Rheology modifier
A technology of additives and additives, which is applied in the field of processing thermoplastic engineering plastics, can solve the problems of expensive and complex preparation processes, and achieve the effects of improved mechanical properties, high surface quality, and short cycle time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment R
[0089] Embodiment RM1 (the present invention)
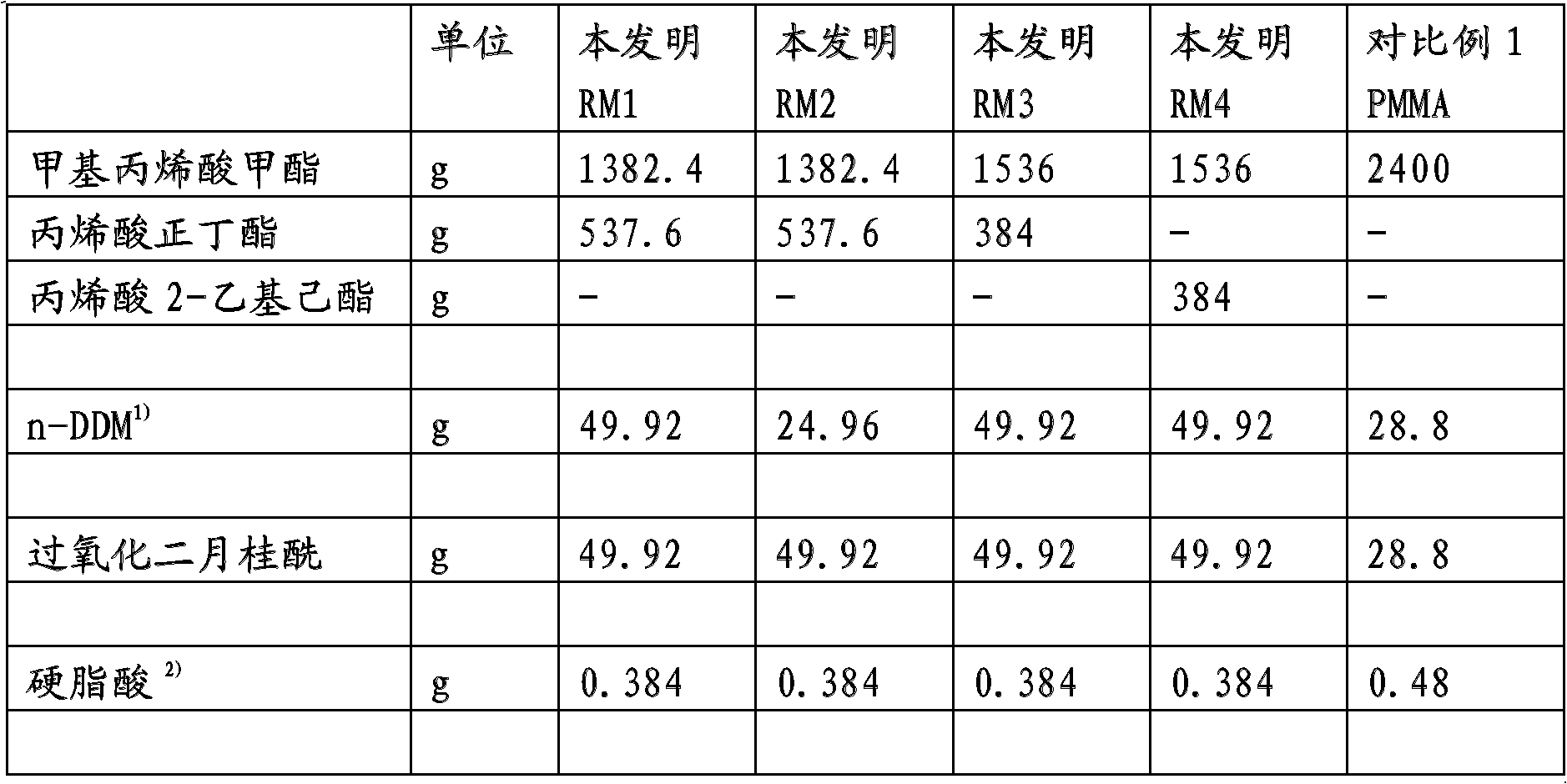
[0090] In a 5 liter polymerization vessel with a heating / cooling jacket equipped with stirrer, reflux condenser and thermometer, an aqueous phase consisting of: 2840 g of fully desalinated water, 0.72 g of Trilon A, was heated to 73°C. 21 g of soda solution (10 wt%), 19.2 g of aluminum sulfate solution (26 wt%), 0.39 g of sodium alkanesulfonate solution (41.4 wt%) and 1.38 g of Lipoxol 6000 solution (10 wt%). This aqueous phase was then added, under stirring, to a mixture of the following in the masses reported in Table 1: methyl methacrylate (MMA), n-butyl acrylate (n-BA), n-dodecyl sulfide alcohol (n-DDM), dilauroyl peroxide and stearic acid. The batch was polymerized at 73°C for 70 minutes and at 90°C for 5 minutes, and then cooled to 50°C, 7.5 g of sulfuric acid (50 wt%) was added and stirred for 5 minutes, further cooled to room temperature. The polymer beads were filtered off, washed well with water and dried in a circula...
