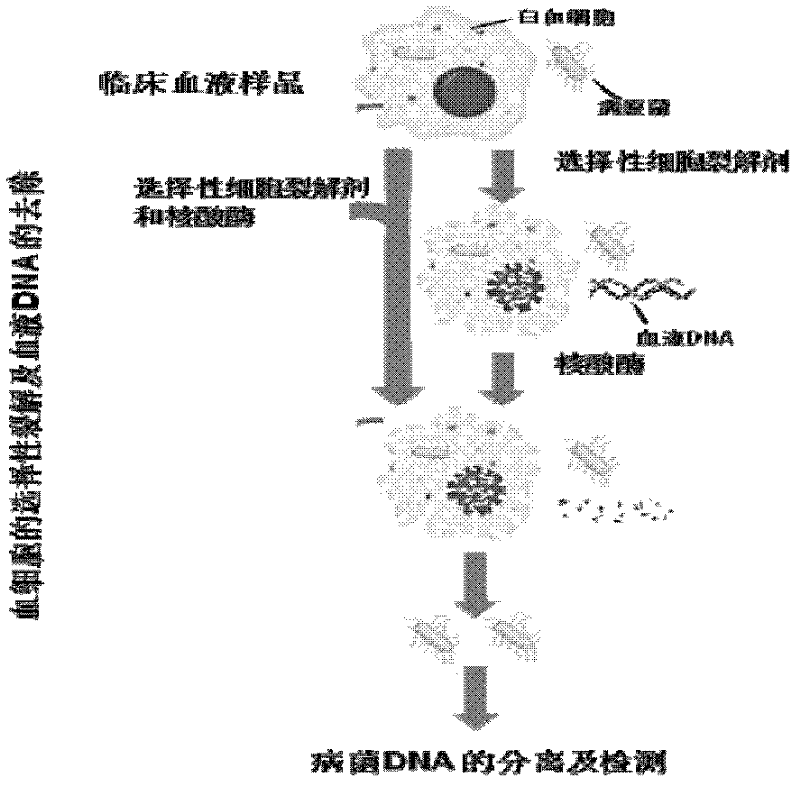
Preparation method of pathogenic bacterium DNAs (Deoxyribonucleic Acids) in clinical blood sample and kit
A technology of blood samples and pathogenic bacteria, applied in the field of molecular diagnostics of pathogenic bacterial infection, can solve the problems of PCR reaction difficulties and achieve the effect of improving specificity and sensitivity and avoiding interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Lysis of blood cells by ox gall powder
[0031] The ox gall powder (produced by sigma company, article number is Fluka, B3883) aqueous solution is that a certain amount of ox gall powder is dissolved in water, and the dissolution is complete.
[0032] Take 1 milliliter of fresh human blood, mix it with 4 milliliters of ox gall powder aqueous solutions with concentrations of 0, 15, 20, 25, 30 and 50 g / L respectively, and place it at room temperature (23-25° C.). Take 10 microliters of samples at regular intervals, put them into 200 microliters of normal saline, and observe the degree of blood cell lysis with a microscope.
[0033] The results are shown in Table 1. As can be seen from Table 1, ox gall powder can rapidly and completely lyse blood cells. In detail, even if the effect is as long as 5 hours, blood cells will not be lysed in normal saline (no ox gall powder), 12g / L ox gall powder can only partially lyse blood cells, and ox gall powder with a concentration abo...
