Positive electrode material for lithium ion cells and preparation method thereof
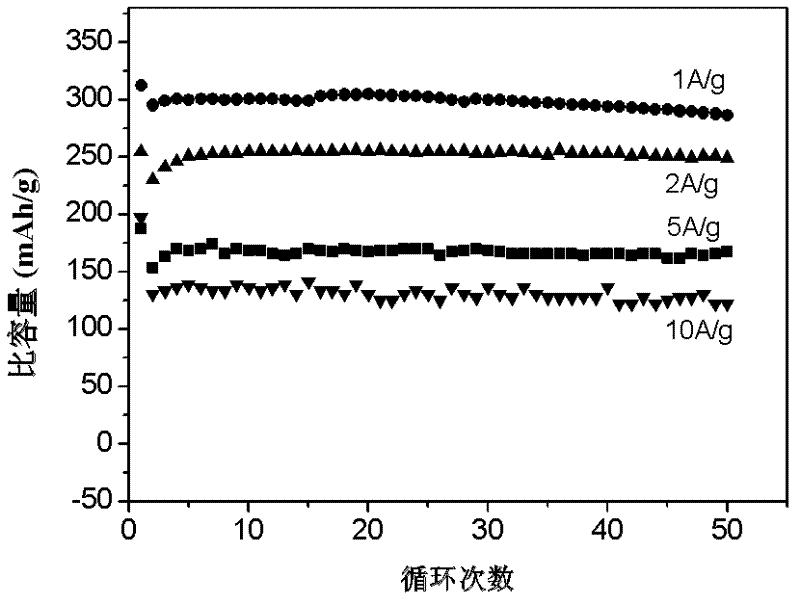
A technology for lithium-ion batteries and positive electrode materials, applied in battery electrodes, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of poor rate characteristics and cycle stability of vanadium pentoxide nanomaterials, poor stability of layered structures, and unsuitability for large currents Charge and discharge and other issues, to achieve the effect of facilitating transportation, improving capacity and cycle stability, and improving rate characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
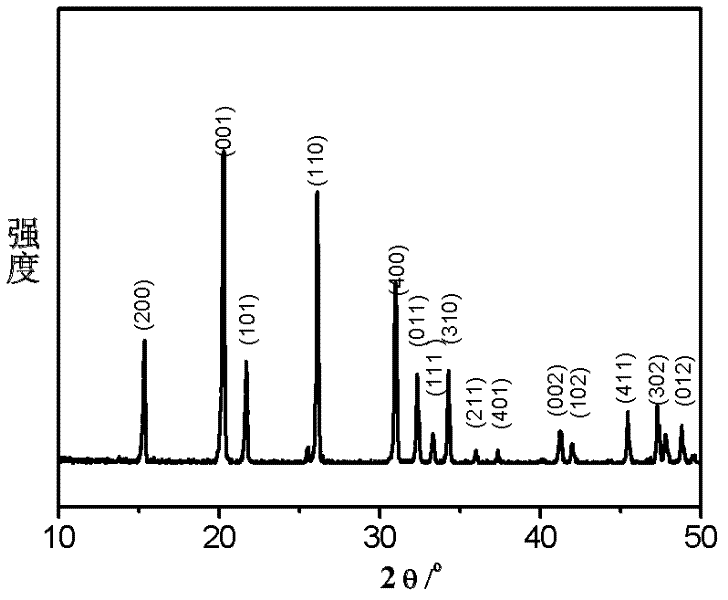
[0023] 1. Mix 1.0 g of vanadium pentoxide and 1.0 g of mesoporous carbon at room temperature, and grind with a mortar until the color is uniform. Then the powder is placed in a tube furnace, and under the protection of inert gas nitrogen, the temperature is raised from room temperature to 750 °C at a rate of 5 °C / min and sintered at a constant temperature of 750 °C for 20 minutes at a high temperature. After cooling to room temperature, di Composites of vanadium and mesoporous carbon.
[0024] 2. Place the obtained composite in a muffle furnace, heat up to 650°C from room temperature at a heating rate of 5°C / min, calcinate in air and at a constant temperature of 650°C for 40 minutes, remove the mesoporous carbon to obtain a porous five Vanadium oxide.
Embodiment 2
[0026] 1. Mix 1.0 g of vanadium pentoxide and 1.0 g of mesoporous carbon at room temperature, and grind with a mortar until the color is uniform. Then the powder is placed in a tube furnace, and under the protection of inert gas nitrogen, the temperature is raised from room temperature to 750 °C at a rate of 5 °C / min and sintered at a constant temperature of 750 °C for 20 minutes at a high temperature. After cooling to room temperature, di Composites of vanadium and mesoporous carbon.
[0027] 2. Place the obtained composite in a muffle furnace, heat up to 600°C from room temperature at a heating rate of 5°C / min, calcinate in air and at a constant temperature of 600°C for 45 minutes, remove the mesoporous carbon to obtain porous five Vanadium oxide.
Embodiment 3
[0029] 1. Mix 1.0 g of ammonium metavanadate and 1.0 g of mesoporous carbon at room temperature, and grind with a mortar until the color is uniform. Then the powder is placed in a tube furnace, and under the protection of inert gas nitrogen, the temperature is raised from room temperature to 750 °C at a rate of 5 °C / min and sintered at a constant temperature of 750 °C for 20 minutes at a high temperature. After cooling to room temperature, di Composites of vanadium and mesoporous carbon.
[0030] 2. Place the obtained composite in a muffle furnace, heat up to 650°C from room temperature at a heating rate of 5°C / min, and calcinate in air and at a constant temperature of 650°C for 45 minutes to remove the mesoporous carbon to obtain porous five Vanadium oxide.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com