Application of AHAS (acetohydroxyacid synthase) inhibitor compound in preparing antifungal medicament
An antifungal drug, acetolactic acid technology, applied in the direction of antifungal agents, medical preparations containing active ingredients, pharmaceutical formulas, etc., can solve the problem of systematic research and reports without inhibitory effect, no inhibition of Cryptococcus and Candida albicans AHAS Active effects and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
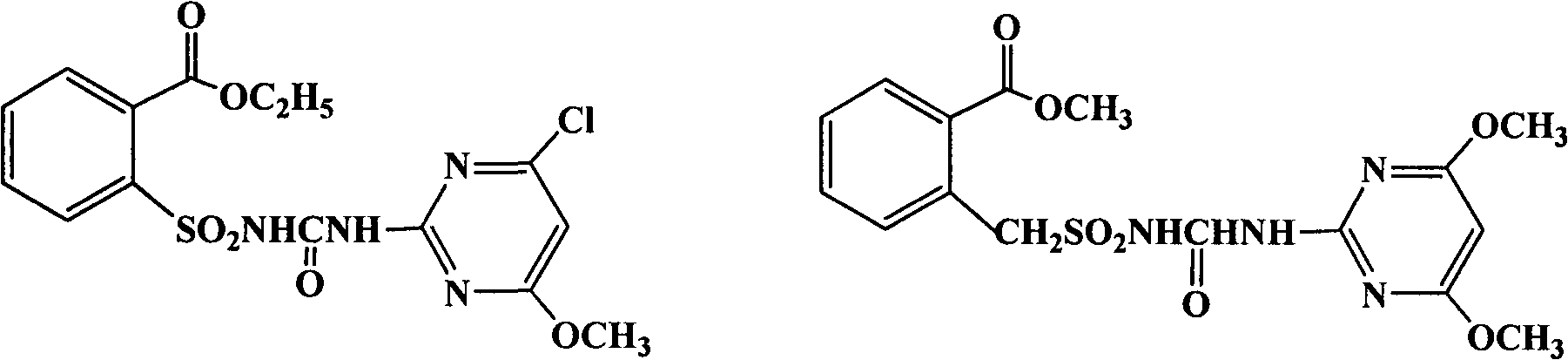
[0020] Embodiment 1. the preparation of chlorimuron-methyl
[0021]
[0022] Add 8g of potassium carbonate, water, 14mL of acetone, and 4.7g (0.02mol) of o-ethoxycarbonylbenzenesulfonamide into a 100mL four-necked reaction flask, stir to form a paste and cool down to 5°C, add 2.8g of methyl chloroformate dropwise for 0.5h After dropping, the temperature was raised naturally, and the reaction was carried out at 20°C for more than 2 hours. Add 50 mL of water to dissolve the material, then use about 8 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH value to about 2, filter the precipitated white solid, and dry in the air to obtain 5.7 g of a white powdery product, methyl o-ethoxycarbonylbenzenesulfonamide formate.
[0023] 100mL four-necked bottle equipped with a rectification column, add 4.3g (0.025mol) of 2-amino-4-chloro-6-methoxypyrimidine, 7.3g (0.025mol) of methyl o-ethoxycarbonylbenzenesulfonamide formate, toluene 50mL. Stir, heat, and add fresh toluene 30mL to ...
