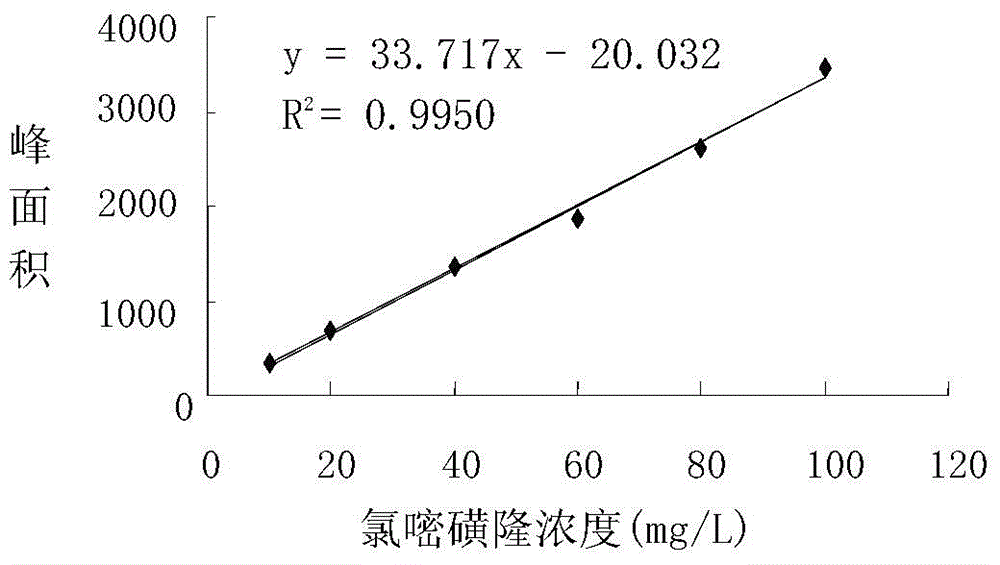
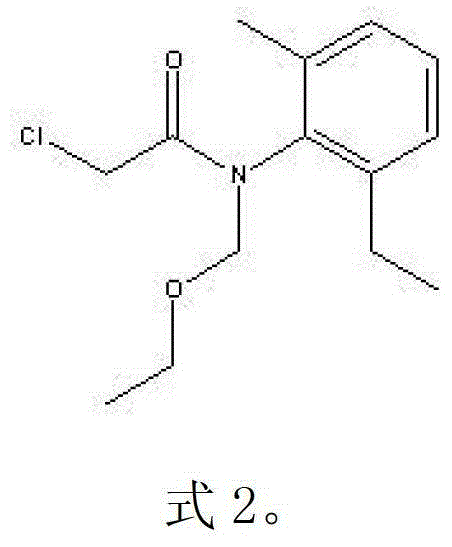
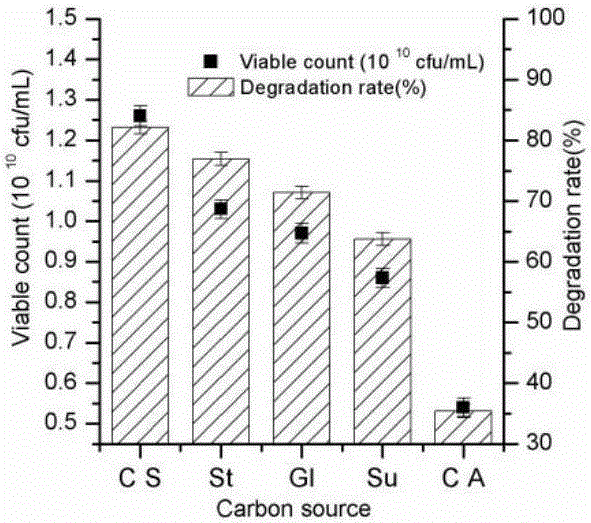
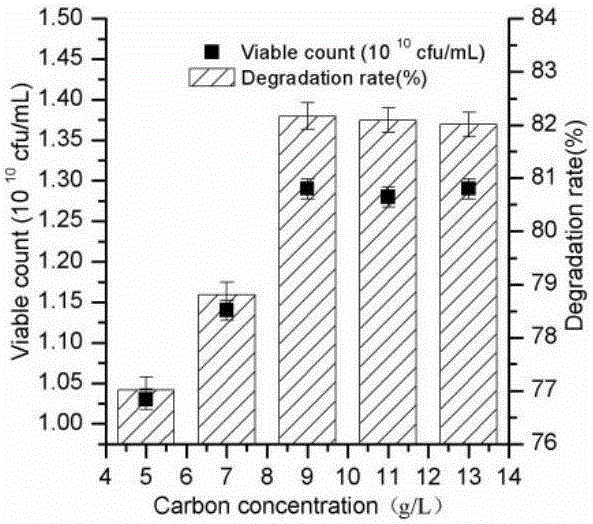
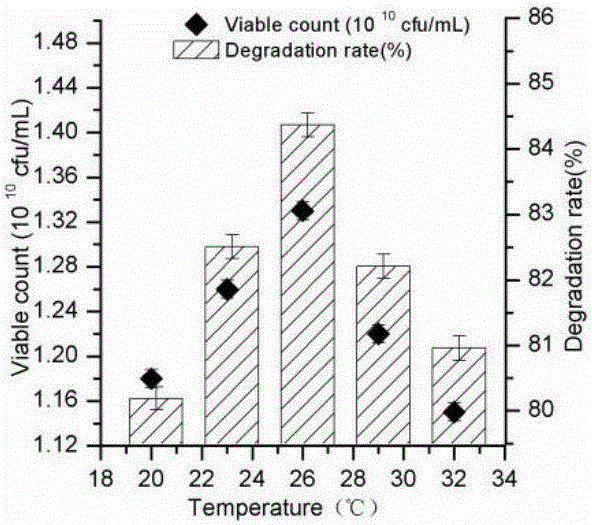
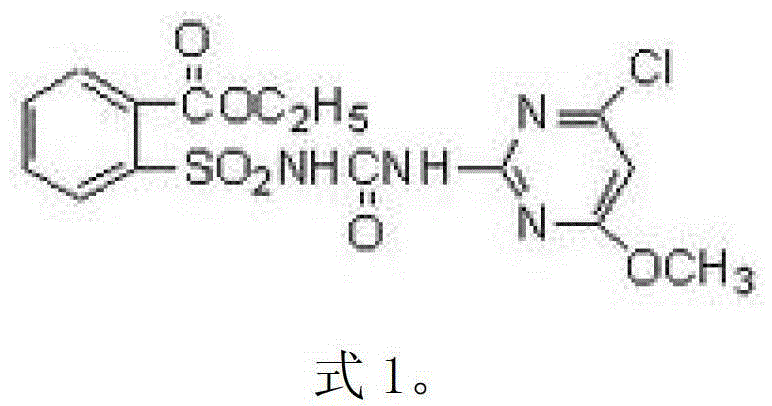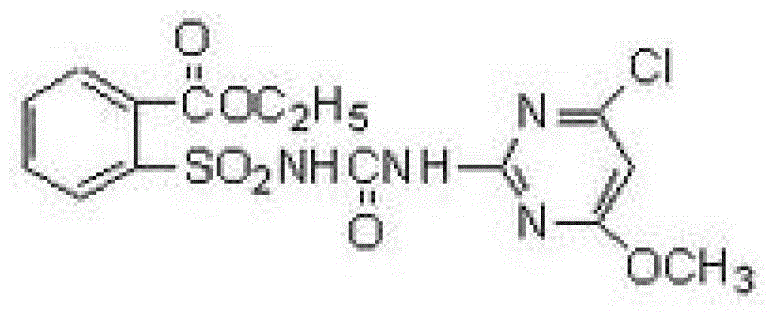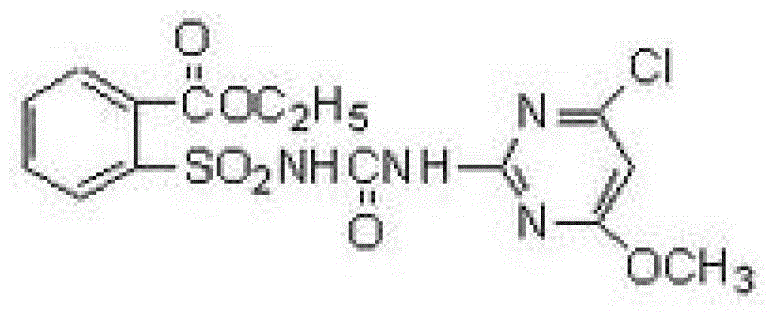Patents
Literature
55 results about "Chlorimuron ethyl" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
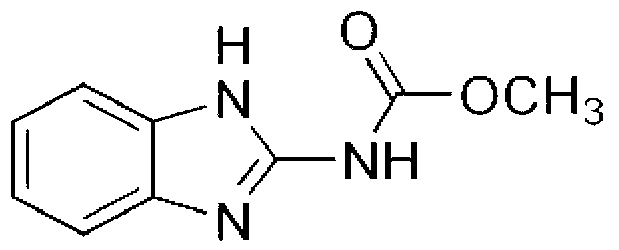
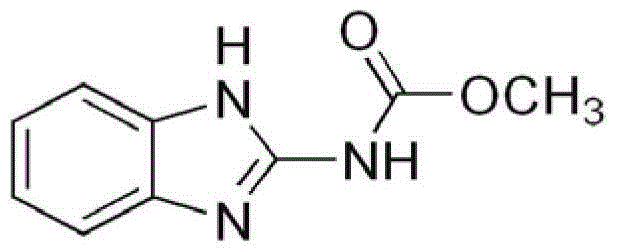
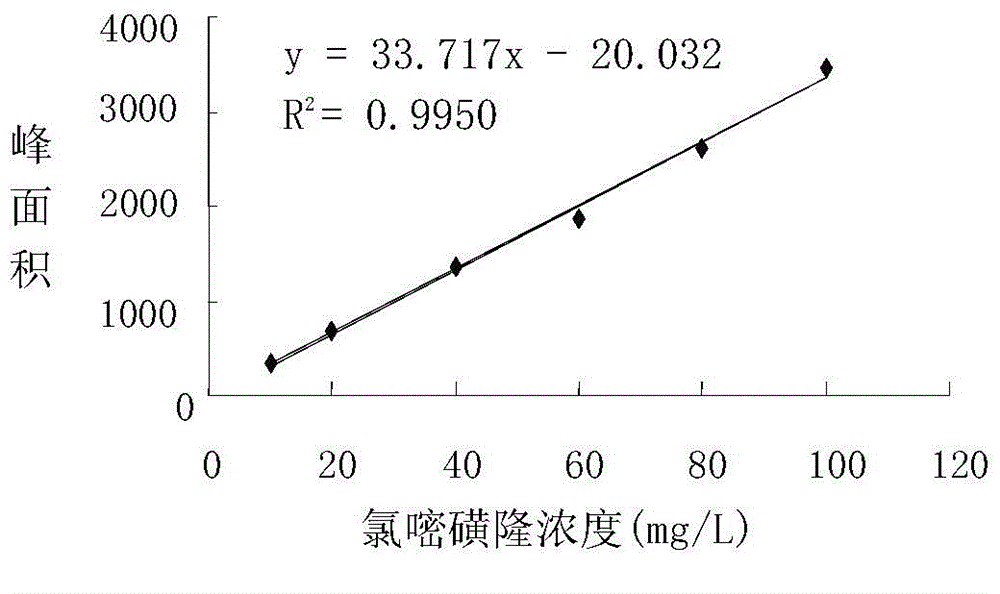
Chlorimuron-ethyl is an ethyl ester resulting from the formal condensation of the carboxy group of chlorimuron with ethanol.A proherbicide for chloimuron, it is used as herbicide for the control of broad-leaved weeds in peanuts, soya beans, and other crops.
