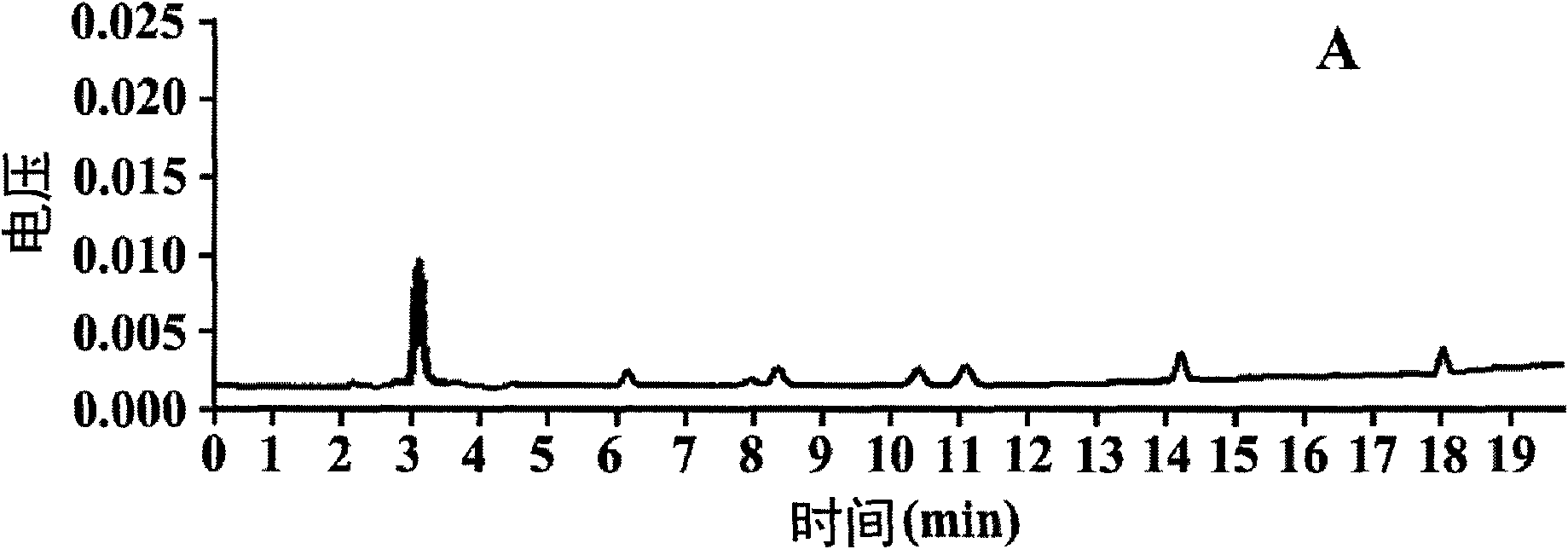
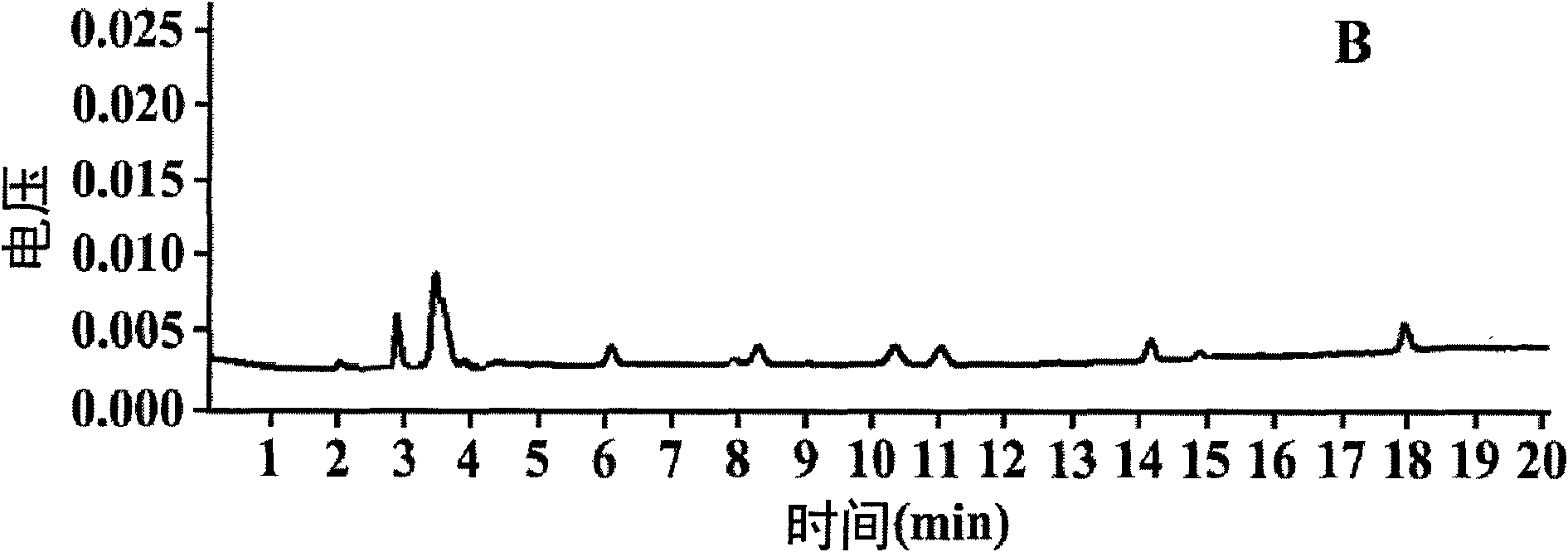
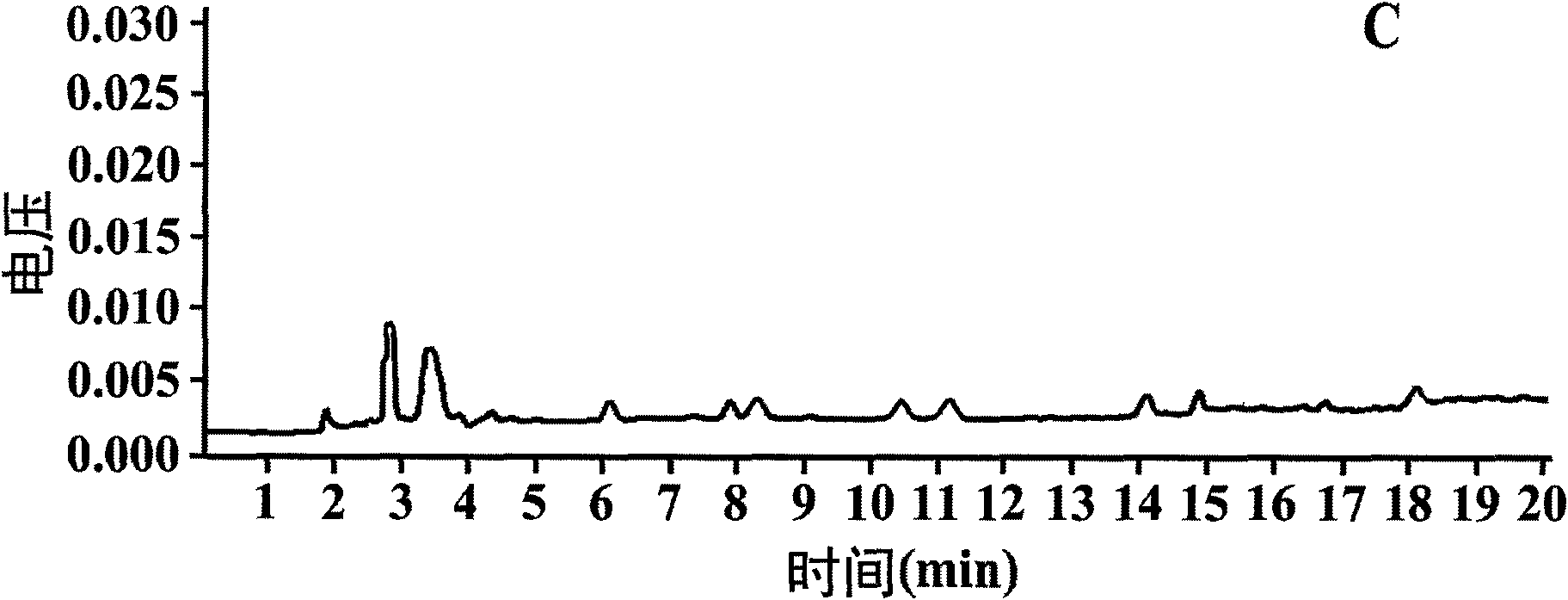
Efficient separation and purification method for multi-residue sulfonamide antibiotics in biological samples
A technology for separation and purification of biological samples, applied in the field of enrichment and purification, rapid separation, and high selectivity of sulfonamide antibiotic residues. good enrichment effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0020] The preparation methods of molecularly imprinted polymers in the following examples are as follows:
[0021] Weigh an appropriate amount of functional monomer methacrylic acid and template molecule sulfadimethoxine (SDM) and dissolve them in 15 mL of acetonitrile diluent, add 5 mL of cross-linking agent ethylene glycol dimethacrylate EGDMA, azobisisobutyronitrile to initiate Dose 120mg, ultrasonic degassing for 5-10 minutes, after mixing evenly, pass nitrogen gas for 10-15 minutes, and seal. Put it in a water bath at 60°C for 24 hours; after the polymerization reaction, take out the synthesized block polymer, grind it, sieve it, and use methanol: formic acid (90:10, v / v) and methanol to remove