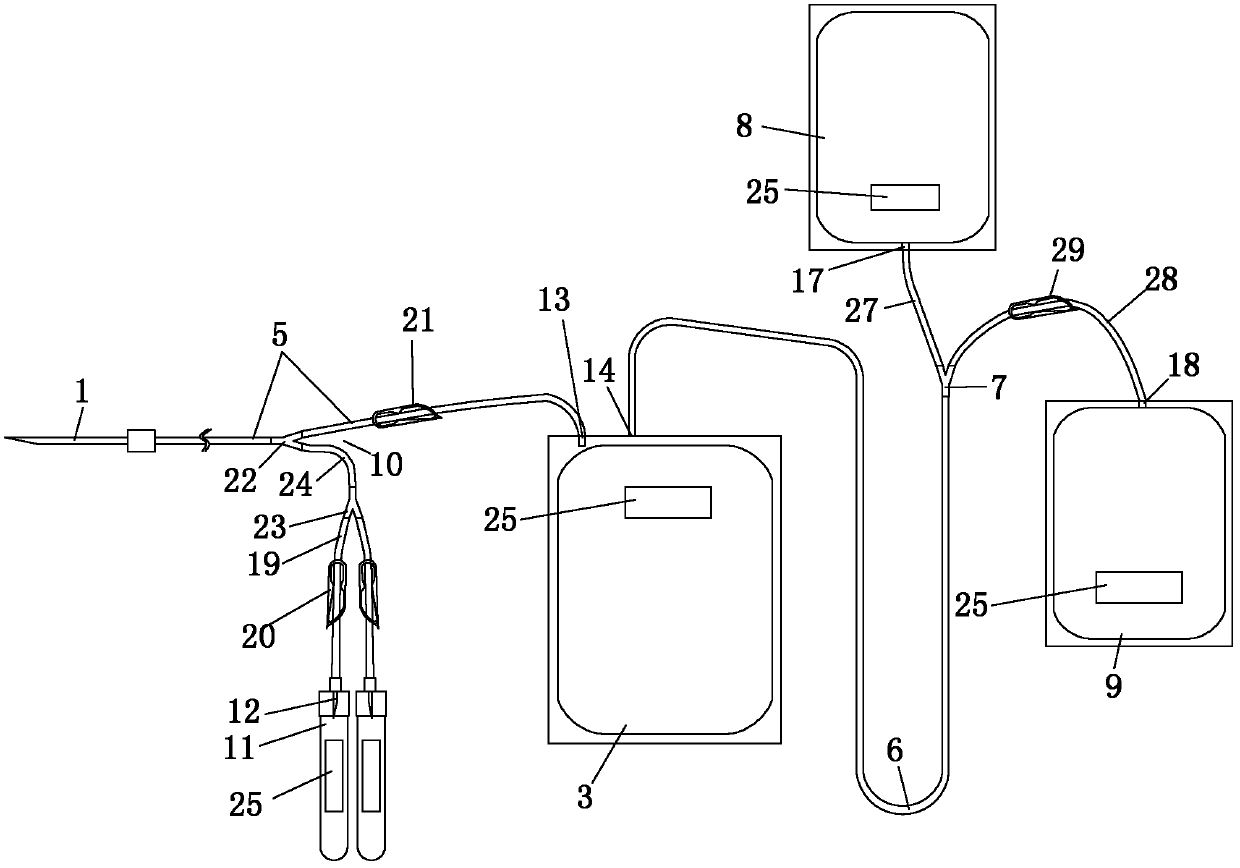
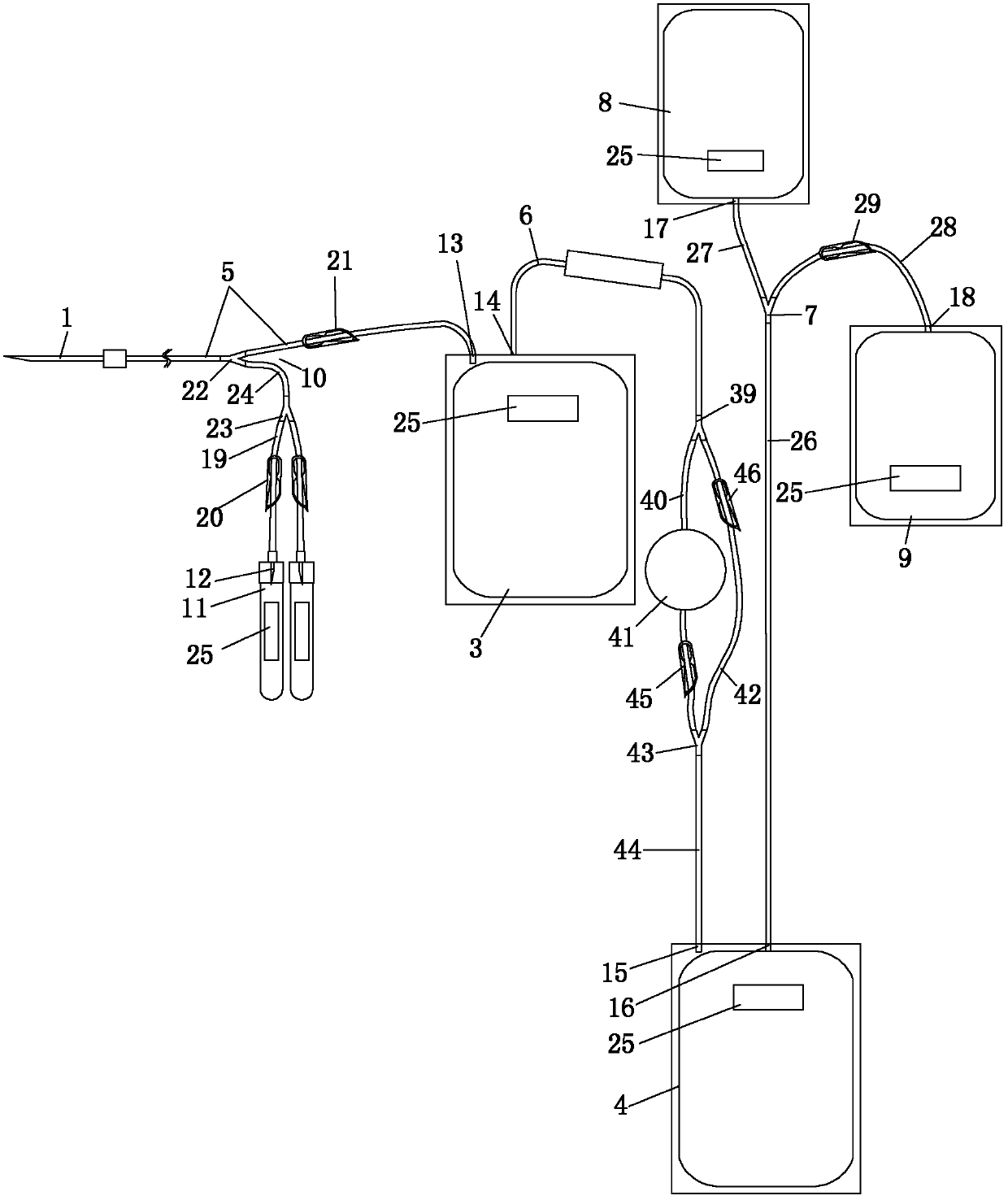
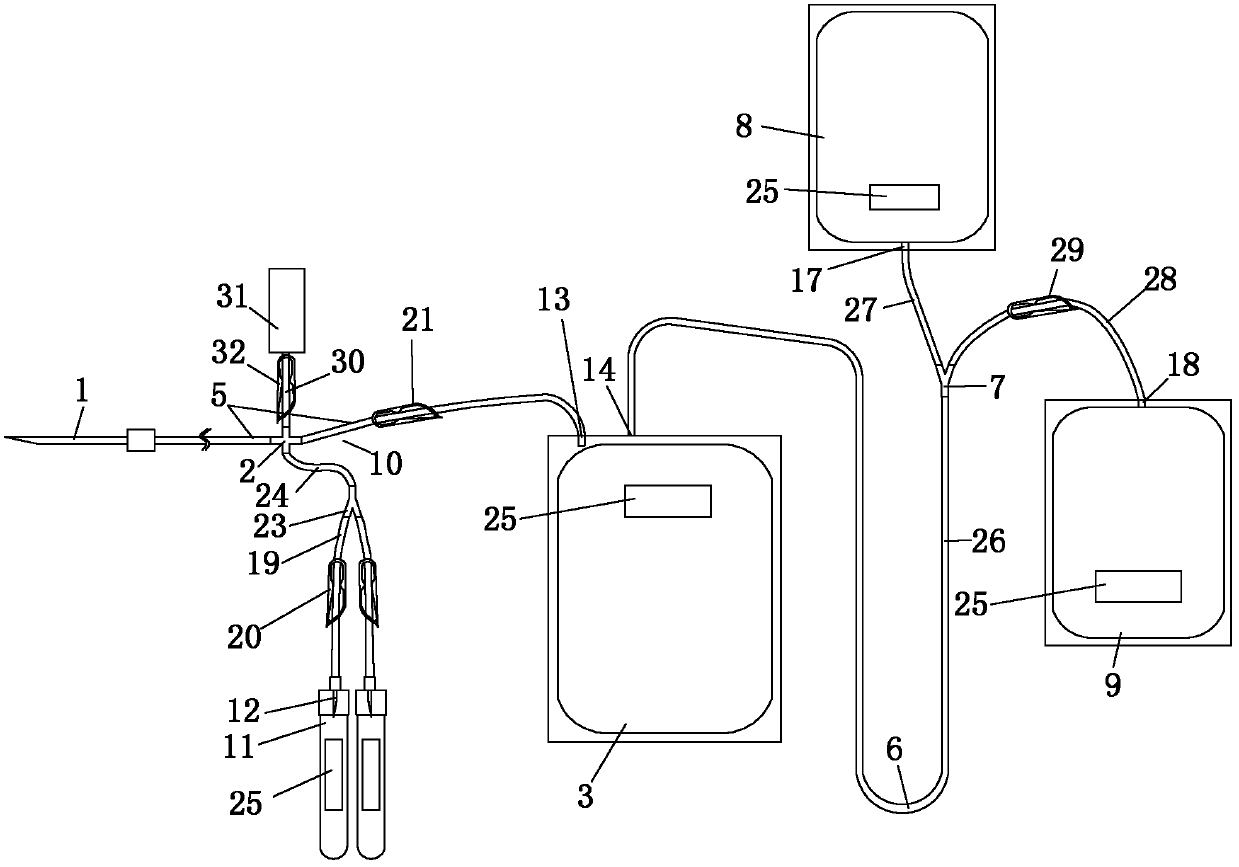
[0002] At present, the disposable blood collection and transfusion devices widely used in the national blood
station system have the following shortcomings: 1.