Embodiment 2
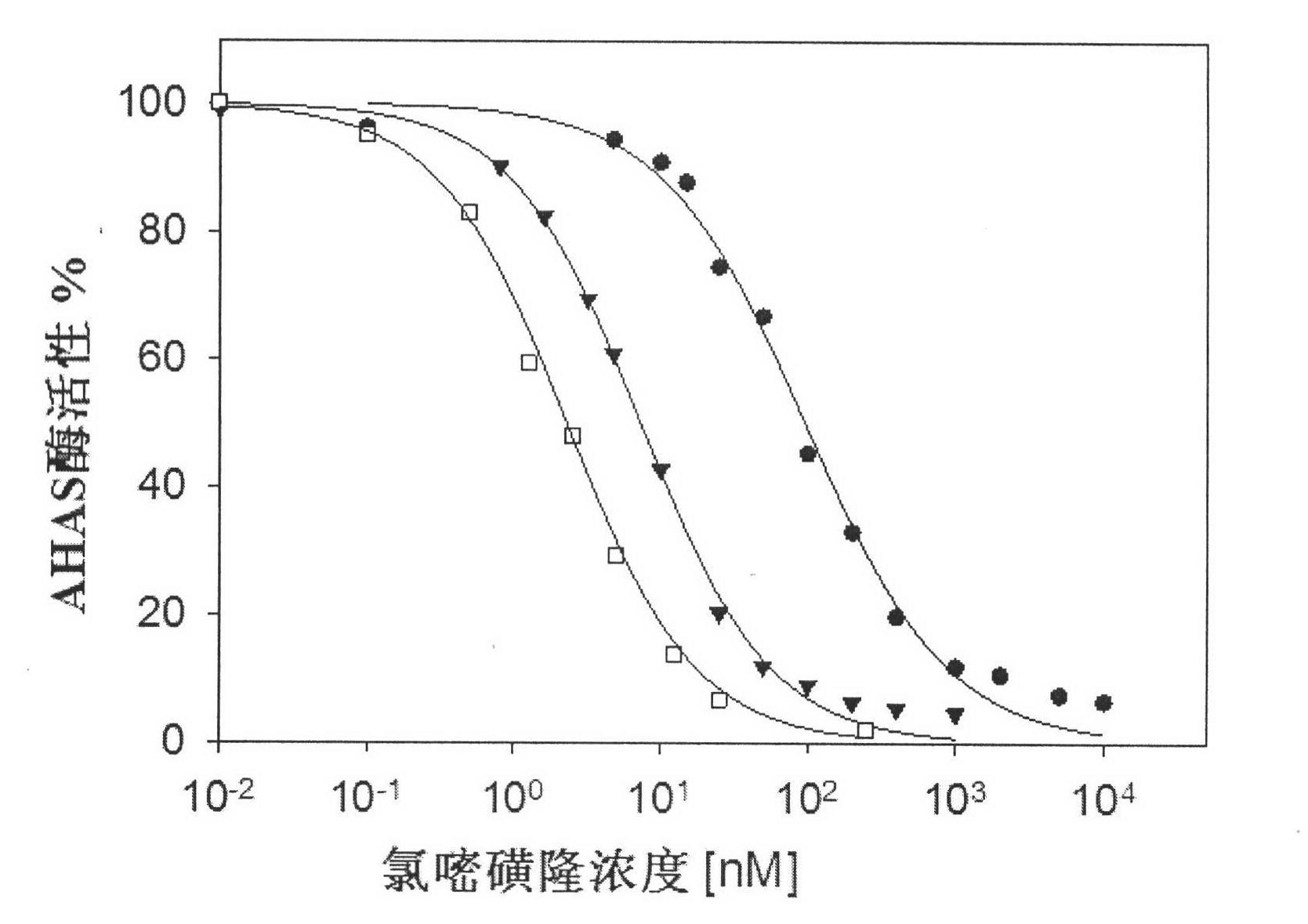
[0025] Embodiment 2. To Saccharomyces cerevisiae AHAS inhibition constant K 1 Determination of
[0026] The gene of yeast AHAS catalytic subunit (pET-YLSU) was overexpressed in Escherichia coli (BL21(DE3)), and purified by immobilized metal affinity chromatography IMAC to obtain pure AHAS (Pang S.S., et al.Biochemistry, 1999, 38 , 5222-5231). When measuring the activity, the pH value of the reaction solution is 7.0, the volume is 250 μL, and contains 50 mM Na 2 HPO 4 / NaH 2 PO 4 Buffer system, 50mM sodium pyruvate, 10mM magnesium chloride, 1mM thiamine diphosphate, 10μM flavin adenine dinucleotide, different concentrations of test compounds, the reaction was initiated at 30°C for 20min, and 25μL of 10% H 2 SO 4 Stop responding. Heat the system at 60°C for 15 min to convert all the acetolactate generated into 3-hydroxy-2-butanone, then add 250 μL of 0.5% creatine and 250 μL of 5% α-naphthol (dissolved in 4M NaOH ), heated at 60°C for 15min, and read the absorbance at 5...
