A Tunable Dual Frequency Laser
A dual-frequency laser and laser cavity technology, applied in the field of lasers, can solve problems such as instability, poor stability, and differences, and achieve the effect of stable operation and small system size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1: A non-polarizing beam splitter is used to split the pump light emitted by the same semiconductor light source into two beams of approximately equal power, the same polarization, and spaced apart.
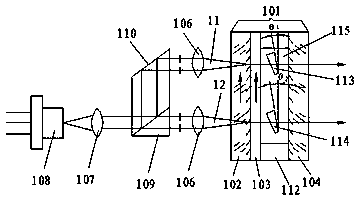
[0026] Such as figure 1 As shown, 101 is a microchip single longitudinal mode laser cavity, 102 is a front cavity lens, 104 is a rear cavity lens, 103 is an ultra-thin laser gain medium sheet, such as Nd: YVO4, 111 and 112 are etalon support frames, 113 and 114 are the first optical parallel flat plate and the second optical parallel flat plate of the ultra-thin optical parallel flat plate, and the laser cavity at the two pumping points can be fine-tuned by fine-tuning the angles of the first optical parallel flat plate 113 and the second optical parallel flat plate 114 Long, so that the frequency difference of the microchip laser can be adjusted. 106 and 107 are optical lenses, which respectively act as coupling pump beams and collimating pump beams; 108 is a ...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Embodiment 2: Two semiconductor light sources of the same type are used to pump separately, so that the polarization directions of the pump light emitted by the semiconductor light sources are consistent.
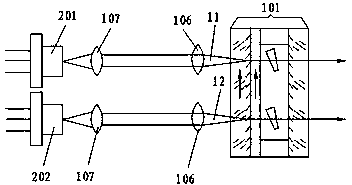
[0028] Such as figure 2 As shown, 201 and 202 are two semiconductor light sources of the same type spaced apart from each other, and the output pump light power and polarization direction are consistent. The semiconductor light sources 201 and 202 are respectively collimated by the collimator lens 107 to emit two pump beams with the same power and polarization direction, and the beam splitting ratio of the non-polarizing beam splitter 109 is 1:1.
Embodiment 3
[0029] Embodiment 3: Two semiconductor light sources with the same polarization are used to simultaneously pump two points on the microchip through a non-polarizing beam splitter and a reflector.
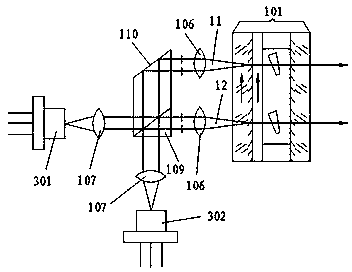
[0030] Such as image 3 As shown, 301 and 302 are respectively two semiconductor light sources with the same polarization arranged vertically and orthogonally, and their output light powers may be inconsistent. Since the two outgoing beams are split into two parts by the non-polarizing beam splitter 109, the power of the first pumping beam 11 and the second pumping beam 12 is half of the output power of the semiconductor light source 301 plus half of the output power of the semiconductor light source 302 , so that even if the output power of the semiconductor light source is inconsistent, the pump light power is the same.
[0031] For all the above-mentioned examples, different nonlinear crystal back-end mirror coatings can be added to the laser cavity at the two pumping points on ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com