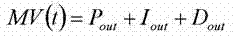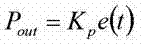Systems and methods for gas supply and usage
A technology for supplying system and gas, applied in the field of gas (for example, it can solve the problems of difficult to automatically start and rise, difficult to adjust and maintain the minimum heating power and temperature, etc., to achieve long heater life, sensitive response, and fast system response. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
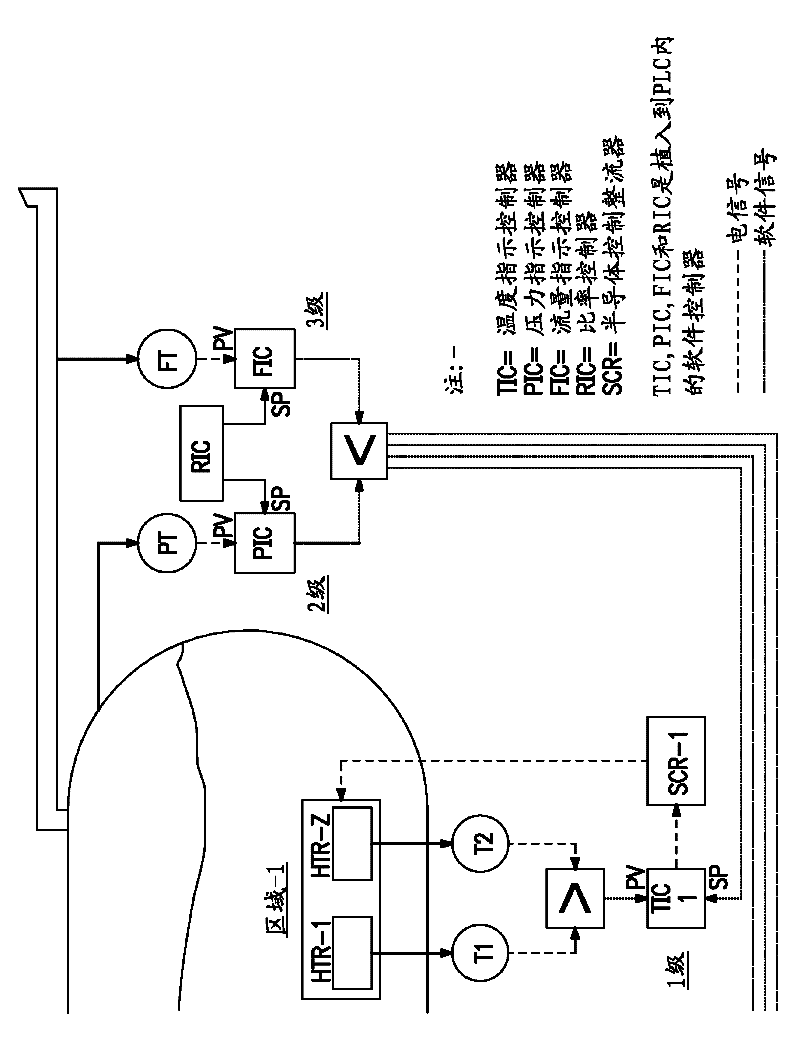
[0108] refer to figure 1 , this example describes a two-stage cascade control system that dynamically adjusts heating power in response to changes in user flow rate. In this two-stage cascade control system, only the pressure indicating controller (PIC) and the temperature indicating controller (TIC) are coupled. At a given time = 0 seconds, the vessel is warmed and the vessel pressure is stabilized at the PIC set point, eg, 120 psig. Steam flow to user site is zero (ie, BSGS is not working). As soon as the user starts drawing steam flow (eg, time = 0 seconds), the vessel pressure is immediately reduced to, eg, 119 psig. The PIC calculates an output signal based on the -1 psig difference between the vessel pressure and the PIC set point at this time. The output signal from the PIC corresponds to a change in the temperature set point of the TIC, in this case eg +10°F (ie, a 10°F increase in the TIC set point). The TIC then increases heating power to meet the new temperature...
example 2
[0110] refer to figure 1 , this example exemplifies a three-stage cascade control system that dynamically adjusts the heating power to the vessel in response to user flow rate changes. In this three-stage cascade control system, a pressure indicating controller (PIC), a temperature indicating controller (TIC) and a flow indicating controller (FIC) are all coupled. At a given time = 0 seconds, the vessel is warmed and the vessel pressure stabilizes at the PIC set point, eg, 120 psig. The steam flow rate stabilized at the FIC set point to the user site, eg 100 standard liters per minute (slpm). As soon as the user starts drawing steam flow (eg, 110 slpm, eg time = 0 seconds), the vessel pressure immediately decreases to eg 119 psig. The PIC calculates an output signal based on the -1 psig difference between the vessel pressure and the PIC set point at this time. The FIC also calculates an output signal based on the difference between the user steam flow rate and the FIC set p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com