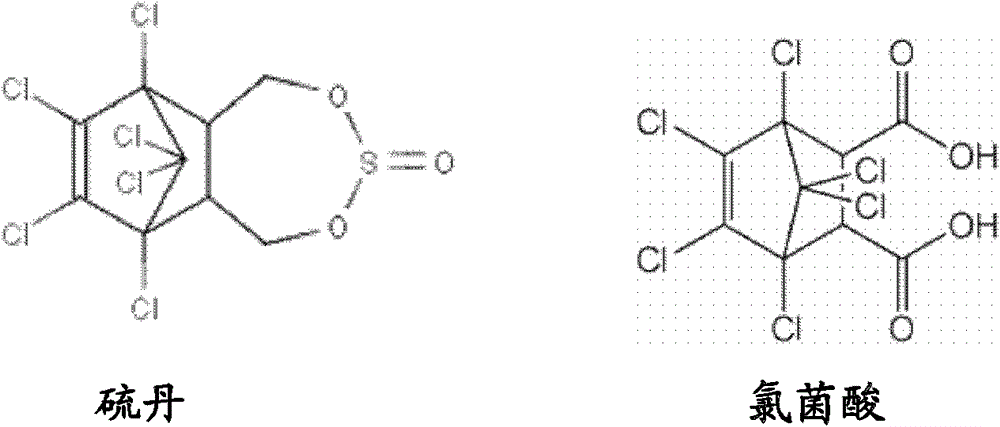
Synthetic method of molecule marking polymer particles or beads conducting selective detoxification on natural water polluted by endosulfans, analogs or derivatives, and product
A technology of polymer particles and molecular imprinting, applied to its analogs or derivatives, preparation of chloramphenicol imprinted polymer compositions, removal of endosulfan field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Synthesis of chlorendic acid-imprinted and non-imprinted polymer particles using ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA)
[0064] 1.0mmol of chlorendic acid (CA) (0.39g), 2.0mmol of 4-vinylaniline (VA) (0.24g) and 1.0mmol of acrylamide (AA) (0.07g) were placed in a 50ml round bottom flask and dissolved in 10 ml of hexane with stirring and cooled to 0°C. 20 mmol of ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) (4 ml) and 50 mg of 2,2'-azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) were added thereto and stirred until a uniform solution was obtained. The monomer mixture was then cooled to 0 °C with N 2 Wash for 10 minutes, seal and heat in an oil bath at 80°C while stirring for about 30 minutes. The resulting material was washed with distilled water, dried overnight and ground to fine particles in a mortar and pestle. The chlorendic acid-imprinted polymer particles were refluxed with methanol for 4 hours in a Soxhlet extractor, filtered, washed with 500 ml of distilled water and left overnight...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Synthesis of chlorendic acid-imprinted and non-imprinted polymer particles using 1,1,1-tris-(hydroxymethyl)-propane trimethacrylate (TRIM)