Resistance to acetohydroxyacid synthase-inhibiting herbicides
InactiveUS20050198705A1High success rateImprove efficiencyBiocideOther foreign material introduction processesRice plantsPyrithiobac sodium
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Crop Plant-Compatible Herbicidal Compositions Containing Herbicides and Safeners
ActiveUS20120184435A1Highly effectiveBiocideDead animal preservationPhosphoric acidCloransulam-methyl
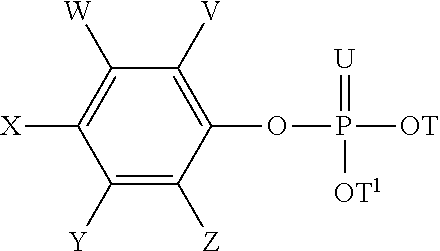
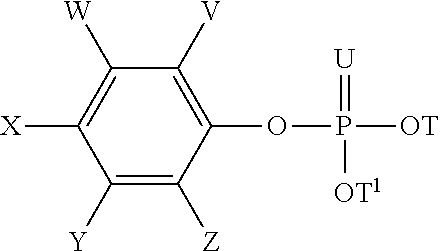
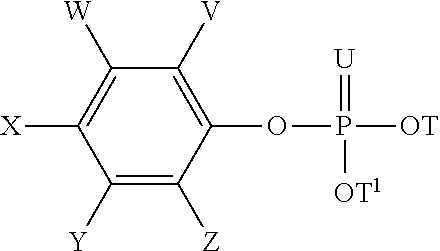
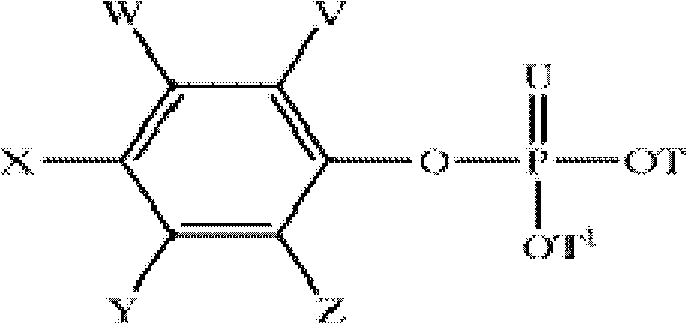
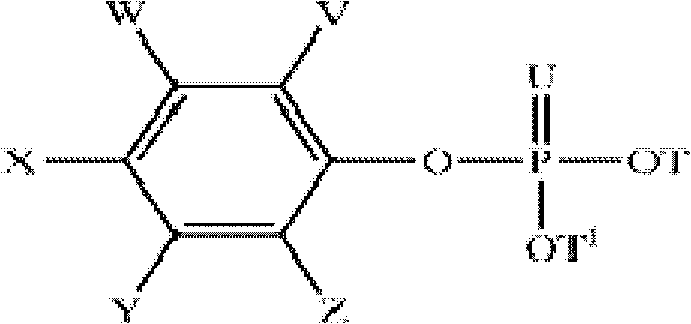
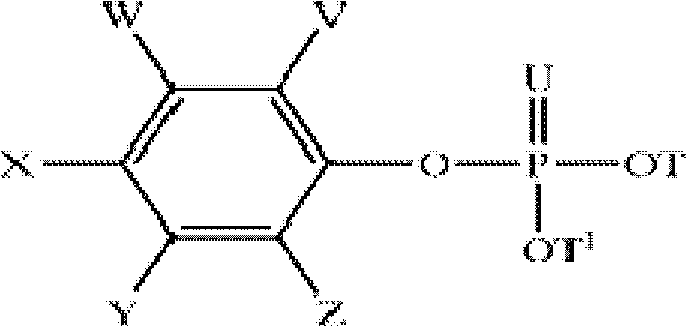
Disclosed herein are herbicidal compositions, characterized in that they comprise:A) an antidotically effective amount of one or more safeners from the group of the phosphorated esters of the formula (I):whereinT and T1 are independently selected from the group of hydrogen, alkyl, haloalkyl, alkoxyalkyl, alkenyl, and alkynyl;U is O or S, andV, W, X, Y, and Z are independently selected from the group of hydrogen, halogen, alkyl, haloalkyl, and alkoxy; andB) one or more sulfonamide or sulfonylurea herbicides selected from the group consisting of amidosulfuron, azimsulfuron, bensulfuron-methyl, chlorimuron-ethyl, chlorsulfuron, cinosulfuron, cyclosulfamuron, ethametsulfuron-methyl, ethoxysulfuron, flupyrsulfuron-methyl, flazasulfuron, foramsulfuron, halosulfuron-methyl, imazosulfuron, iodosulfuron-methyl, mesosulfuron-methyl, metsulfuron-methyl, nicosulfuron, oxasulfuron, primisulfuron-methyl, prosulfuron, thifensulfuron-methyl, tribenuron-methyl, trifloxysulfuron, triflusulfuron-methyl, triosulfuron, cloransulam-methyl, diclosulam, florasulam, flumetsulam, metosulam, penoxsulam, and combinations thereof, and methods for using the same.
Owner:ROTAM AGROCHEM INT CO LTD
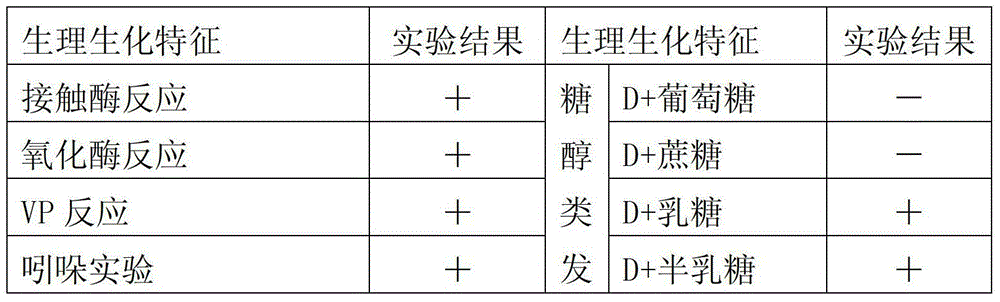
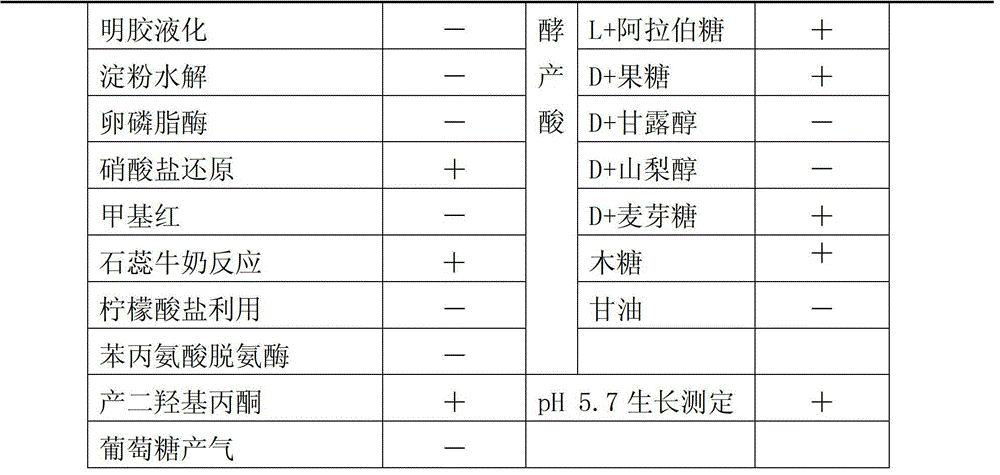
Bacterium capable of degrading pesticides chlorimuron-ethyl and carbendazim and application thereof
The invention discloses a bacterium capable of degrading pesticides chlorimuron-ethyl and carbendazim and an application of the bacterium. The bacterium capable of degrading pesticides chlorimuron-ethyl and carbendazim is rhizobium sp. LD1616 and the preservation number of the bacterium is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.7775. The rhizobium sp. LD1616 with the preservation of CGMCC NO.7775, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages that the degradation rate of the bacterium to chlorimuron-ethyl (45mg / L) is up to 71.56% in 7 days in an inorganic salt culture medium and the degradation rate of the bacterium to carbendazim (100mg / L) is up to 24.92% in 5 days, which indicates that the bacterium is capable of efficiently degrading the chlorimuron-ethyl and the carbendazim and has a broad application prospect in the remediation of soil polluted by residual pesticides chlorimuron-ethyl and carbendazim.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Rhodococcus sp. capable of degrading four herbicides and application thereof
The invention discloses a bacterium capable of degrading herbicides and an application thereof. The bacterium capable of degrading herbicides is rhodococcus sp. 198-R-56, and the collection number of the bacterium in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Centre is CGMCC No. 9868. With regard to the rhodococcus sp. 198-R-56 CGMCC No. 9868 provided by the invention, in an inorganic salt culture medium for 7 days, the degradation rate for 100mg / L of imazethapyr achieves 84.63%, the degradation rate for 50mg / L of acetochlor achieves 69.15%, the degradation rate for 100mg / L of chlorimuron-ethyl achieves 52.20%, and the degradation rate for 100mg / L of acifluorfen sodium achieves 20.16%, which indicates that the strain is capable of degrading the herbicides imazethapyr, acetochlor, chlorimuron-ethyl and acifluorfen sodium; meanwhile, the strain has a capacity of producing plant hormone heteroauxin and has a yield of 62.35+ / -3.76mu g / ml, which indicates that the strain has a capacity of promoting plant growth.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Bacterium for degrading herbicides chlorimuron-ethyl and acetochlor and application of bacterium
The invention discloses a bacterium for degrading herbicides chlorimuron-ethyl and acetochlor and application of the bacterium. The bacterium is cellulosimicrobium sp. LY114, which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center by a preservation number of CGMCC No.7776. The cellulosimicrobium sp. LY114 CGMCC No.7776 reaches a degrading rate of 89.11% on chlorimuron-ethyl (45mg / L) and acetochlor (45mg / L) in an organic salt culture medium within 7d, showing that the strain can effectively degrade the chlorimuron-ethyl and the acetochlor; and the bacterium has a wide application prospect in an aspect of repairing chlorimuron-ethyl and acetochlor pollution of soil.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Bacterium capable of degrading pesticides chlorimuron-ethyl and carbendazim and application thereof