Embodiment C1 to C6
[0125] Examples C1 to C6 (Enhanced PBT)
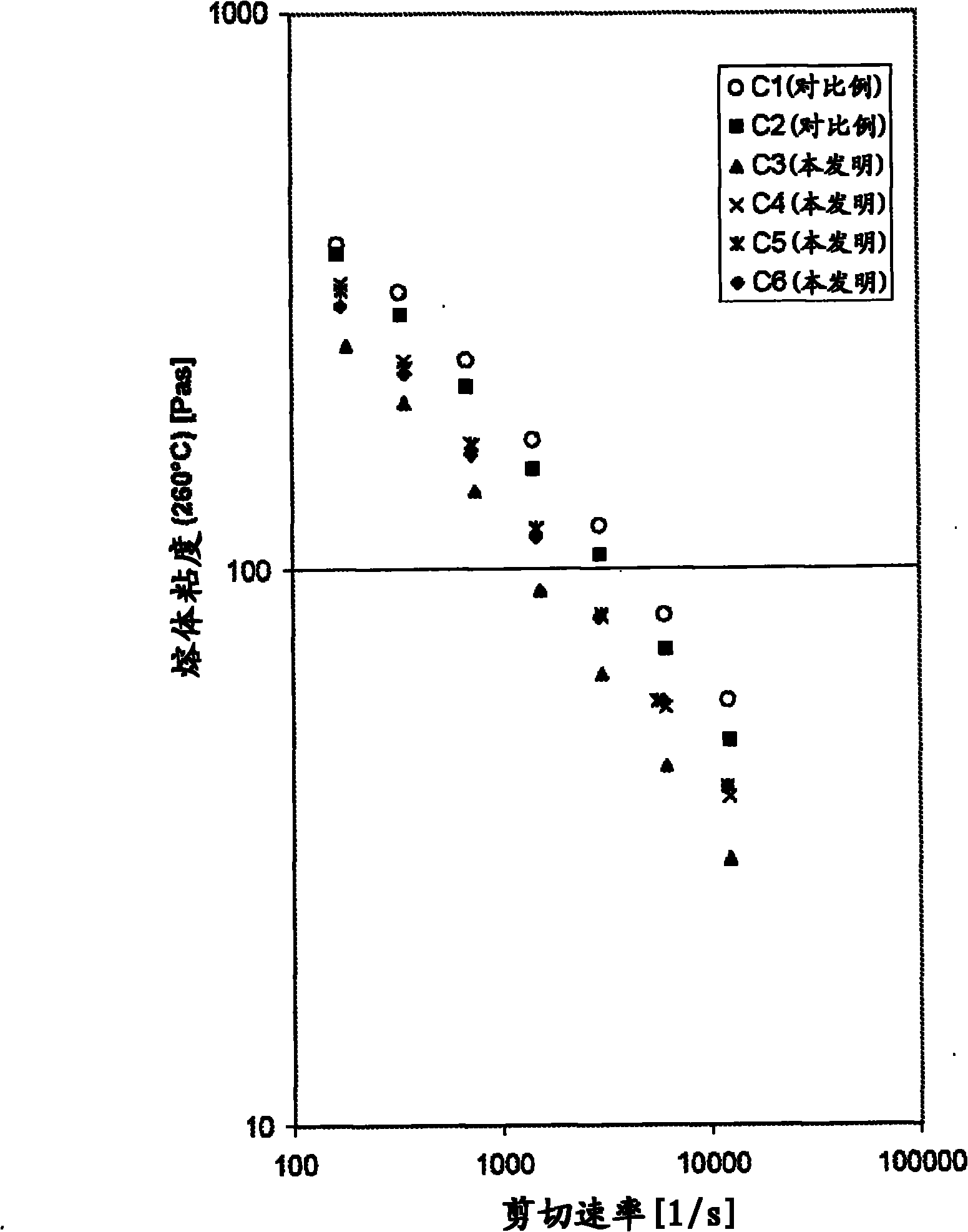
[0126] Compounding (PBT): PBT pellets were pre-dried in a dry air drier at 120° C. for 4 hours. The rheology modifier was pre-dried in a circulating air dryer at 30°C for 24 hours. The PBT-based molding compositions of the compositions stated in Tables 3 and 4 were processed using a ZSK25 type twin-screw extruder (Coperion Werner & Pfleiderer GmbH & Co. KG, Stuttgart, Germany) at a mass temperature of about 250 to 255° C., Compounding was carried out at a throughput of 10 kg / h and a screw speed of 125 rpm, and the melt was led through a water bath into a strand pelletizer and subsequently pelletized. The extruder drive torque reported in Table 3 or Table 4 is measured here. Then at 260°C and 1000l / s and 1500l / s, from figure 1 The flow curves depicted in determine the melt viscosity of the PBT molding compositions.
