Device and method for measuring laser incident angle by sinusoidally modulating multi-beam laser heterodyne secondary harmonics with Doppler galvanometer
A technology of Doppler galvanometer and laser heterodyning, which is applied in the directions of measuring devices, measuring angles, surveying and navigation, etc., can solve the problems of slow signal processing speed, poor quality of collected laser difference frequency signals, etc., and achieve good application prospects and value, fast measurement speed, and good linearity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
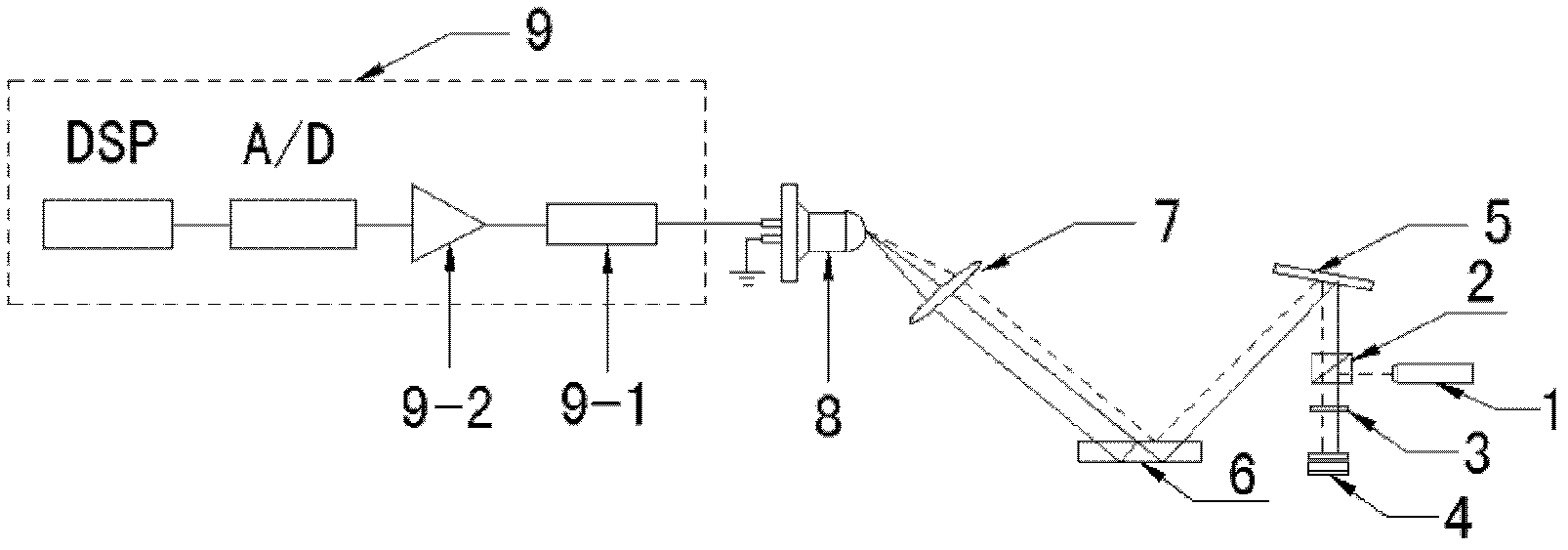
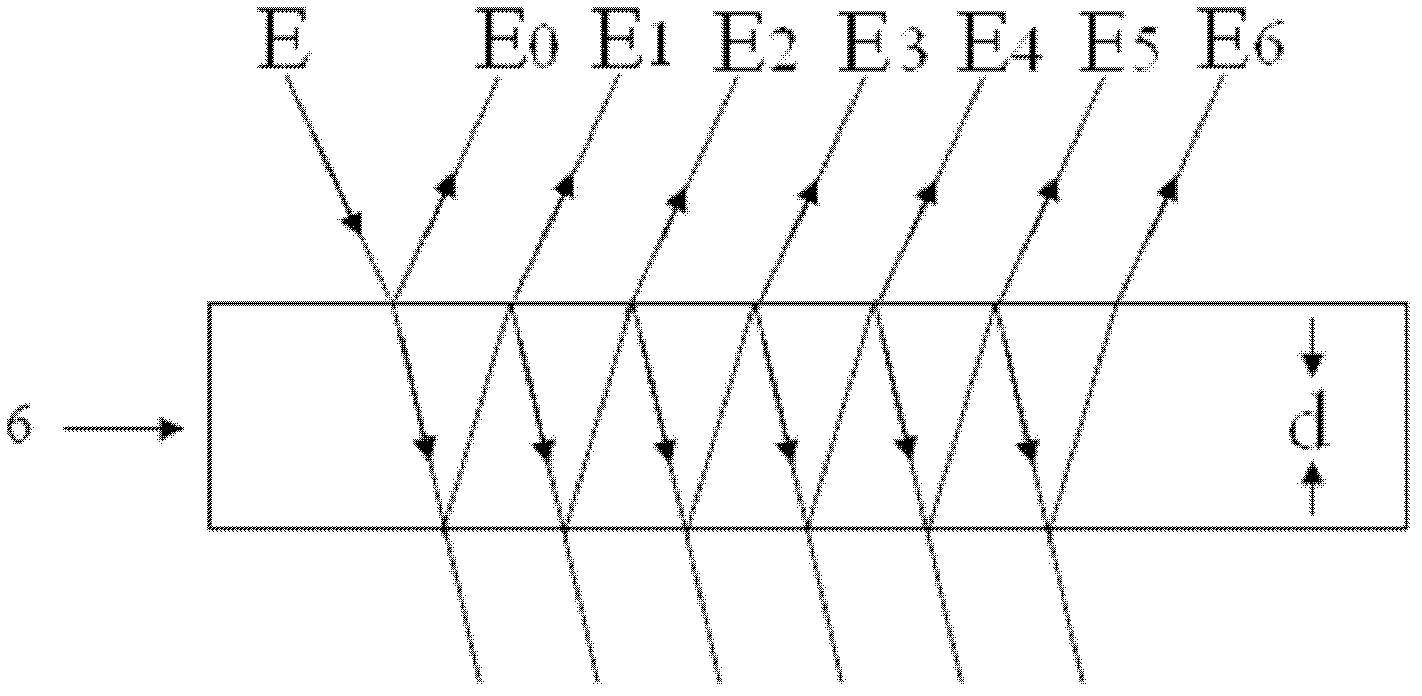
[0021] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 This embodiment is described. The device for measuring the incident angle of the laser by sinusoidally modulating the multi-beam laser heterodyne second harmonic wave of the Doppler vibrating mirror in this embodiment includes a H0 solid-state laser 1, a polarizing beam splitter