Fungus for degrading phthalate ester and application thereof
A phthalate ester and fungus technology, applied in the field of biological treatment of environmental organic pollutants, to achieve the effect of high-efficiency degradation ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
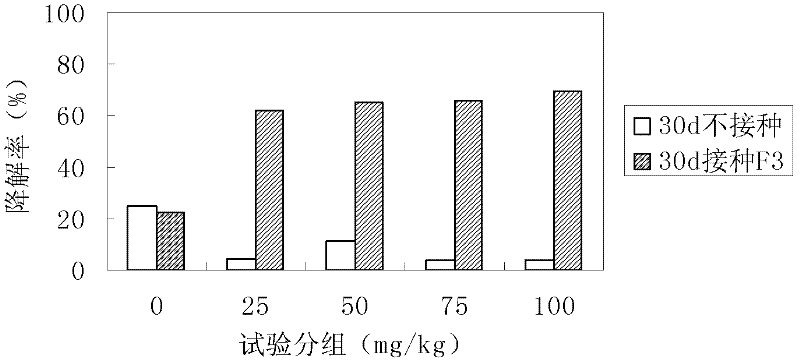
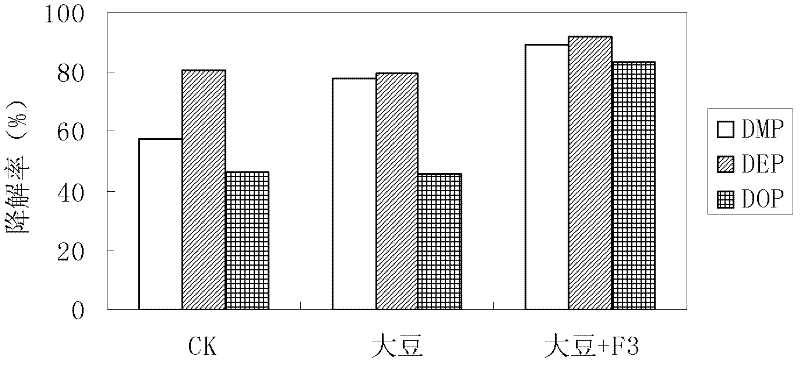
[0019] Isaria sp. F 3 Screening, isolation and identification and its terephthalate degradation performance
[0020] Weigh 10g of fresh paddy soil contaminated by PAEs, put it into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask with 90mL of deionized water and 3g of glass beads, shake at 30°C and 180r / min for 30min, and let it stand for 30min. Then get 10mL supernatant, add the fungus culture medium (MYEA) containing 140mL PAEs (its formula is: malt extract 0.2%; Yeast extract 0.2%, balance is 0.02% chloramphenicol solution, adjust pH value It can be 7.0; if it is made into a solid medium, 2% agar is added; the percentage is the mass-to-volume ratio) to carry out gradient acclimatization for 3 times. The concentrations of the three PAEs (DMP, DEP and DOP) in each gradient were 200, 400, and 600 mg / L (the total concentration of PAEs was 600, 1200, and 1800 mg / L), and each time 10 mL of bacterial liquid was transferred into 140 mL of fresh medium. Cultivate at 30°C and 120r / min for 7 days, and add ...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Isaria sp. F 3 Terephthalate Degradation
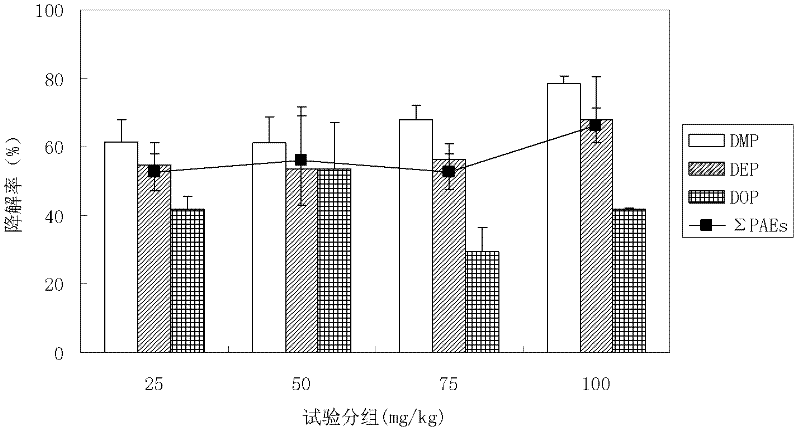
[0025] The selected fungi were picked from the inoculation loop, respectively inoculated with 5 g / L glucose solution, and cultured on a shaking table at 30°C and 120 r / min for 36 hours to induce spore germination and hyphal growth. Spectrophotometer measures the OD value at 660nm of the bacterial solution, and dilutes appropriately to make the concentration consistent (OD 660 ≈0.8). Add 10 mL of bacterial liquid to 90 mL of PAEs inorganic salt medium (the concentrations of the three PAEs are 0, 25, 50, 75, and 100 mg / L, respectively, and the total concentration is 0, 75, 150, 225, and 300 mg / L), at 25°C, 120r / Min cultured for 7 days, the non-biodegradable control was the non-inoculated PAEs inorganic salt medium. Three parallel samples were performed for each treatment, all operated under sterile conditions. After 7 days, samples were taken to analyze the PAHs content and biomass in the culture medium. See the experimenta...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Effects of growth factors on Isaria sp. F 3 Influence of degradation effect
[0030] 1. Select PAEs concentration, C:N and pH as influencing factors ((NH4 ) 2 SO 4 as N source), designed as L 27 (3 3 ) orthogonal experiment, the table header is shown in Table 1.
[0031] 2. Insert the same number of dominant fungal spores (OD 660 ≈0.8), set 3 repetitions; non-inoculated PAEs inorganic salt medium was used as control. Shaking culture (120rpm, 25°C) for 7 days, the degradation rate of ΣPAEs and the pH value of the bacterial solution were measured, and the results are shown in Table 2.
[0032] The preparation method of above-mentioned inorganic salt culture medium is (g·L -1 ): KH 2 PO 4 1.0g / L, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 1.0g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.2g / L, CaCl 2 0.1g / L, FeCl 3 0.01g / L, pH 7.0; distilled water to 1.0L, pH 7.0, steam sterilization at 121°C for 30min.
[0033] The results in Table 2 show that: Isaria sp. F 3 The degradation effect on PAEs is better wh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com