The invention discloses a bacterium capable of degrading pesticides chlorimuron-ethyl and carbendazim and an application of the bacterium. The bacterium capable of degrading pesticides chlorimuron-ethyl and carbendazim is rhizobium sp. LD1616 and the preservation number of the bacterium is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.7775. The rhizobium sp. LD1616 with the preservation of CGMCC NO.7775, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages that the degradation rate of the bacterium to chlorimuron-ethyl (45mg / L) is up to 71.56% in 7 days in an inorganic salt culture medium and the degradation rate of the bacterium to carbendazim (100mg / L) is up to 24.92% in 5 days, which indicates that the bacterium is capable of efficiently degrading the chlorimuron-ethyl and the carbendazim and has a broad application prospect in the remediation of soil polluted by residual pesticides chlorimuron-ethyl and carbendazim.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for quantitatively detecting residual sulfonylurea herbicide trace amount in soil
InactiveCN102539559AHigh detection sensitivityComponent separationSodium bicarbonateMetsulfuron-methyl
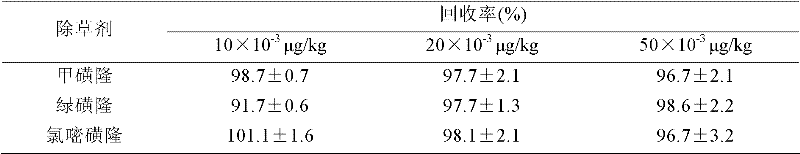
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting residual sulfonylurea herbicide trace amount in soil, which comprises the steps of adding soil to be detected into 0.1mol / L sodium bicarbonate water solution with pH7.8, oscillating for 1h, centrifuging for 5min at a speed of 12000r / min, obtaining sediments and primary liquid supernatant, taking the primary liquid supernatant to be adjusted to be in pH2.5 by 0.1M hydrochloric acid water solution, preparing a sample to be detected, and detecting the sample to be detected by a capillary electrophoresis apparatus; and obtaining contents of metsulfuron-methyl, chlorsulfuron and chlorimuron-ethyl in the sample to be detected according to standard curves of the metsulfuron-methyl, the chlorsulfuron and the chlorimuron-ethyl. The method is high in detecting sensitivity, and reaches detection limit with 10-3 microgram / kg grade, wherein the value of the limit of detection with 10-3g / kg grade is higher than that of the detection limit of other methods of an efficient liquid chromatogram and the like (not more than microgram / kg).
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Chlorimuron-ethyl degrading bacterium, soil bioremediation agent based on same, and application thereof
InactiveCN101798564ARemoval of pesticide residuesReduce manufacturing costBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPesticide residueSludge
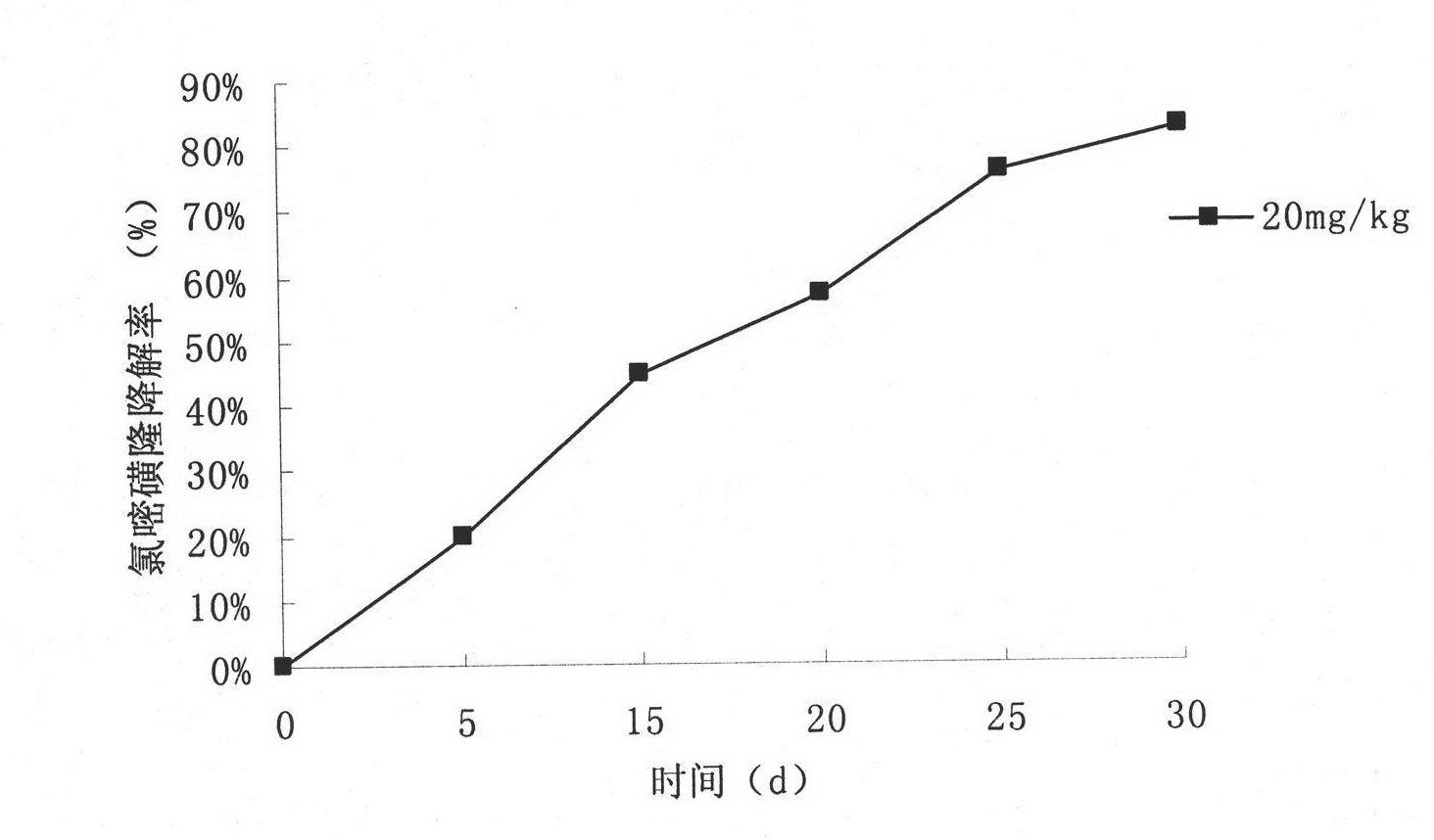
The invention relates to a chlorimuron-ethyl pesticide residue degrading bacterium which is named klebsiella 2N3 (Klebsiella jilinsis H.Zhang 2N3) with the storage No. of CCTCC NO: M 209248 in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), a soil bioremediation agent prepared from the chlorimuron-ethyl pesticide residue degrading bacterium, and application thereof. The chlorimuron-ethyl pesticide residue degrading bacterium is a bacterial strain which has strong degradation capacity to chlorimuron-ethyl and is obtained by carrying out enrichment culture and separation on sludge at a drainage outlet of an insecticide factory for producing chlorimuron-ethyl, the bacterial strain grows by using the chlorimuron-ethyl as the unique nitrogen source, and the activity of the bacterium in a liquid nutrient medium is increased by the induction of the chlorimuron-ethyl so as to improve the degradation capacity to the chlorimuron-ethyl. The preparation method for the bacterium is simple, low in cost and convenient to use, and can be spread in the soil, and the degradation effect in the soil can reach 82.6 percent; therefore, the chlorimuron-ethyl pesticide residue degrading bacterium has good application prospect.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Weeding composition for monocotyledon crops and application thereof
InactiveCN105532657ADelay drug resistanceImprove efficacyBiocideDead animal preservationSuspending AgentsEffective volume
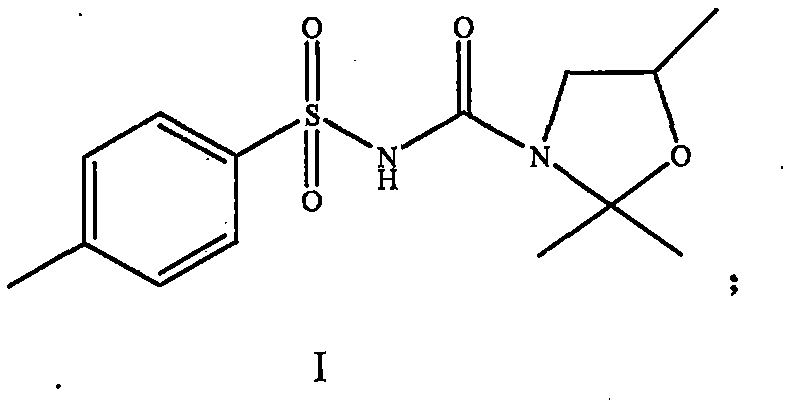
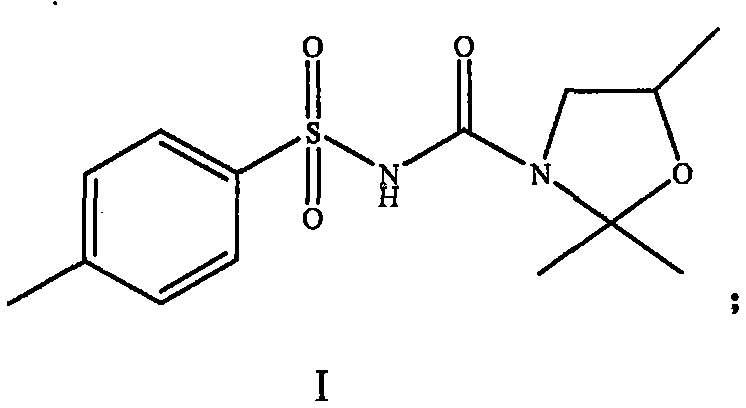
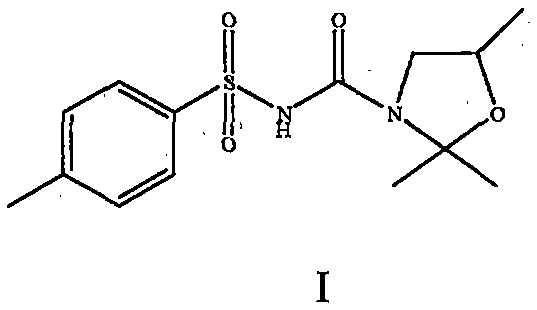
The invention provides a weeding composition for monocotyledon crops and application thereof. The weeding composition contains a component A and a component B serving as active components, wherein the component A is an effective detoxification quantity of 2,2-dimethyl-N-[(4-methyl phenyl) sulfonyl]-5-(methyl)-3-oxazolidine formamide, the component B is one of chlorsulfuron, chlorimuron-ethyl, imazethapyr or fomesafen. The weight ratio of effective volume of the component A to effective volume of the component B is (1-8):2. The dosage form is wettable powder, missible oil, a suspending agent, water dispersed granules or a seed coating agent. The weeding composition is applied to monocotyledon crop fields, and compared with mono-agents, the efficacy is improved, a weeding spectrum is also expanded, and the herbicide resistance of weeds can be further delayed. The weeding composition is safe to current-reap crops and after-reap crops, does not bring secondary herbicide damage and can effectively prevent and control the damage brought by herbicides. The performance of the weeding composition can obviously exceed the conventional technological level.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing biodegradable herbicide chlorimuron-ethyl
