Agrobacterium-mediated transgenic method for mature seed embryos of corn
An Agrobacterium-mediated, seed embryo technology is applied in horticultural methods, botanical equipment and methods, angiosperms/flowering plants, etc. Effects of Limiting and Avoiding Maize Callus Tissue Differentiation and Plant Regeneration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0035] (3) Preparation and wounding of naked embryos of mature corn seeds;
[0036] (4) Agrobacterium-mediated gene transformation of naked and wounded corn mature seed embryos in step (2);
[0037] (5) Re-screening of herbicide resistance of regenerated seedlings;
[0038] (6) Transplanting the surviving seedlings after the herbicide screening treatment;
[0039] (7) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) identification of maize transgenic plants.
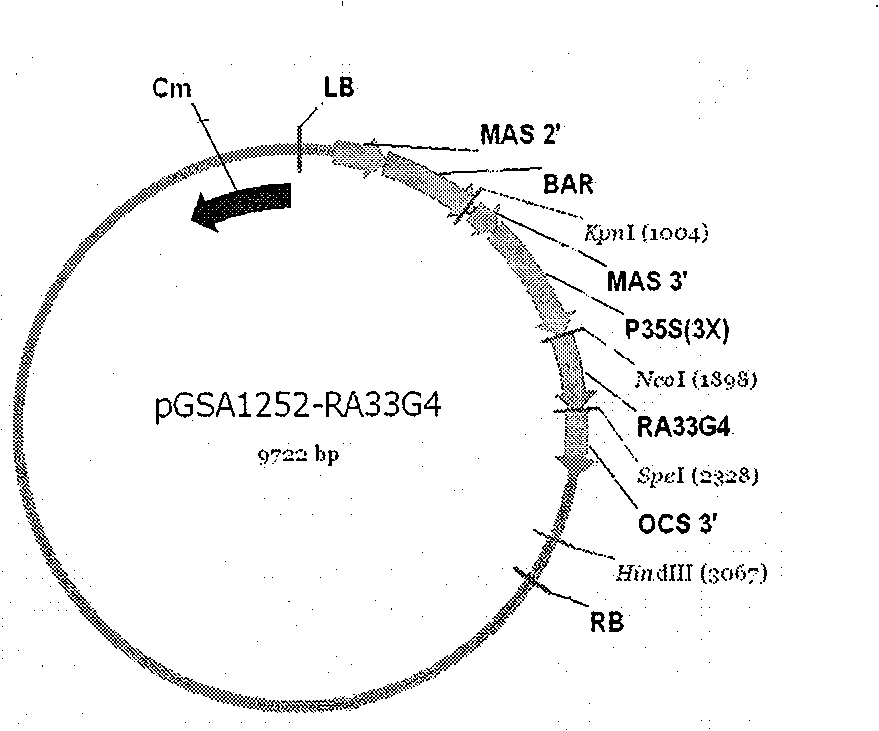
[0040] Such as figure 1 As shown, the plasmid vector pGSA1252::RA33G4 for plant gene expression constructed in step (1);
[0041] In order to verify the method of the present invention, we used the common plant expression vector plasmid pGSA1252 and our own cloned RA33G4 gene as examples for the example operation process of the cloning construction step of step (1) of the method of the present invention. RA33G4 gene is an early drought-induced protein gene we cloned from corn; pGSA1252 plasmid itself contains a chloramphenicol-resistant gene and a...
Embodiment 1
[0050] Construction of plasmid vector pGSA1252::RA33G4 for plant gene expression
[0051] Plasmid DNA was extracted according to the routine method of the laboratory. Enzyme digestion and DNA ligation methods were performed in accordance with the instructions provided by the manufacturer of the enzyme used. The extracted DNA of pGSA1252 was digested with Ncol and Spel, and then ligated with the DNA fragment of RA33G4 gene that was also digested with Ncol and Spel under the action of T4DNA ligase to form a transgene expression plasmid vector pGSA1252::RA33G4 .
[0052] Construction of Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain LBA4404 containing plant gene expression plasmid vector pGSA1252::RA33G4.
[0053] All involved implementation processes are carried out under aseptic conditions.
[0054] (1) A single colony of Agrobacterium LBA4404 without plasmid was inoculated into a common YEB medium in the laboratory containing rifampicin at an appropriate concentration, and cultured at 28°C on a 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com