Pattern transfer method and apparatus therefor
A pattern transfer and pattern technology, applied in transfer printing, printed circuit manufacturing, rotary printing machines, etc., can solve the problems of uneven pattern boundary, uniform pattern, difficult alignment of mask and target, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0095] Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. However, those skilled in the art should know that the description of the accompanying drawings is only for further facilitating the disclosure of the content of the present invention, so the scope of the present invention is not limited to the scope shown in the accompanying drawings.
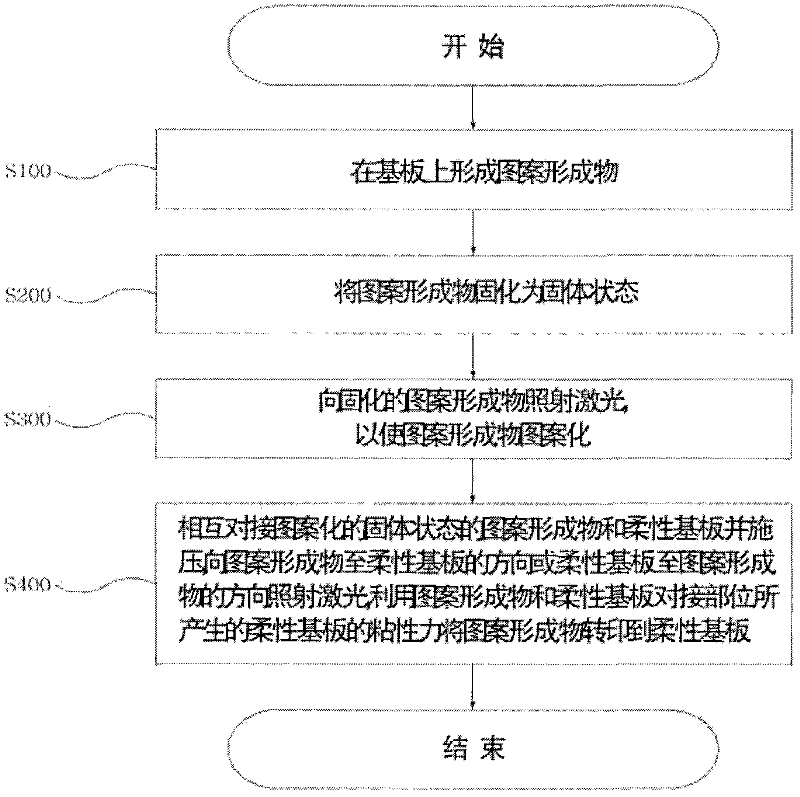
[0096] figure 2 is a flowchart showing the sequence of the pattern transfer method according to the first embodiment of the present invention. figure 2 Among them, in order to pattern the pattern formation 110, when the opening of the pattern is not wide, a positive resist method is used in which the part receiving the laser light is peeled off. In addition, the substrate is, for example, a glass substrate, and the substrate will not be deformed or damaged by heat even if the transfer material is peeled off when irradiated with laser light. This substrate is commonly used in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com