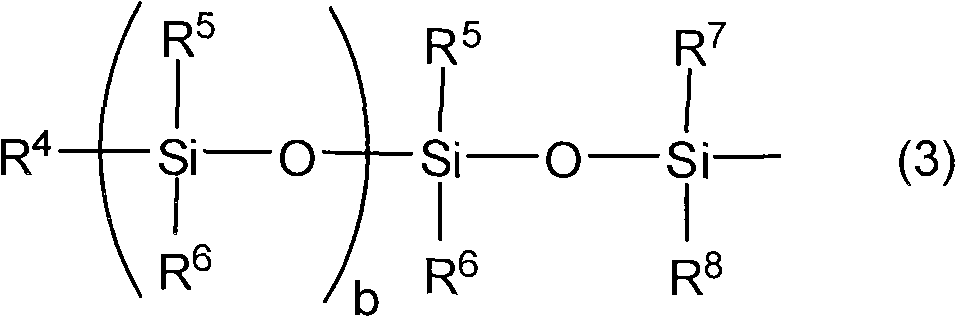
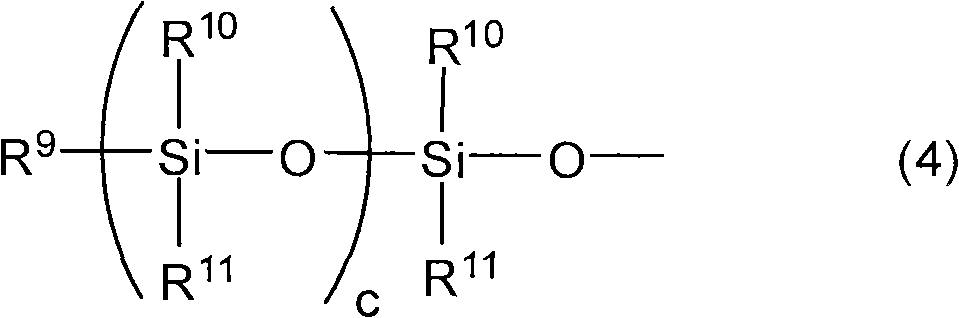
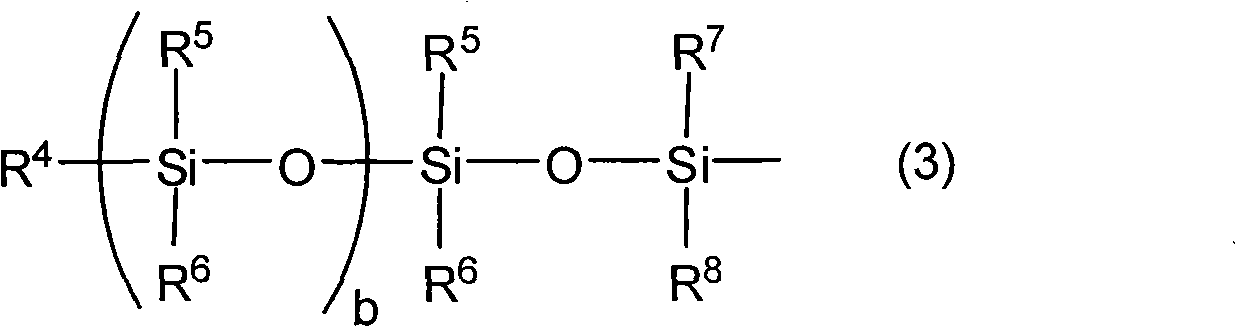
Positive radiation-sensitive composition, interlayer insulating film and method for forming the same
A radiation and sensitivity technology, applied in the field of positive radiation-sensitive compositions, can solve the problems of high flatness obstacle and unevenness of the interlayer insulating film
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Synthetic example 1
[0199] In a container with a stirrer, after adding 25 parts by mass of propylene glycol monomethyl ether, add 30 parts by mass of methyltrimethoxysilane, 23 parts by mass of phenyltrimethoxysilane and 0.1 part by mass of aluminum tetraisopropoxide, Heat to a solution temperature of 60°C. After the solution temperature reached 60°C, 18 parts by mass of ion-exchanged water was added, heated to 75°C, and kept for 3 hours. Next, 28 parts by mass of methyl orthoformate was added as a dehydrating agent, and stirred for 1 hour. Then, the temperature of the solution was set to 40° C., and the solution was evaporated while maintaining the temperature to remove ion-exchanged water and methanol produced by hydrolytic condensation. As above, the hydrolysis-condensation product (A-1) was obtained. The solid content concentration of the hydrolytic condensate (A-1) was 40.5% by mass, the number average molecular weight (Mn) of the obtained hydrolytic condensate was 1,500, and the molecular...
Synthetic example 2
[0201] In a container with a stirrer, add 25 parts by mass of propylene glycol monomethyl ether, then add 22 parts by mass of methyltrimethoxysilane, 12 parts by mass of γ-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane, 20 parts by mass of Phenyltrimethoxysilane and 0.1 parts by mass of tetraisopropoxyaluminum were used in the same manner as in Synthesis Example 1 to obtain a hydrolysis condensate (A-2). The solid content concentration of the hydrolytic condensate (A-2) was 39.8% by mass, the number average molecular weight (Mn) of the obtained hydrolytic condensate was 1,600, and the molecular weight distribution (Mw / Mn) was 2.
[0202] The [C] component is a copolymer formed from a monomer having a specific structure
Synthetic example 3
[0204] In a glass flask with a stirring device, a condenser and a thermometer, add 28.4 parts by mass of the compound shown in the above formula (c1-1) as (c1) compound, 20.7 parts by mass of Shin Nakamura Chemical ( Co., Ltd.), 18.1 parts by mass of a compound represented by the following formula (c3-1-1-1) as a (c3) compound, 5.9 parts by mass of acetone as a (c4) compound methyl acrylate and 23.5 parts by mass of 2-ethylhexyl acrylate, 3.4 parts by mass of the compound 1,4-butanediol as (c5) and 414 parts by mass of isoacrylate as the solvent. Propanol, in a nitrogen stream, under reflux, after adding 0.7 parts by mass of 2,2'-azobisisobutyronitrile as a polymerization initiator and 4 parts by mass of lauryl mercaptan as a chain transfer agent, at 75°C Copolymerization was carried out under reflux for 8 hours to obtain a solution containing a copolymer (C-1). Then, using an evaporator, the solvent is removed under heating conditions of 70° C. or lower, and the copolymer (C...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com