distillation flask, and distill under reduced pressure at a temperature of 130°C and a vacuum of -0.09~-0.1Mpa to remove the water blended with the ionic liquid. Distill until no water can be evaporated, and the remaining in the distillation flask Is the recovered ion...
Embodiment 3
[0059] (1) Pretreatment of wheat straw
[0060] Put 150mg of 40-60 mesh wheat straw in 5g of ionic liquid (AMIM) Cl at four temperatures of 90℃, 100℃, 110℃, and 120℃, and treat them at 90℃ under magnetic stirring at 500rpm. 4, 6, 8 , 10, 12h; 100℃ treatment for 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4h; 110℃ treatment for 1, 1.5, 1.75, 2, 2.5h; 120℃ treatment for 15, 30, 45, 60, 75min.
[0061] (2) Regeneration of wheat straw
[0062] Add 5 times the volume of deionized water to the ionic liquid mixture to the conical flask after the above treatment, stir for 30 min, centrifuge the mixture at 4000 rpm for 10 min, and rinse the precipitate repeatedly until the supernatant is colorless and transparent.
[0063] (3) Enzymatic hydrolysis of regenerated wheat straw
[0064] Completely transfer 150mg of precipitate to a 50ml Erlenmeyer flask, add 30ml, 50mmol pH 4.8 acetate buffer, then add 90mg of cellulase (11U / mg), put in a shaking water bath, 50℃, 100rpm for enzymatic hydrolysis After 6h, after the reaction, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com