A process for preparing a biodegradable herbicide includes such steps as taking the soil to which the chlorimuron-ethyl is applied several years, suspending it in aseptic physiological saline to obtain the object to be treated, adding chlorimuron-ethyl to the peptone type culture medium, sterilizing, cooling, inoculating said soil suspension, shake-flask culture, repeating previous 5 steps 10 times, slant culture, class-one amplifying culture, class-two amplifying culture, adding the degradating bacteria, and fermenting culture.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Herbicide formula for leguminous plants
The invention aims to provide a herbicide formula for leguminous plants, which is characterized by comprising the following components in proportion by weight: 1-5 parts of imazethapyr water aqua, 0.05-0.5 part of chlorimuron-ethyl, 0.1-5 parts of clomazone, and 200-300 parts of water. The herbicide formula has the advantages of rapidness, high efficiency, no residues and no pollution.
Owner:吴晶晶
Complex microbial inoculant capable of efficiently degrading chlorimuron-ethyl and application thereof
InactiveCN105274036ACompatibility is simpleReduce manufacturing costBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationEcological environmentSoil remediation
The invention relates to a complex microbial inoculant capable of efficiently degrading chlorimuron-ethyl and an application technology thereof. The complex microbial inoculant is formed by rhodococcus erythropolis and stenotrophomonas in a volume ratio of 1:1 at the same concentration of bacterial liquid, and the complex microbial inoculant is used for soil bioremediation for reducing residual chlorimuron-ethyl in soil. The complex microbial inoculant is simple in compatibility, low in production cost, good in degradation effect, good in soil remediation quality, easy to use and beneficial to ecological environmental protection and production of green agricultural products.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Crop plant-compatible herbicidal compositions containing herbicides and safeners
Disclosed herein are herbicidal compositions, characterized in that they comprise: A) an antidotically effective amount of one or more safeners from the group of the phosphorated esters of the formula (I): wherein T and T1 are independently selected from the group of hydrogen, alkyl, haloalkyl, alkoxyalkyl, alkenyl, and alkynyl; U is O or S, and V, W, X, Y, and Z are independently selected from the group of hydrogen, halogen, alkyl, haloalkyl, and alkoxy; and B) one or more sulfonamide or sulfonylurea herbicides selected from the group consisting of amidosulfuron, azimsulfuron, bensulfuron-methyl, chlorimuron-ethyl, chlorsulfuron, cinosulfuron, cyclosulfamuron, ethametsulfuron-methyl, ethoxysulfuron, flupyrsulfuron-methyl, flazasulfuron, foramsulfuron, halosulfuron-methyl, imazosulfuron, iodosulfuron-methyl, mesosulfuron-methyl, metsulfuron-methyl, nicosulfuron, oxasulfuron, primisulfuron-methyl, prosulfuron, thifensulfuron-methyl, tribenuron-methyl, trifloxysulfuron, triflusulfuron-methyl, triosulfuron, cloransulam-methyl, diclosulam, florasulam, flumetsulam, metosulam, penoxsulam, and combinations thereof, and methods for using the same.
Owner:JIANGSU ROTAM CHEM
Soybean field herbicide
InactiveCN1887087AGood killing effectMany types of weedingBiocideAnimal repellantsCocklebursChlorimuron ethyl
The soybean field herbicide consists of chlorimuron-ethyl in 0.9-1.25 weight portions, and sethoxydim in 100-150 weight portions or fluazifop-P-butyl in 75-130 weight portions mixed together. It has the advantages of wide herbicidal spectrum, no effect on the next crop and low cost, and possesses high killing effect on malignant weeds field thistle and cocklebur especially.
Owner:王相国
Bacterium for degrading herbicides and application thereof
The invention discloses a bacterium for degrading herbicides and application thereof. The bacterium for degrading the herbicides is Rhizobium sp. 198-L-30 which has the collection number of CGMCC No. 9864 in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. According to the Rhizobium sp. 198-L-30 with the collection number of CGMCC No. 9864 provided by the invention, the degradation rate on 100mg / L of imazethapyr in an inorganic salt culture medium within 7 days is 93.40 percent; the degradation rate on 50mg / L of acetochlor is 88.44 percent; the degradation rate on 100mg / L of chlorimuron-ethyl is 41.15 percent; and the degradation rate on 100mg / L of acifluorfen is 12.28 percent. According the strain, the herbicides such as imazethapyr, acetochlor, chlorimuron-ethyl and acifluorfen can be degraded.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Bacterium for degrading herbicide chlorimuron-ethyl and application of bacterium
The invention discloses a bacterium for degrading a herbicide chlorimuron-ethyl and application of the bacterium. The bacterium is enteriobacter sp. LMHL1716, which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center by a preservation number of CGMCC No.7772. The enterobacter sp. LMHL1716 CGMCC No.7772 reaches a degrading rate of 70.44% on 45mg / L of chlorimuron-ethyl in an organic salt culture medium within 7d, showing that the strain can effectively degrade the chlorimuron-ethyl; the bacterium has a wide application prospect in an aspect of repairing chlorimuron-ethyl pollution of soil.