the template molecule through Soxhlet extraction. , repeated sedimentation with acetone to remove superfine polymer particles, and then vacuum-dry the polymer without template molecules at 50°C to obtain a molecularly imprinted polymer with specific recognition function for sulfon...
Embodiment 1
[0023] (1) Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers for sulfonamide antibiotics
[0024] Accurately weigh 2mmol of functional monomer methacrylic acid and 1mmol of template molecule sulfadimethoxine and dissolve in 15mL of acetonitrile, add 25mmol of cross-linking agent EGDMA, 120mg of initiator azobisisobutyronitrile, ultrasonically degas for 5min, and mix well , into the nitrogen 10 ~ 15min, sealed. Put it in a water bath at 60°C for 24 hours; after the polymerization reaction, take out the synthesized block polymer, grind it, sieve it, and use methanol: formic acid (90:10, v / v) and methanol to remove the template molecule through Soxhlet extraction. , repeated sedimentation with acetone to remove superfine polymer particles, and then vacuum-dried the polymer from which template molecules were removed at 50° C. to obtain molecularly imprinted polymers.
[0025] (2) sulfa antibiotic matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction method, concrete steps are as follows
[0026]...
Embodiment 2
[0033] (1) Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers for sulfonamide antibiotics
[0034] Accurately weigh 4mmol of functional monomer methacrylic acid and 1mmol of template molecule sulfadimethoxine and dissolve in 15mL of acetonitrile, add 25mmol of crosslinking agent EGDMA, 120mg of initiator azobisisobutyronitrile, ultrasonically degas for 5-10min, mix After uniformity, nitrogen gas was introduced for 15 minutes and sealed. Put it in a water bath at 60°C for 24 hours; after the polymerization reaction, take out the synthesized block polymer, grind it, sieve it, and use methanol: formic acid (90:10, v / v) and methanol to remove the template molecule through Soxhlet extraction. , repeated sedimentation with acetone to remove superfine polymer particles, and then vacuum-dried the polymer from which template molecules were removed at 50° C. to obtain molecularly imprinted polymers.
[0035] (2) sulfa antibiotic matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction method, concrete step...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com