[0067] 1.0mmol of chlorendic acid (CA) (0.39G), 2.0mmol of 4-vinylaniline (VA) (0.24g) and 1.0mmol of acrylamide (AA) (0.07g) were placed in a 50ml round bottom flask and dissolved in 10 ml of hexane with stirring and cooled to 0°C. 20 mmol of 1,1,1-tris-(hydroxymethyl)-propane trimethacrylate (TRIM) (7 ml) and 50 mg of 2,2'-azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) were added thereto and stirred until a homogeneous solution is obtained. The monomer mixture was then cooled to 0 °C with N 2 Wash for 10 minutes, seal and heat in an oil bath at 80°C while stirring for about 30 minutes. The resulting material was washed with distilled water, dried overnight and ground to fine particles in a mortar and pestle. CA imprinted polymer particles (2 g) were refluxed with methanol for 4 hours in a Soxhlet extractor, filtered, washed with 500 ml of dis...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Synthesis of chlorendic acid-imprinted polymer microbeads
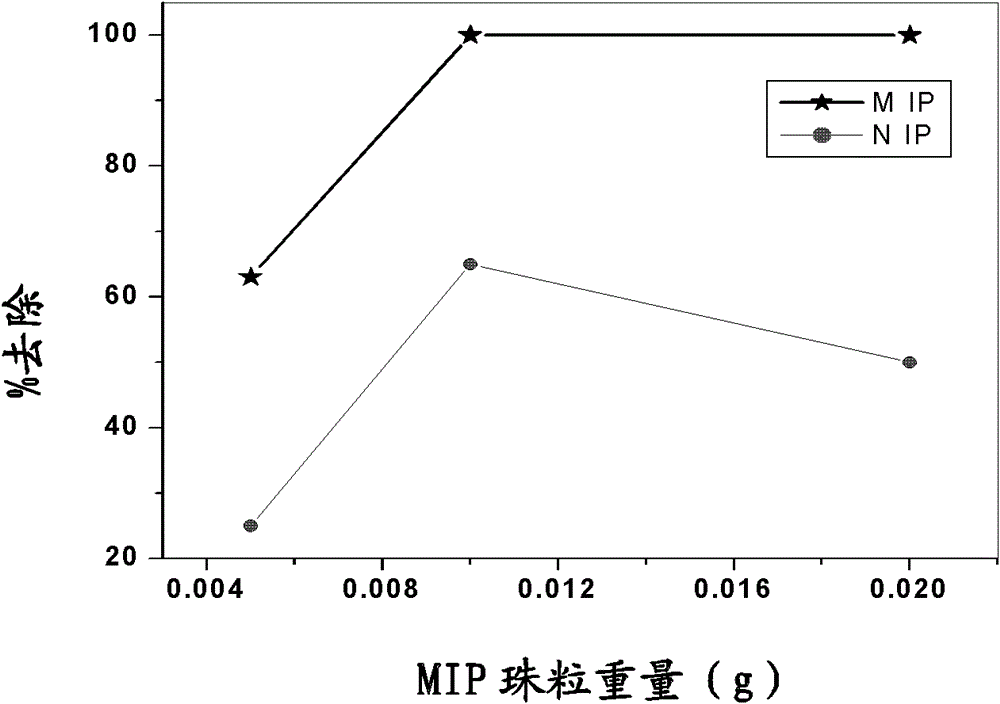
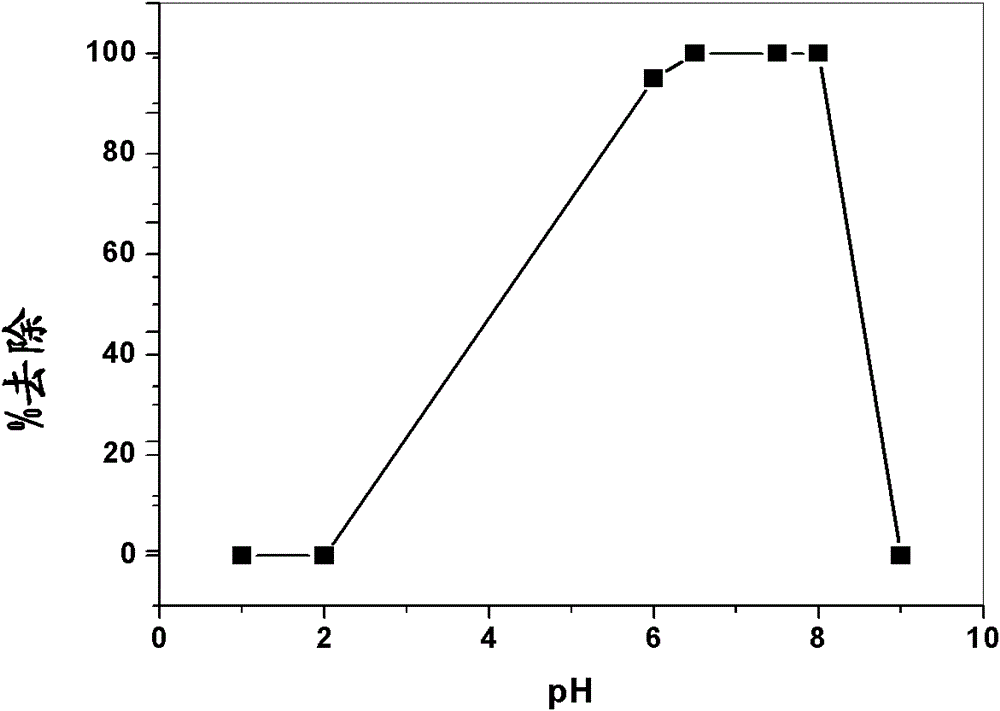
[0070] 1.0mmol of CA (0.39g), 2.0mmol of VA (0.24g) and 1.0mmol of AA (0.07g) were placed in a 100ml round bottom flask and dissolved in 5ml of tetrahydrofuran (THF) by stirring, followed by It was cooled to 0 °C. 20 mmol of TRIM (7 ml) and 50 mg of AIBN were added thereto and stirred until a homogeneous solution was obtained. Add 50 ml of 0.5% (w / v) polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution (prepared by heating to 60° C.) dropwise to the monomer mixture during 30 min, and cool it to 0° C. 2 Wash for 10 minutes, seal and heat in an oil bath at 80°C while stirring for about 3 hours. The resulting microbeads were filtered, dried at 50° C. and then refluxed with methanol in a Soxhlet extractor for 4 hours. The resulting washed beads were filtered, washed again with 500 ml of water and dried at 50°C. This yielded 7.05 g of pseudotemplate-imprinted polymer beads (see Figure 5 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com