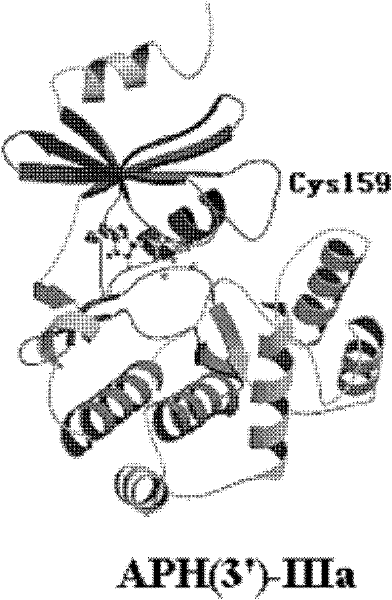
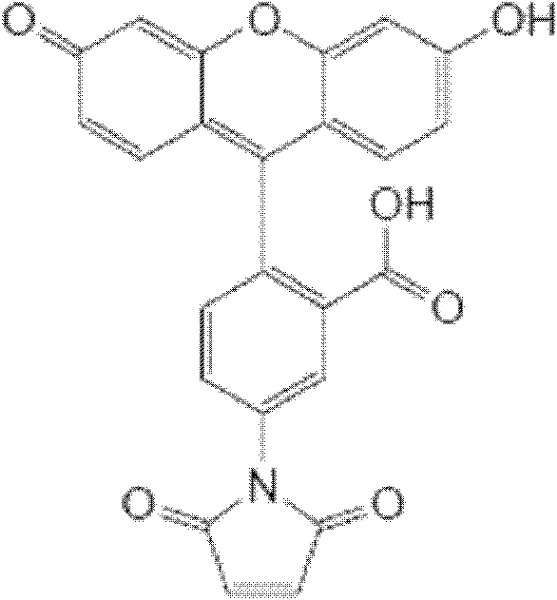
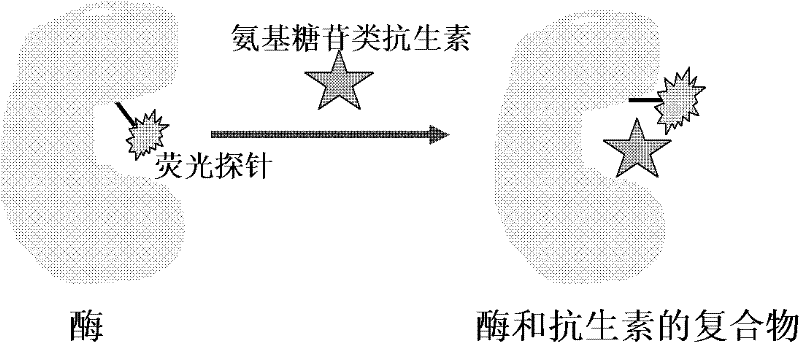
Aminoglycosides phosphate modifying enzyme and detection method for detecting antibiotics
An aminoglycoside and antibiotic technology, applied in the field of aminoglycoside phosphate modification enzymes, can solve the problems of interfering with the binding of antibiotics and ribosomes, and the loss of efficacy of antibiotics, achieving high-throughput detection and analysis, fast detection speed, and convenient operation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1: the establishment of the standard curve of antibiotic concentration and fluorescent probe intensity: use the light source of 494nm as excitation light source, irradiate to quartz cuvette sample cell, then place receiver in vertical 90 degree direction, detect the fluorescence of emission, and Record data collection.
[0032] Sample preparation: Dissolve known kanamycin A in neutral TrisHCl buffer (pH 7.4, 100mMNaCl) at room temperature, and make standard products with different concentrations (0.1μM, 0.5μM, 1μM, 5μM , 10 μM, 20 μM, 50 μM, 100 μM, 200 μM, 500 μM, 1 mM). Blank experiment: Aminoglycoside phosphate modification enzyme (APH(3')-III), ATP, MgCl 2 Dissolve in neutral TrisHCl buffer (pH 7.4, 100mM NaCl). enzyme, ATP, MgCl 2 Make up the mixed solution, the final concentration of enzyme is 300 μM, the final concentration of ATP is 1 mM, MgCl 2 The final concentration of is 1.5mM, and it is put into the sample cell as a substrate to observe the e...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Embodiment 2: detection of residual neomycin B in milk:
[0044] The problem of antibiotic residues in milk has become one of the hidden dangers of industry development and food safety. At the source of the dairy industry, antibiotics are used frequently, especially for the treatment of bovine mastitis, and are often used repeatedly in large doses. In dairy cow feed, antibiotic additives are also contained. Therefore, the problem of antibiotic residues in milk is very serious. This protocol can be applied to the rapid detection of aminoglycoside antibiotics in milk, taking neomycin B as an example. Weigh 10g of milk, dissolve it in 10ml TrisHCl buffer (pH 7.4, 100mM NaCl), filter or high-speed centrifuge the sample to be tested, some biological macromolecules in the solution, such as protein, will precipitate, and the molecular weight of neomycin B is relatively small , remained in the supernatant solution. Add MgCl to aminoglycoside phosphate modifying enzyme (APH(...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3: Detection of residual tobramycin in honey: Honey is rich in nutrition and is an important product for exporting foreign exchange in my country. However, with the abuse of antibiotics, the United States, Japan and the European Union have strengthened the inspection of antibiotics in honey, which has caused my country's honey export industry to face a severe test. This protocol can be applied to the rapid detection of aminoglycoside antibiotics in honey, taking tobramycin as an example. Weigh a certain volume of honey, add 5ml of water, and mix quickly on a liquid mixer for 1min to completely dissolve the sample. Add 15ml of ethyl acetate, oscillate on the shaker for 10min, centrifuge at 3000r / min for 10min, absorb 12ml of ethyl acetate from the upper layer and transfer it to the evaporation tube of the automatic concentrator, concentrate and evaporate to dryness. Add 5ml of TrisHCl buffer (pH 7.4, 100mM NaCl) to dissolve the residue. Add MgCl to aminoglycosi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com