Embodiment 2
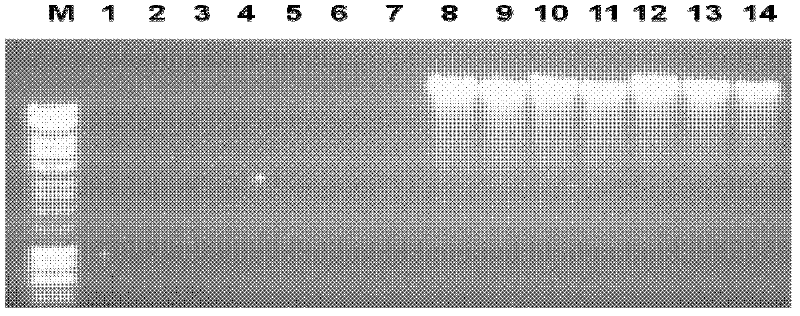
[0037] 1. Preparation of simulated clinical blood samples
[0038] A typhoid colony was inoculated into 2 ml of tryptone soybean broth (OXOID Tryptone Soya Broth, UK: TSB for short), and cultured on a constant temperature shaker at 37° C. at 200 rpm for 2 hours to obtain a typhoid culture medium. First dilute the Salmonella typhi culture solution to A 600 Next, the OD was 0.25, and then a further 10-fold serial dilution was made. Take 100 microliters from each of the dilutions and culture them on tryptone soybean agar medium at 37°C to determine the content of Salmonella typhi in each dilution.
[0039] Human blood is drawn with a sterile syringe and immediately placed into a test tube containing heparin. 900 ml of fresh blood was mixed with 100 microliters of dilutions containing different numbers of typhoid bacteria. The mixture thereof is a simulated clinical blood sample, and the simulated clinical blood sample is used for the separation and preparation of DNA.
[0040...
Embodiment 3
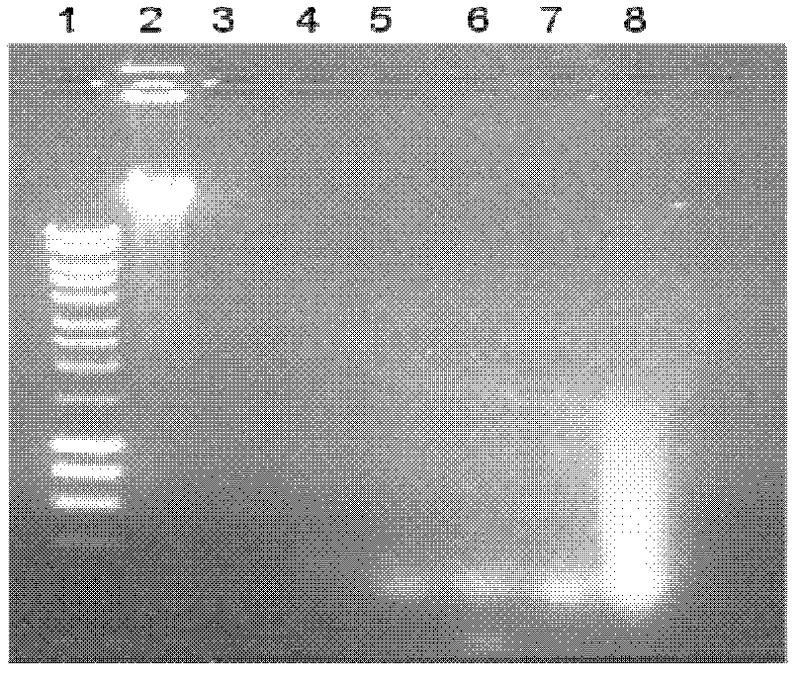
[0053] Effects of different concentrations of ox gall powder aqueous solution on the biological activity of Micrococcus deoxyribonuclease
[0054] (1) Get 7 20 microliters containing 0.5 micrograms of human blood DNA, and respectively containing 0, 10, 30, 50, 70 and 90 g / L of ox gall powder aqueous solution, and put them into reaction tubes. Add 2x10 to each 3 1 unit of Micrococcal DNase, mixed well and left at room temperature for 10 minutes, and then checked for DNA degradation in the reaction solution by agarose gel electrophoresis. The result is as image 3 Shown: micrococcal deoxyribonuclease can completely degrade human blood DNA, and under the reaction conditions of ox gall powder concentration up to 90g / L, micrococcal deoxyribonuclease still has its biological activity.
[0055] (2) Take 10 microliters of ox gall powder aqueous solutions with a concentration of 0, 50 or 100 g / L, and put them into a reaction tube. Add 10 microliters of micrococcal deoxyribonuclease ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com