Owner:优农道(北京)科技有限公司
Method for screening mixed bacterium degradation microbial inoculum taking chlorimuron-ethyl as substrate
InactiveCN101845393AHigh activityReduce pesticide residuesMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementPesticide residueScreening method
The invention relates to the technical field of biodegrading pesticide residue, in particular to a method for screening a mixed bacterium degradation microbial inoculum taking chlorimuron-ethyl as a substrate. The method comprises the following steps of: adding the chlorimuron-ethyl at the concentration of 100mg / L into a 1 / 5LB culture medium, and inoculating the bacterial suspension which accounts for 5 to 10 volume percent of the culture medium; performing shake cultivation on the bacterial suspension at the temperature of between 28 and 30 DEG C and at a speed of 50 to 180 r / min for 5 to 7 days, and inoculating nutrient solution which accounts for 5 to 10 volume percent of the culture medium into the novel 1 / 5LB culture medium, wherein the concentration of the chlorimuron-ethyl is increased progressively in a ratio of 100mg / L, and after inoculating for 5 times, the concentration of the chlorimuron-ethyl in the culture medium is 500mg / L; and then inoculating the nutrient solution which accounts for 5 to 10 volume percent of the culture medium for 5 times to obtain the mixed bacterium strain, wherein the adding concentration of the chlorimuron-ethyl is always 500mg / L. The degradation rate reaches over 70 percent after the mixed bacterium strain is detected by a liquid chromatography. The mixed bacterium degradation microbial inoculum taking the chlorimuron-ethyl as the substrate is obtained by performing fermentation and expanding culture on the bacterium strain.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
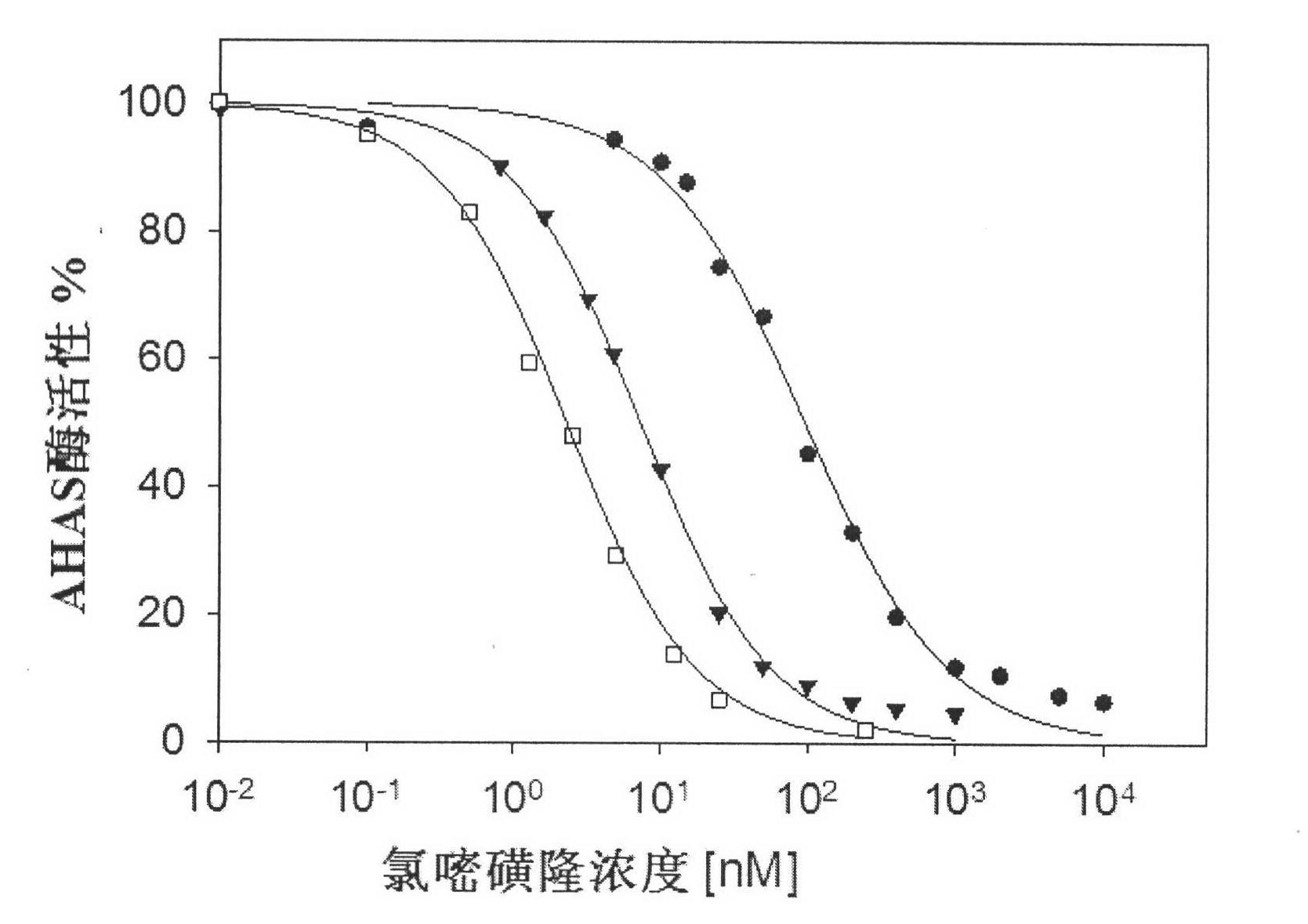
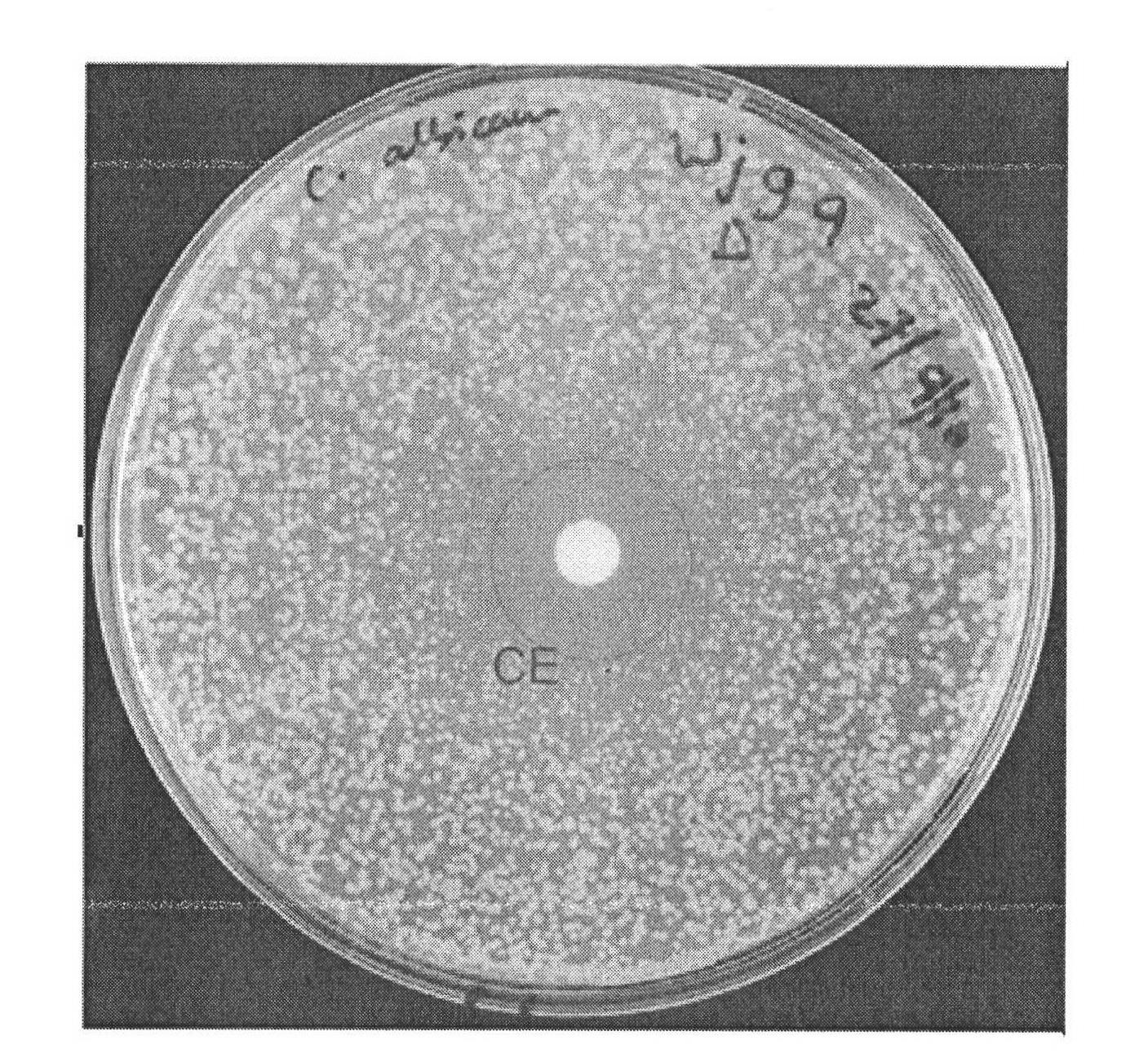
Application of AHAS (acetohydroxyacid synthase) inhibitor compound in preparing antifungal medicament
InactiveCN102488692AInhibited stronglyOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsCandida famataPyrazosulfuron-ethyl
The invention relates to an application of an AHAS (acetohydroxyacid synthase) inhibitor in preparing a medical antifungal medicament, and mainly relates to an application of sulfonylurea compounds (chlorimuron ethyl, ethoxysulfuron, bensulfuron methyl and pyrazosulfuron ethyl) in preparing medicaments capable of resisting Candida albicans, Cryptococcus neoformans, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Candida parapsilopis and Candida glabrata and the like. The compounds can be used for intensely restraining the AHAS from fungal, and has a higher restraint effect on multiple types of fungi capable of causing infection at the cellular level.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Wheat field herbicide
InactiveCN105409998AReduce dosageGood weeding effectBiocideAnimal repellantsSURFACTANT BLENDChlorimuron ethyl
The invention discloses a wheat field herbicide, which comprises the following raw materials by weight: 5-7 parts of pyroxsulam, 3-5 parts of talcum powder, 4-6 parts of a surfactant, 3-5 parts of carfentrazone-ethyl, 4-6 parts of chlorimuron-ethyl, 8-12 parts of tribenuron-methly, 4-6 parts of sodium polyacrylate, 3-5 parts of aminopyralid, and 10-20 parts of water. The wheat field herbicide provided by the invention has simple and environment-friendly preparation method, good weeding effect, can control weeds of crops within a whole growth period by one application, and has no influence to next-stubble crops.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIYICHENG MANAGEMENT TECH CO LTD
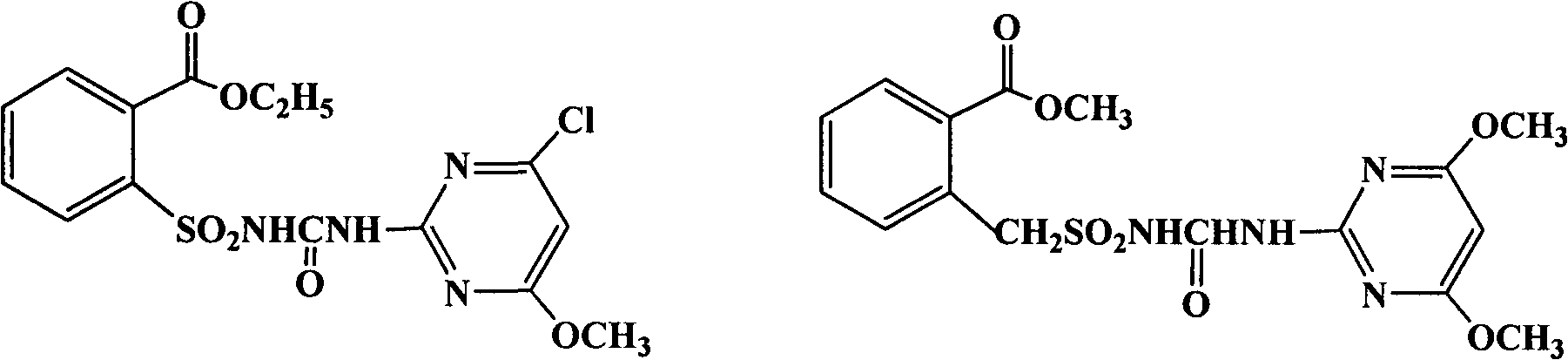
Novel synthesis process of high-purity pesticide intermediate
The invention discloses a novel synthesis process of a chlorimuron-ethyl intermediate, i.e., high-purity 2-amino-4-chlorin-6-methoxypyrimidine (chloropyrimidine for short). The process comprises the following steps of: adding 2-amino-4,6-dichloropyrimidine (dichloropyrimidine for short) into a mixed solvent; raising the temperature and dropwise adding sodium methoxide; after reacting, adding a decolorizing agent; filtering, cooling, crystalizing and washing to obtain a high-purity target; and after a mixed mother solution is used for sufficient batches, performing distillation treatment. Due to the adoption of the process, the yield and total yield level of a high-purity product are increased, and the production difficulty is lowered greatly; and a high-end chlorimuron-ethyl product synthesized by using the high-purity chloropyrimidine intermediate produced with the process has strong competitive strength in domestic and international markets.