Blood collection and transfusion devices can only be used for blood collection, and do not have the function of retaining samples, because blood collection and sample retention are two completely separate operations , the operator will assign a unique blood donation code to the
blood donor before or after blood collection, and at the same time paste the same identification (blood donation code) on the blood bag and the sample after blood collection respectively, so as to achieve the consistency of the three However, in actual work, it is inevitable that there will be inconsistencies between the collected samples, blood and blood donors due to human factors (for example: errors in cross-
staking and cross-pasting identity marks when two people collect blood at the same time), resulting in errors Accidents; 2. It is easy to cause blood waste and may affect the volume of blood in the blood bag. There is often 7ml of blood wasted in the catheter between the blood collection needle of the leukocyte blood collection transfusion set and the blood bag (because the white blood cells are filtered, the blood is removed from the blood bag) After the mother bag is moved to the transfer bag, the mother bag and the catheter will be discarded), and cannot be used, and there is also a certain loss when the blood passes through the leukocyte filter disc. When increasing the reserved samples (such as
bone marrow specimens), it is possible to 3. Affect the test results. The general sample retention mode is to take the blood that has been taken into the blood bag (which has been fully mixed with the
blood preservation solution in the blood bag) through the blood collection needle, and negatively insert it in the
test tube. Under the action of pressure, the blood is sucked into the
test tube from the blood bag through the catheter. The first sample is the blood in the catheter, which is usually not diluted, but the second and third samples taken will be diluted (in actual work At least two specimens need to be retained), which may affect the authenticity and accuracy of the test results to varying degrees; 4. There is a risk of
contamination. The existing sample retention and blood collection mode is to collect the blood first and then retain the specimen. Then, the blood collected first must flow into the blood bag first, therefore, it is easy to bring the residual
bacteria on the
skin into the blood collection bag, and there is a certain risk of blood being contaminated by
bacteria; It is not safe. When the specimen needs to be re-examined and re-examined, the inspector needs to go to the blood storage department to search for the blood bag, and extract the blood in the catheter for re-examination. The procedure is complicated and the
workload increases (the staff needs to
cut the catheter , put the blood back into the
test tube, and tear off the blood donation code
label on the catheter, and paste it on the test tube for testing). At the same time, the extracted catheter braids are also prone to errors due to human negligence; 6. Existence
Occupational exposure hazards. Staff are prone to puncture their fingers with blood collection needles. During the process of sample retention, staff hold the test tube with their left hand and the blood collection needle with their right hand to pierce the needle into the cap of the test tube. Due to the small area, it is easy to prick their fingers; 7. It is not conducive to the
release management of blood. Since the control link of reserved samples cannot be guaranteed to be 100% correct, when the Ministry of Health promulgated the
quality management regulations of blood stations, in order to control and discover the inconsistency of reserved samples, the batch release of blood was formulated. Control procedures, in order to implement the batch release operation, artificially set up blood samples that are closely related in time and space as a bound batch, and only when all samples in the same batch have been tested and confirmed to be correct can the samples be associated If the blood is released, it will
delay the
release time of the blood. In the case of blood shortage, in order to release the blood as soon as possible, speeding up the detection speed will also increase the cost of detection; 8. It is not conducive to blood from The effective monitoring and
traceability of the whole process from the
blood vessel of the blood donor to the
blood vessel of the patient, blood collection, sample retention, and assignment of a blood donation code are still three different manual operations. Effective monitoring of the whole process and reduction of risks caused by human factors; 9. There are certain risks in centralized testing. Centralized testing is the development trend of blood collection and supply institutions, but it can only be responsible for the tested samples (retesting and retesting still use The original specimens are tested), and when the blood, specimens, and blood donors cannot be guaranteed to be 100% correct and consistent, there is a certain risk in releasing the blood according to the test results of the specimens.
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More