Embodiment 3
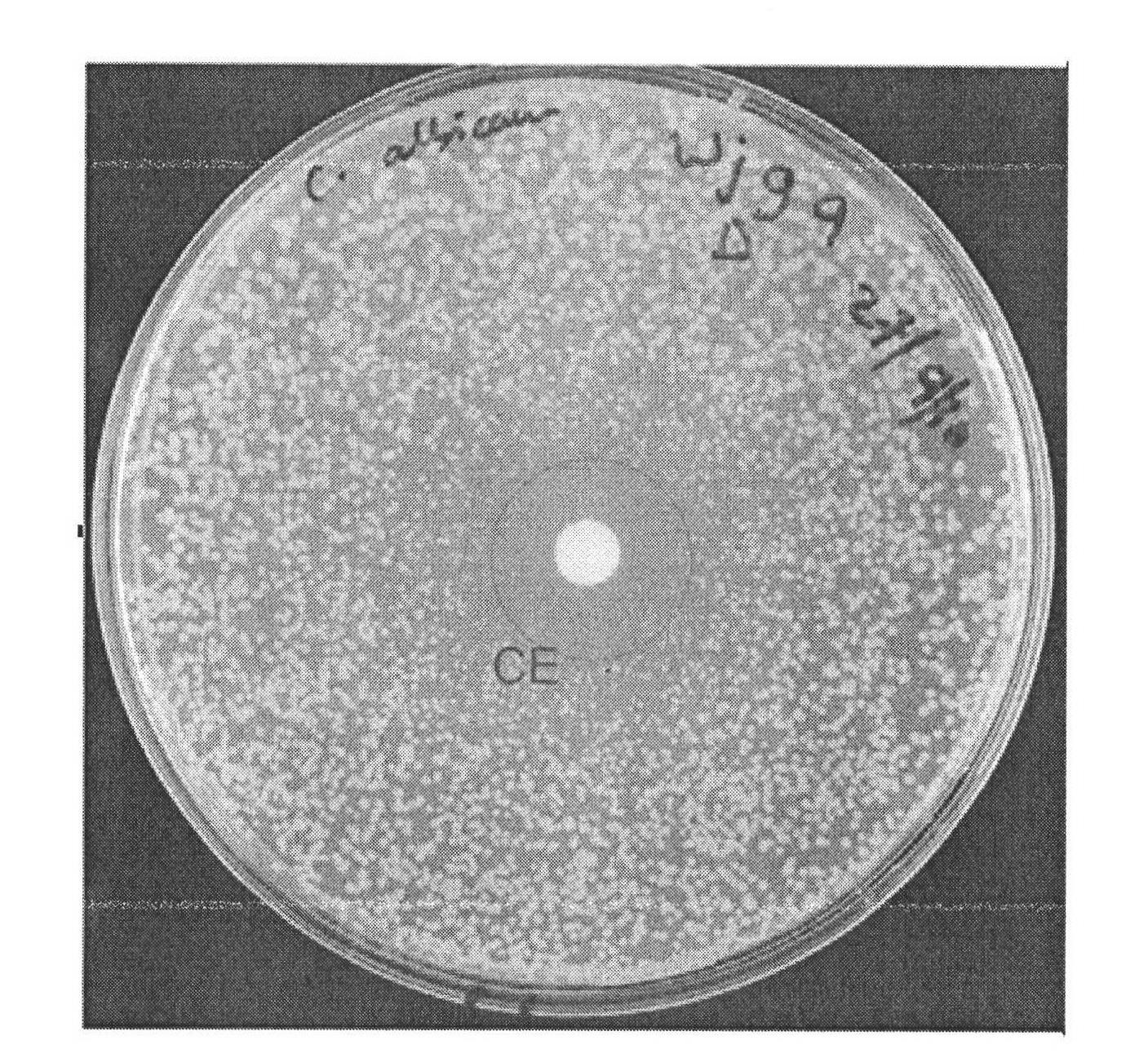
[0033] Embodiment 3. Compound is to Candida albicans minimum inhibitory concentration MIC 50 Determination of
[0034] Several fungi used in the experiment were provided by the Australian Center for Infectious Disease Research, University of Queensland, Australia, and their code names are Candida albicans (ATCC 90028), Cryptococcus neoformans (ATCC 90113), Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sigma 1278b), Candida parapsilosis Saccharomyces (ATCC 22019) and Candida glabrata (PAT 21SO3). The test compounds were chlorimsulfuron-methyl, ethimethuron-methyl, bensulfuron-methyl, pyrazosulfuron-methyl and the control drug fluconazole.
[0035] Firstly, the antifungal activity of sulfonylurea compounds was preliminarily determined by disc diffusion method. 10 μL of 1 nM compound to be tested was placed on the inoculated plate, incubated at 35° C. for 24 h, 48 h and 72 h, and the inhibition zone was read.
[0036] The minimum inhibitory concentration MIC of sulfonylurea compounds against Cand...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com