Owner:ANHUI FENGLE AGROCHEM
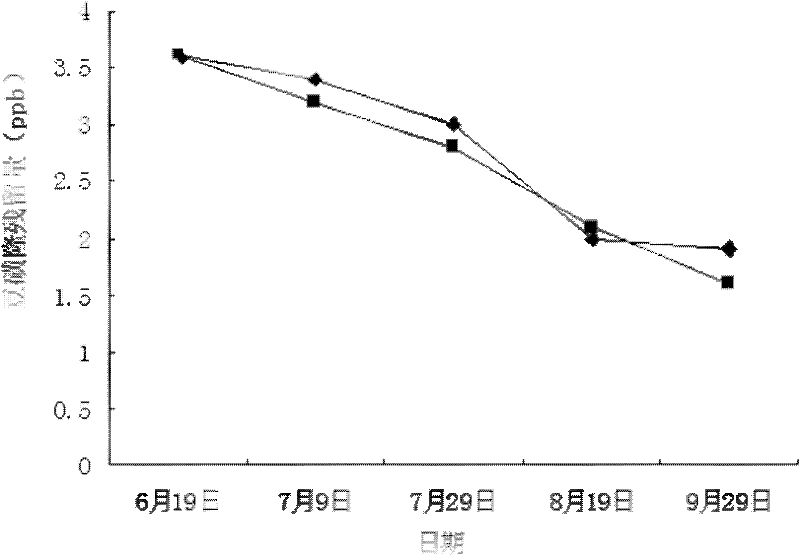
Method for degrading long residual herbicide chlorimuron-ethyl in bean field by adopting biological organic fertilizer
InactiveCN102217450AAvoid pollutionReduce or eliminate the hazardFertilising methodsHorticultureBiotechnologyMetabolite
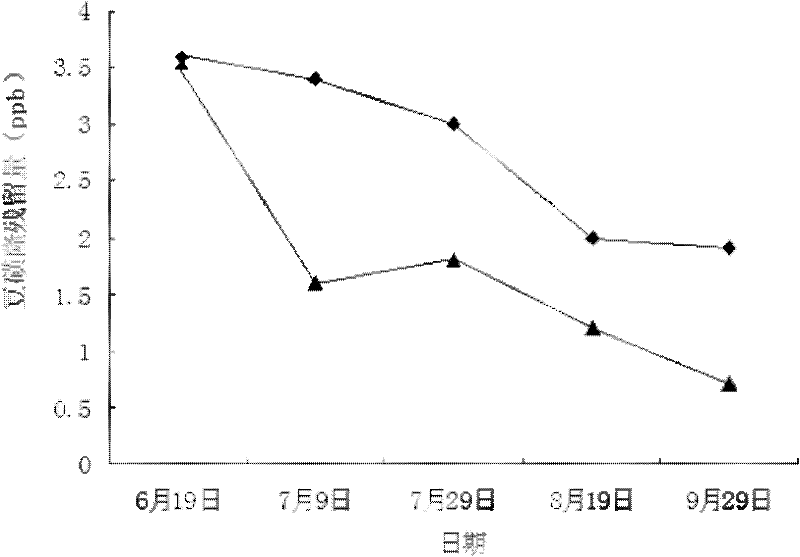
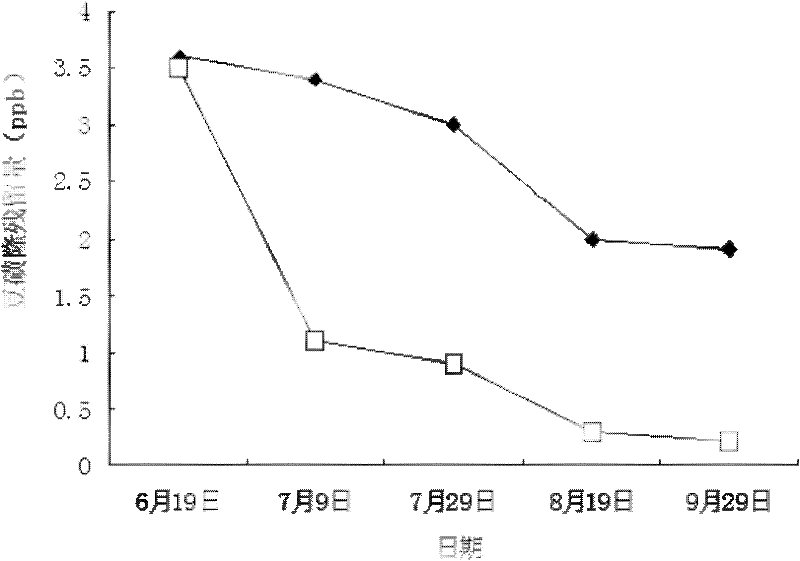
The invention discloses a method for degrading long residual herbicide chlorimuron-ethyl in a bean field by adopting a biological organic fertilizer, and relates to a method for degrading chlorimuron-ethyl. The method solves the problem of poor biodegradable effect in the treatment of the long residual herbicide chlorimuron-ethyl in the bean field. The method comprises the following steps of: sequentially ridging, applying a base fertilizer, sowing Dongnong No.42 soybean and spraying chlorimuron-ethyl in the first ten days of May every year, and then performing conventional management till the soybean is harvested. The adopted biological organic fertilizer contains actinomycetes (streptomyces microflavus), and the actinomycetes (streptomyces microflavus) has good effect of degrading sulfonylurea herbicides and can thoroughly solve product and environmental pollution caused by the chlorimuron-ethyl and metabolic products thereof under the synergistic action of azotobocter chroococcum, bacillus megatherium and bacillus mucilaginosus so as to lighten or eliminate the harm to subsequent crops; and the residual quantity of the chlorimuron-ethyl in the bean field after the soybean is harvested is 0.25 to 1.6ppb, and the biodegradable effect is good.
Owner:黑龙江省科学院生物肥料研究中心
Composite herbicide containing s-metolachlor and chlorimuron-ethyl
InactiveCN104186519AImprove herbicidal activityReduced resistance generation rateBiocideAnimal repellantsMetolachlorToxin
The invention discloses a composite herbicide containing s-metolachlor and chlorimuron-ethyl. The composite herbicide takes s-metolachlor and chlorimuron-ethyl as effective components and the mass ratio of s-metolachlor to the chlorimuron-ethyl is (1-50) to (0.1-20); and the content of s-metolachlor and chlorimuron-ethyl accounts for 10%-70% of the herbicide by mass percent. The composite herbicide has the low toxin, weak sensitization and low toxin to people and livestock; compared with a single agent, for the composite herbicide disclosed by the invention, the pesticide effect is improved, the hybridization resistance is delayed, the weeding spectrum is wide and the lasting period is long; and the composite herbicide has the reliable safety on soybean plants and crops.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
Formula and preparation method of pollution-free herbicide
InactiveCN106472607AReasonable ratioLow costBiocideDead animal preservationFluazifop-butylSalvia miltiorrhiza
The invention discloses a pollution-free herbicide and a preparation method thereof. The pollution-free herbicide comprises the raw materials: ethylene oxide, chlorimuron-ethyl, metsulfuron-methyl, tribenuron-methyl, sodium polyacrylate, diuron, chlorpropham, fluazifop-butyl, fipronil, paraquat, kaolin, a dispersant, a sterilization agent, a motherwort extract liquid, a pinellia extract liquid, a white atractylodes rhizome extract liquid, a Chinese yam extract liquid, a radix scrophulariae extract liquid, a liquorice extract liquid, a radix saposhnikoviae extract liquid, an astragalus membranaceus extract liquid, a radix bupleuri extract liquid, a salvia miltiorrhiza extract liquid, an anemarrhena asphodeloides bunge extract liquid, carbonate, tripterygium wilfordii, and radix stemonae. The pollution-free herbicide has the advantages of reasonable proportion of raw materials, low cost, and easily obtained raw materials; and the raw materials are all pollution-free non-chemical components, so the pollution-free herbicide is pure natural and pollution-free, can prevent various kinds of weeds, has high weeding effect and wide weeding spectra, has no harm to environments and human beings, and is suitable for promotion and application; therefore, the pollution-free herbicide has no impact on planting of organic food, has good absorption, and is suitable for promotion and use.
