Methods and compositions for inactivating glutamine synthetase gene expression
A gene and binding domain technology, applied in cell culture, cell line generation and protein preparation, genome engineering, and can solve problems such as laborious
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0114] Preparation of lipid:nucleic acid complexes, including targeting liposomes, such as immunolipid complexes, is well known to those of ordinary skill in the art (see, e.g., Crystal, Science 270:404-410 (1995); Blaese et al. al., Cancer Gene Ther. 2: 291-297 (1995); Behr et al., Bioconjugate Chem. 5: 382-389 (1994); Remy et al., Bioconjugate Chem. 5: 647-654 (1994); Gao et al., Gene Therapy 2: 710-722 (1995); Ahmad et al., Cancer Res. 52: 4817-4820 (1992); , 4,837,028 and 4,946,787).
[0115] RNA or DNA delivery systems for nucleic acids encoding engineered ZFPs take advantage of the highly evolved process of targeting viruses to specific cells in vivo and transporting the viral payload to the nucleus. Viral vectors can be administered directly to a patient (in vivo), or can be used to treat cells in vitro and administer the modified cells to a patient (ex vivo). Conventional viral systems for ZFP delivery include, but are not limited to, retroviruses, lentiviruses, aden...
Embodiment 1
[0137] Example 1: Engineering and Structure of ZFNs
[0138] A. Glutamine Synthetase (GS) ZFN
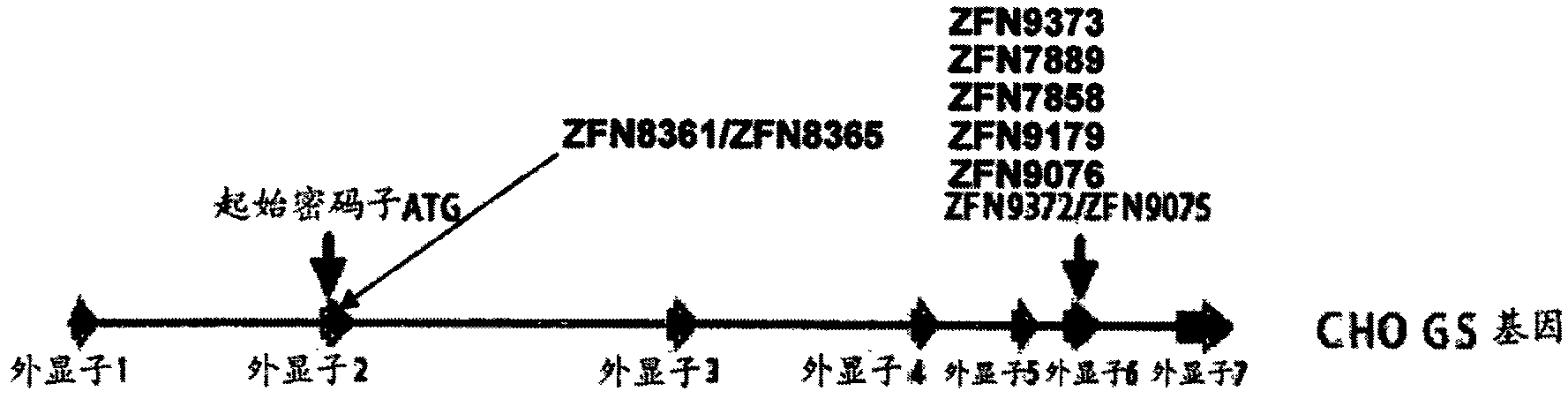
[0139] Because the full sequence of the CHO genome is not available, the CHO GS gene was cloned and sequenced to generate the target DNA sequence for ZFN engineering. Figure 13 shows the complete CHO GS sequence, with introns and exons also specified.
[0140] The ZFN target site within exon 6 of the CHO GS gene was chosen because this region encodes amino acids critical to the catalytic function of the GS protein based on available crystal structures (see, e.g., Almassy et al. (1986) Nature 323:304-309; Gill et al. (2002) Biochem.41:9863-9872; Liaw et al. (1994) Biochem.33:675-681), as such, ZFN-mediated mutations at this site are expected to cause Reduction of functional GS activity. The partial sequence of CHO GS exon 6 is shown below. Capital letters indicate exon sequences; lowercase letters indicate intron sequences; ZFN target site 9372 / 9075 (Table 1, Figure 1A and F...
Embodiment 2
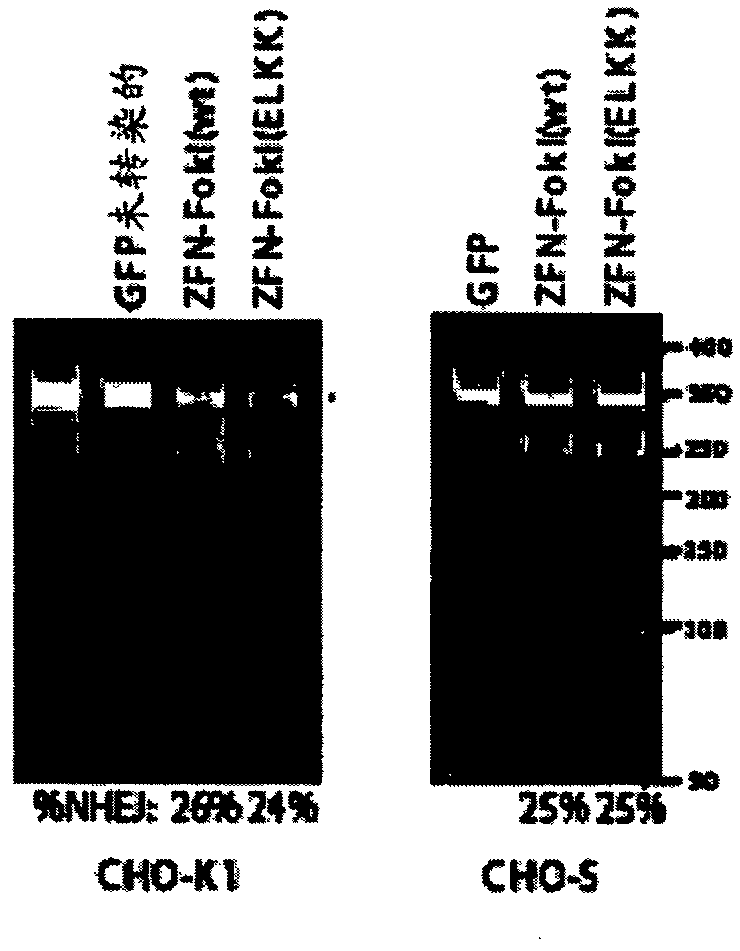
[0155] Example 2: GS-ZFN modification of endogenous GS
[0156] To determine whether GS targeted the ZFN-modified endogenous GS locus as expected, a CEL-1 mismatch assay was performed essentially following the manufacturer's instructions (Trangenomic SURVEYOR™). Briefly, appropriate ZFN plasmid pairs were transfected into CHO K-I cells grown adherently in serum-containing medium or CHO-S cells grown in suspension in chemically defined medium without serum.
[0157] CHO K-I cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection and are recommended for growth in F-12 medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with 10% qualified fetal calf serum (FCS, Hyclone). CHO-S cells were purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA) and grown in chemically defined protein- and animal-component-free CD-CHO medium maintained in suspension culture at 37°C, containing 5% carbon dioxide, at 125 rpm in a humidity-controlled shaking incubator (ATR, inc., Laurel, Maryland) supplemented with 8 mM L-glut...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com