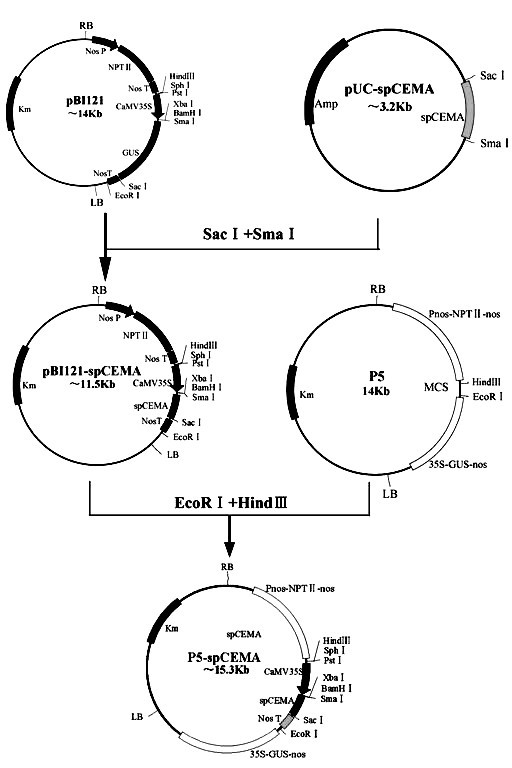
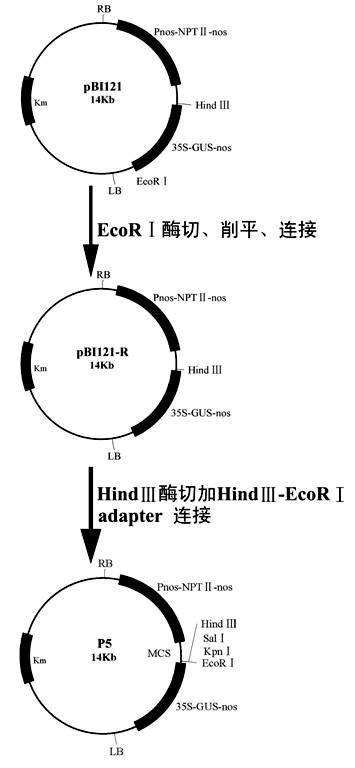
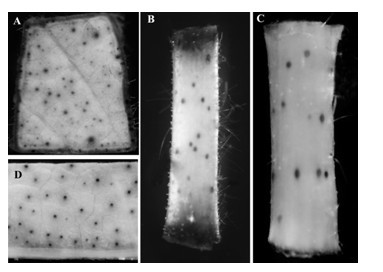
Method for culturing anti-greensickness cotton by using artificially synthesized antimicrobial peptide gene
An artificially synthesized, antimicrobial peptide technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve the problems of pathogenic bacteria that are easy to produce resistance, pathogen specificity, broad-spectrum and long-lasting resistance, and affecting plant growth and development, so as to improve plant disease resistance, Overcome the toxic effect, the effect is remarkable
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0042] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, the present invention will be described in further detail, but the following description does not limit the present invention, any deformation and change of the present invention, as long as they do not depart from the spirit of the present invention, all should belong to the definition of the appended claims of the present invention scope.
[0043] The pharmaceutical reagents in the implementation examples of the present invention are domestic conventional chemical reagents that are not specified, and the materials and methods that are not specified are referred to "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide" (Sambrook and Russell, 2001).
[0044] (1) Obtaining and molecular verification of genetically modified cotton:
[0045] 1. Extraction of DNA:
[0046] 1.1 DNA extraction buffer:
[0047] (1) Plant DNA extraction buffer:
[0048] CTAB extract: 100 mmol / L Tris-HCl (pH8.0), 20 mmol / L EDTA (pH8.0), 1.5 mol / L NaCl, 2% CTAB (w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com