Owner:JIANGSU JIANSHEN BIOLOGY AGROCHEM
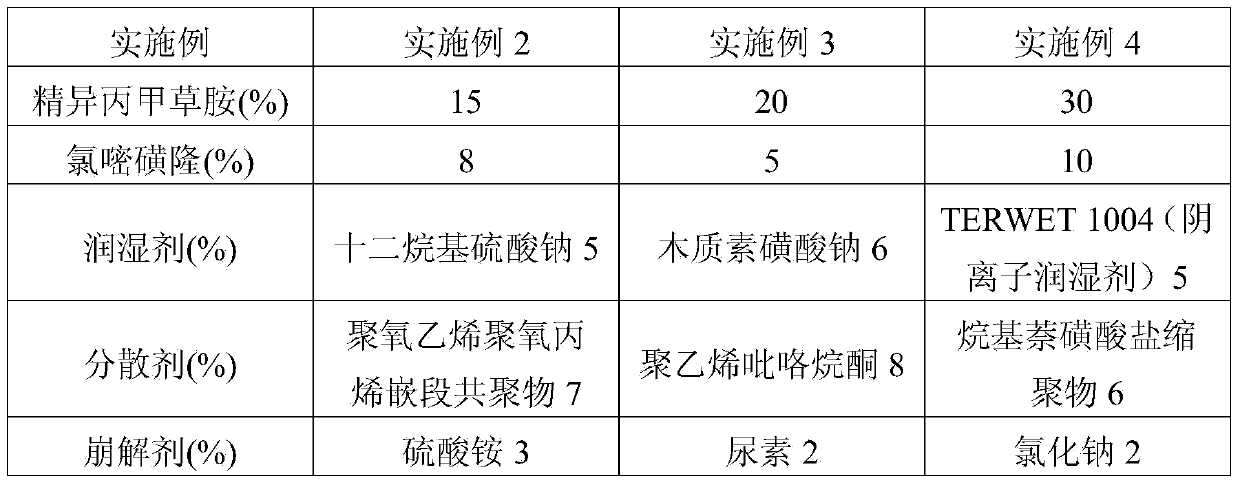
Chlorimuron-ethyl water dispersion particle
InactiveCN108378026AGood water dissolving effectEasy to makeBiocideAnimal repellantsFilling materialsDissolution
The invention discloses a chlorimuron-ethyl water dispersion particle, which is prepared from 77 percent of chlorimuron-ethyl raw powder, 6 to 8 percent of dispersing agents, 3 to 5 percent of salt-forming agents, 6 to 8 percent of disintegrating agents and the balance of filling materials. The 75-percent chlorimuron-ethyl water dispersion particle can be realized; the preparation process is simple. Compared with the existing chlorimuron-ethyl water dispersion particle, the chlorimuron-ethyl water dispersion particle has a better water dissolution effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG PIONEER CROPSCI CO LTD
Chlorimuron-ethyl soluble water particulate agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104872124AMeet the quality technical indicatorsRelieve stressBiocideAnimal repellantsParticulatesSpray nozzle
The invention discloses a chlorimuron-ethyl soluble water particulate agent and a preparation method thereof. The chlorimuron-ethyl soluble water particulate agent comprises the following components by weight percent: 15 to 90 percent of chlorimuron-ethyl raw medicine, 1 to 10 percent of dispersing agent, 1 to 7 percent of salt forming agent, 1 to 5 percent of disintegrating agent, 0 to 3 percent of water and the balance of filler. The chlorimuron-ethyl soluble water particulate agent and the preparation method disclosed by the invention have the advantages that the preparation process is simple, the production cost is low, equipment or a special production process does not need to be added, and the pollution to the environment is less; since the specific salt forming agent is selected, the chlorimuron-ethyl soluble water particulate agent can be rapidly dispersed and uniformly dissolved in water, is less in use amount, good in weed killing effect, low in drug damage and high in crop yield; the dispersion is more uniform in diluted aqueous solution, a spraying nozzle is not blocked in use, the preparation is more environmental friendly, the cost is low, the packaging requirement is low, the use is convenient and the chlorimuron-ethyl soluble water particulate agent is suitable for large-area promotion.
Owner:JIANGSU RUIDONG PESTICIDE
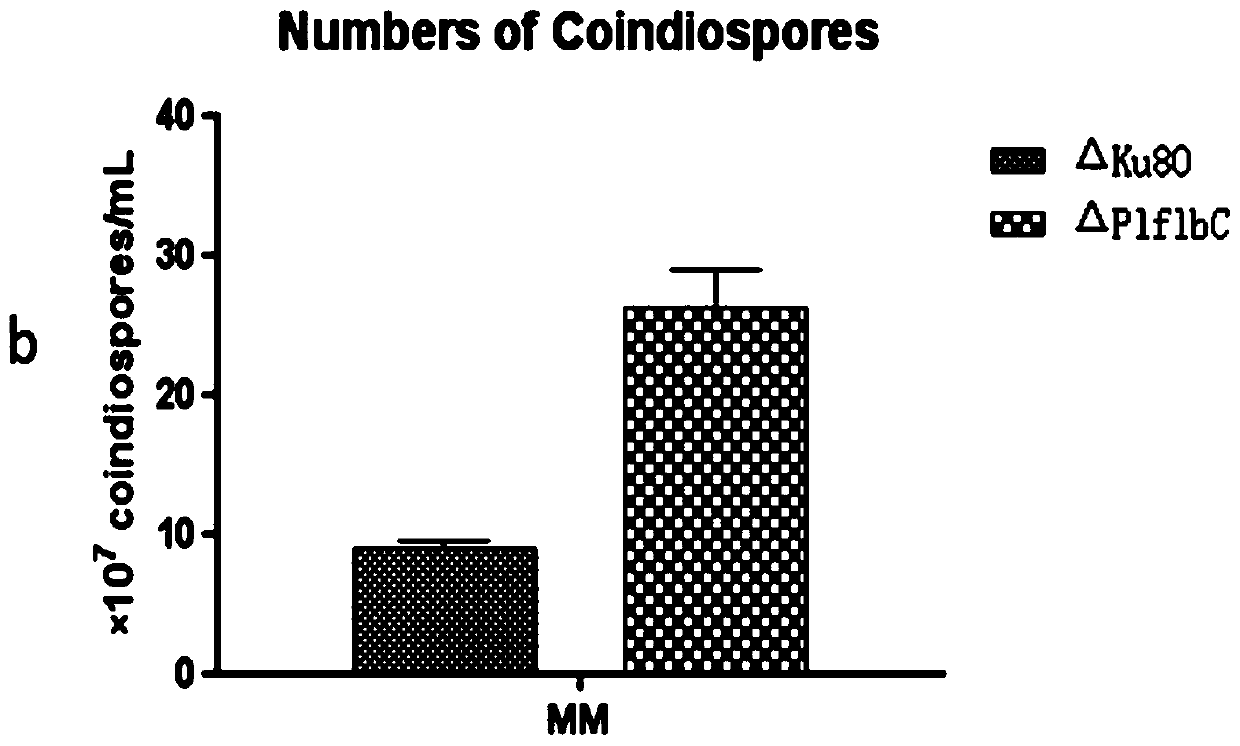
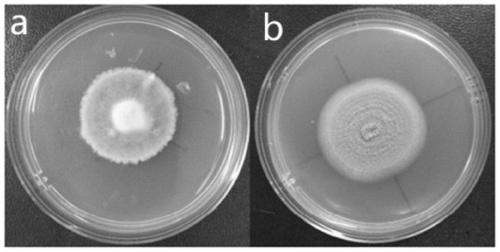
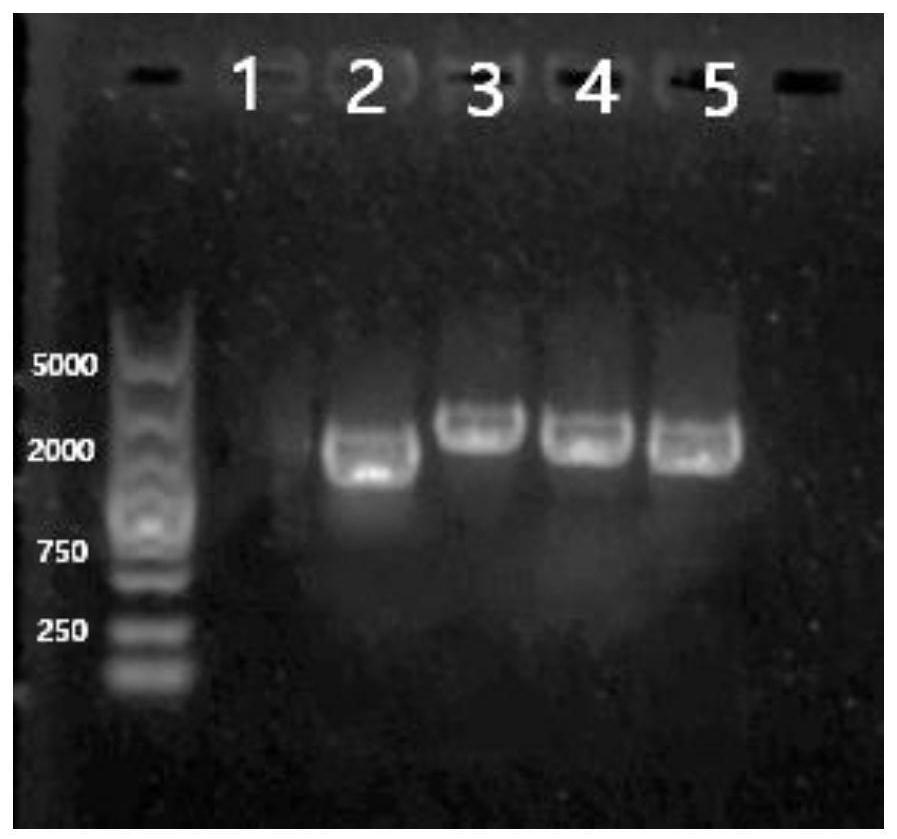
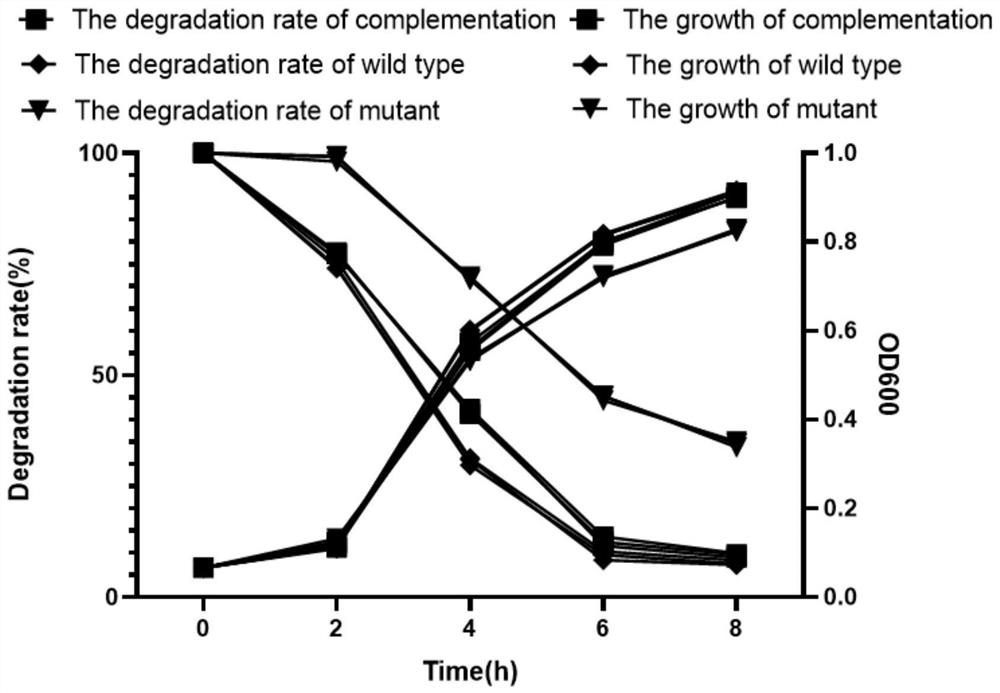
Genetically engineered bacterium delta PlflbC of purpureocillium lavendulum with high sporulation quantity, and construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium delta PlflbC
ActiveCN110423702AIncrease the number of spores producedHigh sporulationBiocideFungiBiotechnologyResistant genes
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium delta PlflbC of purpureocillium lavendulum with the high sporulation quantity, and a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium delta PlflbC, and belongs to the technical field of biological pesticides. The genetically engineered bacterium delta PlflbC is a PlflbC gene for knocking out the purpureocillium lavendulum; and the preservation number of the genetically engineered bacterium is CCTCC M 2019348, the sequence of the PlflbC gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence of the PlflbC isshown as SEQ ID NO.2. A PlflbC gene knocking-out carrier is constructed through an OSCAR method; donor plasmid pA-sur(chlorimuron-ethyl resistant gene)-OSCAR, a receptor pPK2-OSCAR-GFP, a PlflbC gene5'end homologous recombination fragment and a PlflbC gene 3'end homologous recombination fragment are subjected to Gateway BP reaction to obtain the PlflbC gene knocking-out carrier; the PlflbC geneknocking-out carrier is transferred into agrobacterium to obtain the agrobacterium containing the PlflbC gene knocking-out carrier; the agrobacterium containing the PlflbC gene knocking-out carrier isconverted into the purpureocillium lavendulum; flbC transformants are screened, verification primers are sequentially adopted to verify primer flbC verification 5 / flbC verification 3, random primersare sequentially adopted to verify randomly inserted verification 5 / randomly inserted verification 3, and thus the genetically engineered bacterium delta PlflbC of the purpureocillium lavendulum withthe high sporulation quantity is obtained.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