[0127] Preparation of test pieces (PBT): After drying the PBT molding composition at 120° C. for 4 hours in a circula...
Embodiment C7 to C11
[0138] Examples C7 to C11 (enhanced PA6)
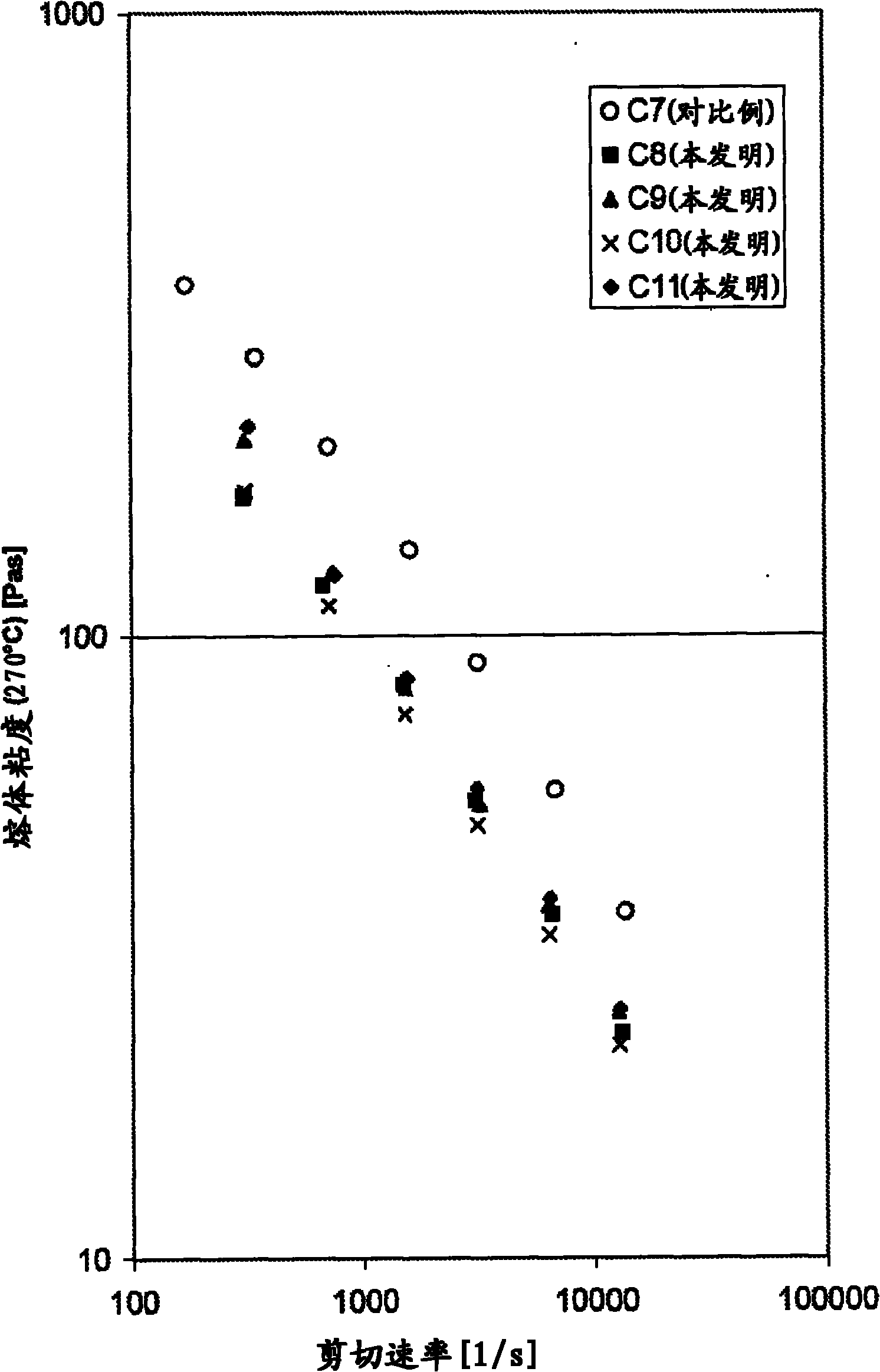
[0139] Compounding (PA6): The PA6 pellets were predried in a dry air drier at 100° C. for 4 hours. The rheology modifier was pre-dried in a circulating air dryer at 30°C for 24 hours. The PA6-based molding compositions of the compositions mentioned in Table 5 were used in a twin-screw extruder type ZSK25 (Coperion Werner & Pfleiderer GmbH & Co.KG, Stuttgart, Germany) at a mass temperature of about 255 to 260 °C, and the mass was passed through Compounding was carried out at an amount of 10 kg / h and a screw speed of 125 rpm, and the melt was led through a water bath into a strand pelletizer and subsequently pelletized. The extruder drive torques reported in Table 5 were observed here. Then at 270°C and 1000l / s and 1500l / s, from figure 2 The flow curves depicted in determine the melt viscosity of PA molding compositions.
[0140] Preparation of test pieces (PA6): After drying the reinforced PA6 molding composition at 80°C in a circul...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melt flow index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melt flow index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com