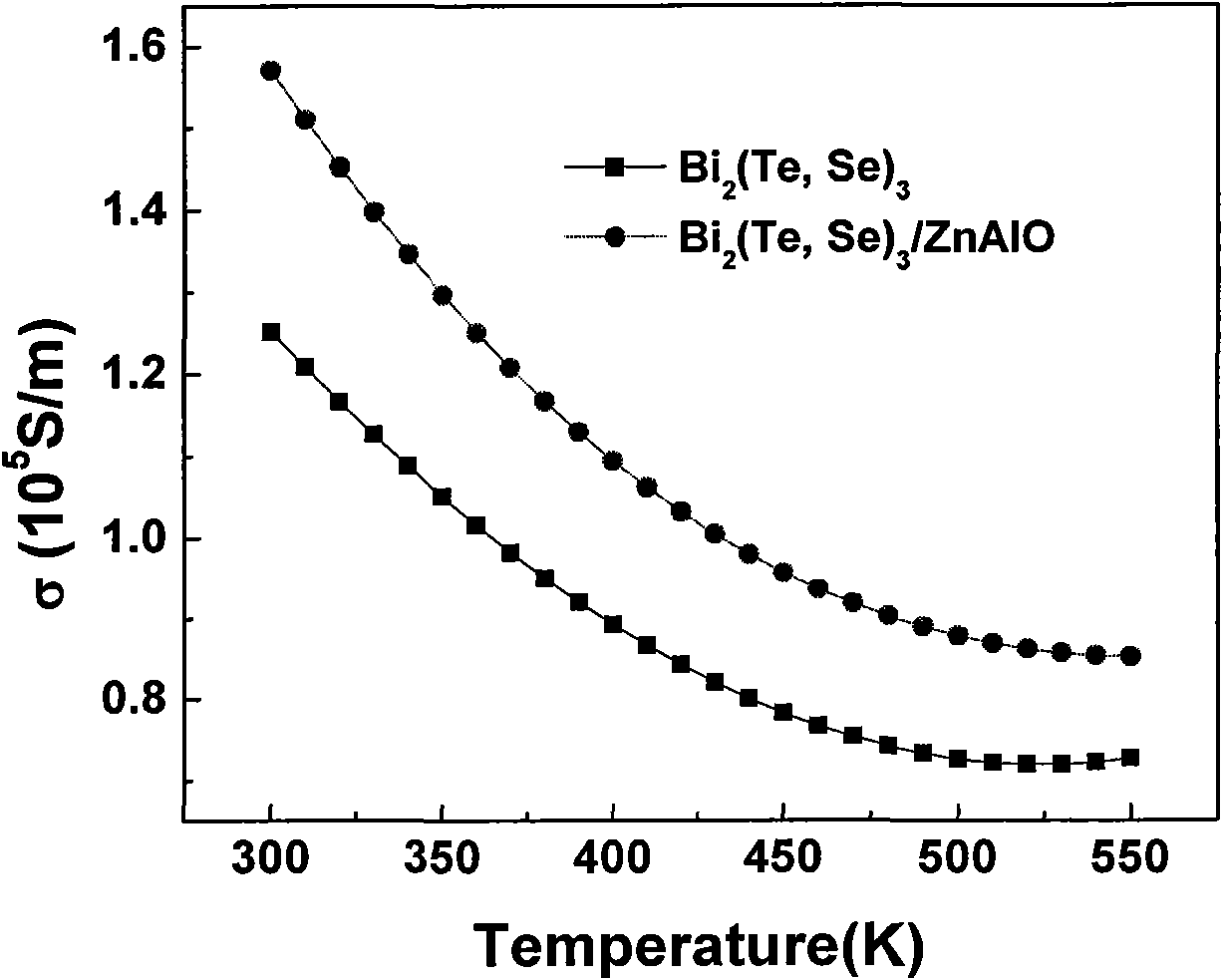
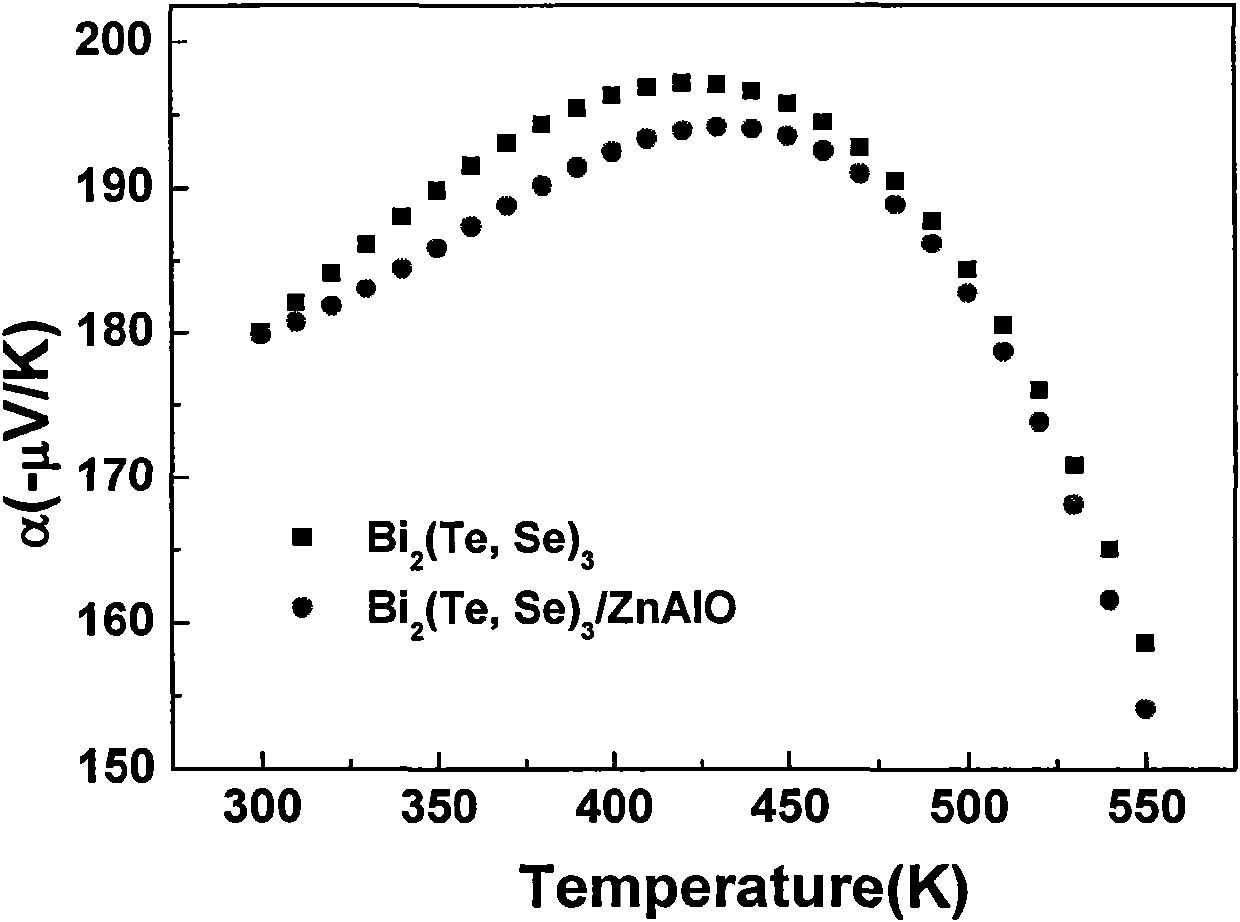
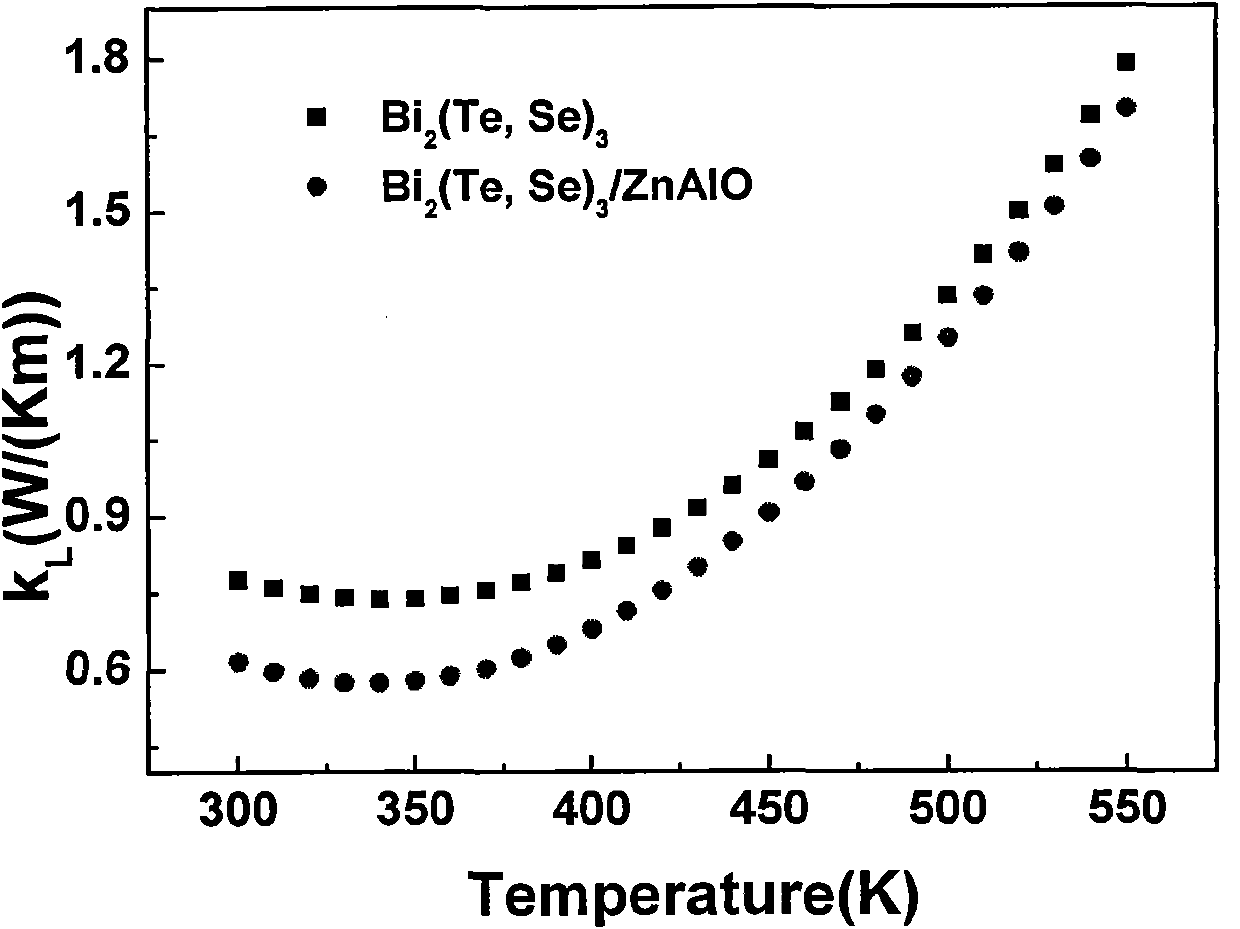
Nanoparticle composite bismuth telluride-based thermoelectric material and preparation method thereof
A technology of nano-particles and thermoelectric materials, which is applied in the fields of thermoelectric device junction lead-out material and thermoelectric device manufacturing/processing, etc. Achieve good chemical stability, reduce lattice thermal conductivity, and optimize thermoelectric performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] In the matrix material composed of bismuth Bi, tellurium Te and selenium Se elements, zinc-aluminum alloy oxide with nanoparticles is mixed to form N-type Bi composited with zinc-aluminum alloy oxide nanoparticles 2 (Te, Se) 3 A crystalline thermoelectric material in which zinc-aluminum-aluminum oxide nanoparticles account for 1.5% of the matrix material. The specific preparation method is as follows:
[0029] With the elements Bi, Te, Se as the matrix raw materials, according to the N-type Bi 2 (Te, Se) 3 The composition ratio of the matrix element powder is weighed with a total amount of 50g, and then 0.75g of