High efficient pesticide for controlling normal wheat diseases and insects
InactiveCN104255821APest controlImprove qualityBiocideAnimal repellantsHouttuyniaPolyethylene glycol
A high efficient pesticide for controlling normal wheat diseases and insects is composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 2 to 6 parts of amitraz, 3 to 7 parts of catechol, 6 to 10 parts of methyl silicone oil, 1 to 5 parts of polyethylene glycol, 0.6 to 2 parts of avilamycin, 2 to 4 parts of radix trichosanthes, 1 to 3 parts of glutinous rehmannia, 0.2 to 0.6 part of emulsifier, 1 to 5 parts of synergist, 1 to 2 parts of cordate houttuynia, 3 to 7 parts of pomegranate rind, 2 to 6 parts of Chinese prickly ash, 0.5 to 2 parts of chlorimuron ethyl, and 0.3 to 0.9 part of butachlor. The provided high efficient pesticide can effectively control the normal wheat diseases and insects, and is capable of greatly improving the crop quality, and moreover the residue of the pesticide is few.
Owner:QINGDAO BAOLIKANG NEW MATERIALS
A herbicidal composition containing sulfentrazone and chlorimuron-methyl and its application
The invention discloses a herbicidal composition containing sulfentrazone and chlorimuron-methyl and an application thereof. The composition uses sulfentrazone and chlorimuron-methyl as active components. The herbicidal composition of the present invention can effectively control broad-leaved weeds and grass weeds such as cocklebur, quinoa, and morning glory in soybean fields and peanut fields, and the control effect is obviously higher than that of sulfentrazone or chlorimuron-methyl alone. prevention effect. In addition, the use of the composition can not only improve the efficacy of the drug, reduce the dosage of the drug, save economic costs, greatly reduce the dosage of each active substance, reduce the residue of the drug in the environment, and at the same time delay the emergence of weed resistance , to prolong the service life of the agent, which has important ecological and environmental significance.
Owner:SHANDONG WEIFANG RAINBOW CHEM
Special herbicide formula for corn field
InactiveCN103609579AHas the development and application prospectsLow costBiocideAnimal repellantsPendimethalinChlorimuron ethyl
The invention relates to a special herbicide formula for a corn field, belonging to the technical field of pesticide processing. The special herbicide formula comprises the following components in parts by weight: 1-5 parts of alachlor, 0.05-0.5 part of chlorimuron-ethyl, 0.1-5 parts of butachlor, 2-3 parts of pendimethalin and 100-200 parts of deionized water. The special herbicide formula for the corn field has the advantages of low cost, wide herbicide controlling spectrum, quick acting, high efficiency and no residue or harm, and has a good development and application prospect.
Owner:李文斌
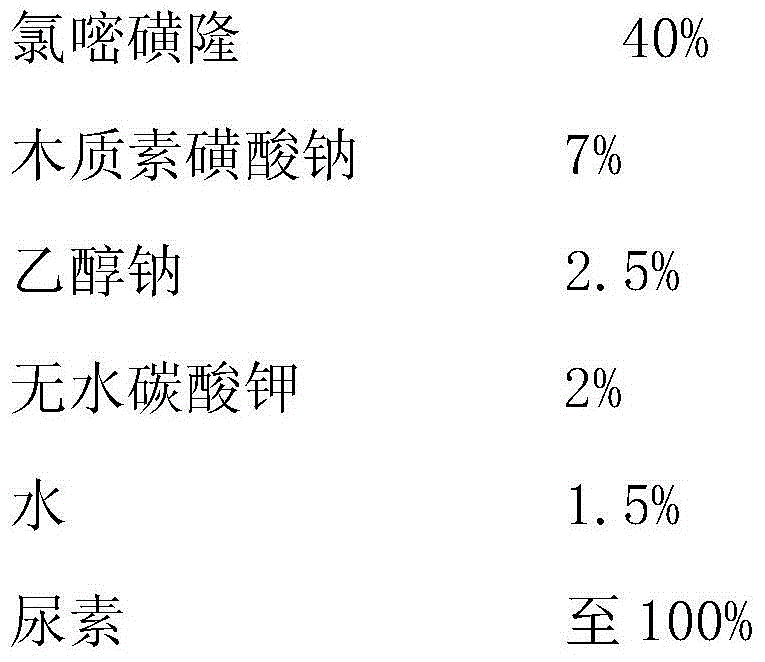
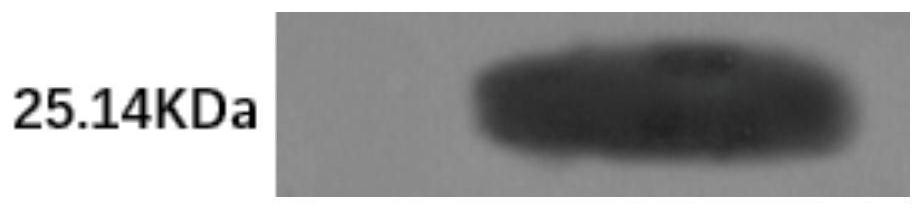
Chlorsulfuron-methyl-degrading enzyme kj-gst, its coding gene kj-gst and application
A chlorimuron-methyl-degrading enzyme Kj-GST, its coding gene Kj-gst and its application belong to the technical field of microbial genetic engineering. We successfully cloned the gene KJ‑gst from Klebsiella jilinsis 2N3, and the comparison results in GenBank showed that the gene is a glutathione S-transferase gene with a full length (from the start codon to the stop codon) of 669bp, encoding 222 amino acids. The chlorimuron-methyl degrading enzyme Kj-GST of the present invention can efficiently degrade chlorimuron-methyl, and simple analysis shows that it can hydrolyze chlorimuron-methyl to produce o-sulfonic acid imide and 2-amino-6-methoxy base pyrimidine. The gene KJ-gst can be used to construct transgenic microorganisms or plants that degrade chlorimsulfuron-methyl, and can also be used to produce enzyme preparations that degrade chlorimsulfuron-methyl, and can be used to eliminate chlorimuron-methyl residues in soil, water and agricultural products.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com