PBS2, and a quarter-wave plate 3. Vibrating mirror 4, flat mirror 5, glass plate of known thickness 6, converging lens 7, photodetector 8 and signal processing system 9,
[0022] The linearly polarized light emitted by the H0 solid-state laser 1 is reflected by the polarization beam splitter PBS2 and then incident on the quarter-wave plate 3, and the light beam transmitted by the quarter-wave plate 3 is incident on the light-receiving surface of the vibrating mirror 4 , the light beam reflected by the galvanometer 4 is sent to the polarization beam splitter PBS2 after being transmitted by the quarter-wave plate 3 again, and the light beam transm...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0024] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that the signal processing system 9 is composed of a filter 9-1, a preamplifier 9-2, an analog-to-digital converter A / D and a digital signal processor DSP , the filter 9-1 filters the received electrical signal output by the photodetector 8 and sends it to the preamplifier 9-2, and the signal amplified by the preamplifier 9-2 is output to the analog-to-digital converter A / D, the analog-to-digital converter A / D sends the converted digital signal to the digital signal processor DSP. Other compositions and connection methods are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
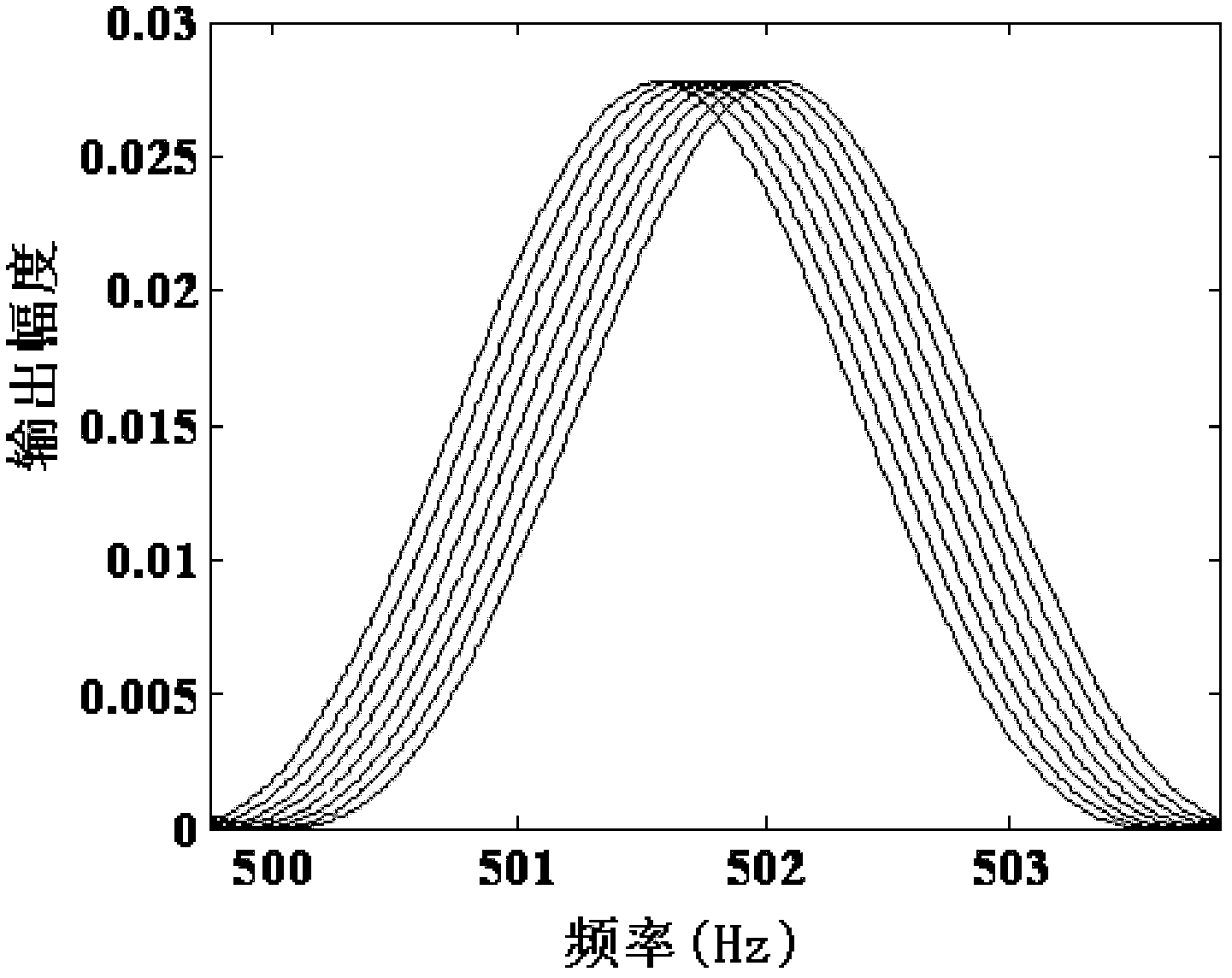
[0025] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that the vibrating mirror 4 is a Doppler vibrating mirror, and the simple harmonic vibration equation of the vibrating mirror 4 is:
[0026] x(t)=x 0 cos(ω c t)
[0027] The velocity equation of the vibrating mirror 4 is:
[0028] v(t)=-ω c x 0 sin(ω c t)
[0029] In the formula, the parameter ω 0 is the laser angular frequency, parameter x 0 is the vibration amplitude of the galvanometer, parameter ω c is the angular frequency of the vibrating mirror, c is the speed of light; t is time. Other compositions and connection modes are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com