nano-powder of zinc-aluminum alloy oxide is weighed according to 1.5% of the total mass of the matrix element powder as the second phase; the second phase and the matrix element powder Mix them into a quartz glass tube, vacuum seal the quartz glass tube at 0.01Pa, place it in a swing furnace, heat and melt it at 700°C for 2 hours, so that the second phase and...
Embodiment 2
[0032] In the matrix material composed of bismuth Bi, tellurium Te and antimony Sb elements, zinc-aluminum alloy oxide with nanoparticles is mixed to form a P-type (Bi, Sb) composite of zinc-aluminum alloy oxide nanoparticles. 2 Te 3Crystalline thermoelectric materials in which zinc-aluminum-aluminum oxide nanoparticles account for 2% of the matrix material. The specific preparation method is as follows:
[0033] With the elements Bi, Te, Sb as the base material, according to the P type (Bi, Sb) 2 Te 3 The composition ratio of the matrix element powder is weighed with a total amount of 50g, and then 1g of nano-powder of zinc-aluminum alloy oxide is weighed according to 2% of the total mass of the matrix element powder as the second phase; the second phase is mixed with the matrix element powder Put it into a quartz glass tube, vacuum seal the quartz glass tube at 0.01Pa, then place it in a swing furnace, heat and melt it at 700°C for 1 hour, so that the second phase and the...
Embodiment 3
[0036] In the matrix material composed of bismuth Bi, tellurium Te and antimony Sb elements, zinc-aluminum alloy oxide with nanoparticles is mixed to form a P-type (Bi, Sb) composite of zinc-aluminum alloy oxide nanoparticles. 2 Te 3 A crystalline thermoelectric material in which zinc-aluminum-aluminum oxide nanoparticles account for 10% of the matrix material.
[0037] The specific preparation method is as follows:
[0038] With Bi, Te, Sb as matrix elements, according to P type (Bi, Sb) 2 Te 3 The proportion of ingredients weighed a total of 50g matrix element powder; Zn, Al, Bi 2 o 3 As the precursor of zinc-aluminum alloy oxide, the precursor undergoes oxidation-reduction reaction to obtain zinc-aluminum alloy oxide. According to the zinc-aluminum alloy oxide accounts for 10% of the total mass of matrix element powder, the required precursor Zn, Al and Bi 2 o 3 The respective mass, and weigh the precursor Zn, Al and Bi of this mass 2 o 3 ; mix the precursor and ma...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com