Rancidity-prone waste biogas utilization method based on in-subarea inoculation and quick start
A technology for waste and biogas, applied in the field of solid waste pollution control, can solve the problems of increasing reactors, increasing production costs, and difficulty in starting the waste gas production process, and achieving the effect of promoting degradation and avoiding loss.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Example 1 - quick start of biogas utilization of kitchen waste
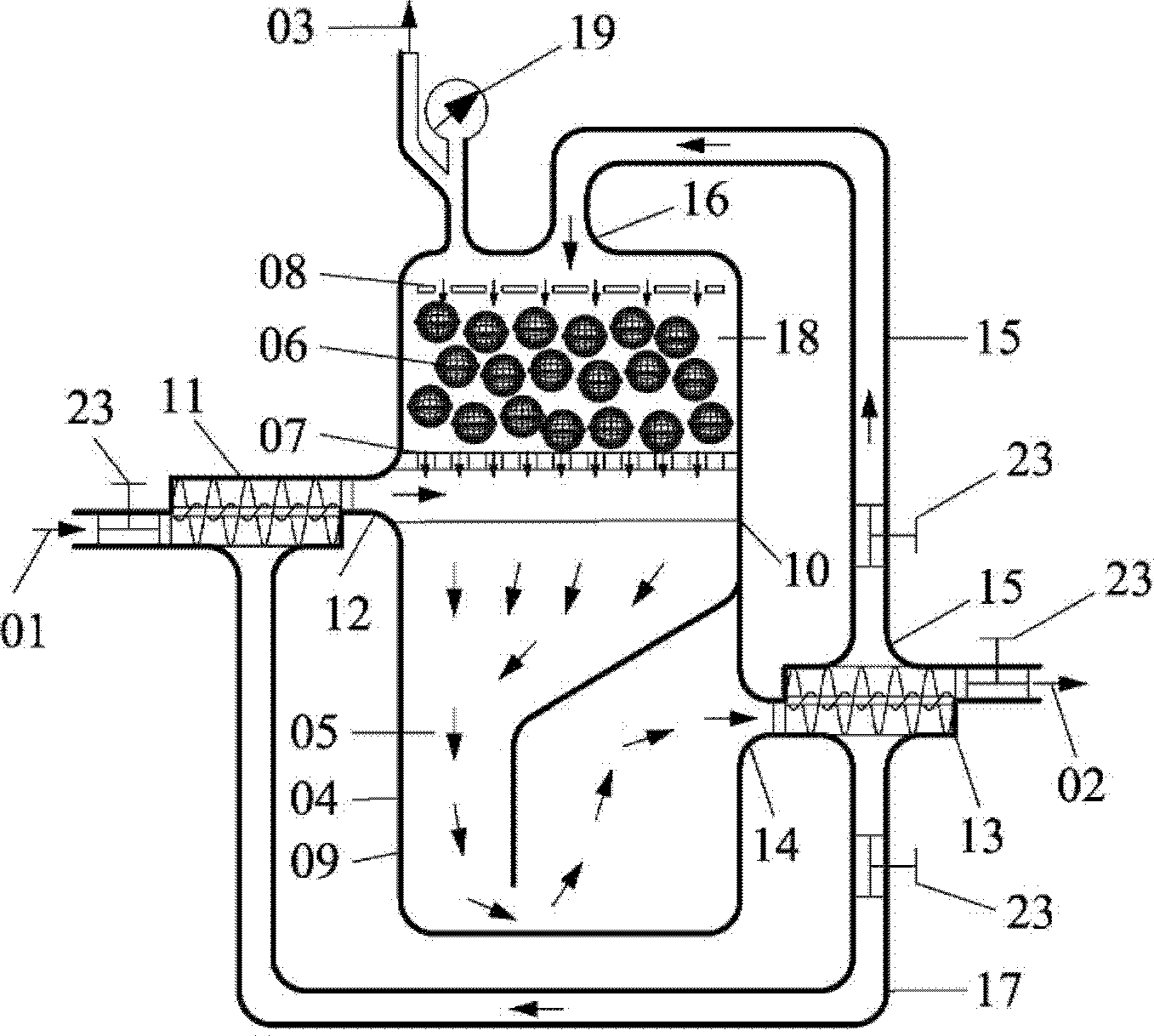
[0059] (1) From the feed port 12 to the garbage filling area 05, start-up liquid containing nutrient salts and a small amount of organic matter is pumped in once until it exceeds the liquid level of the discharge pump 13; the solid concentration of the material in the garbage filling area does not exceed 5%.
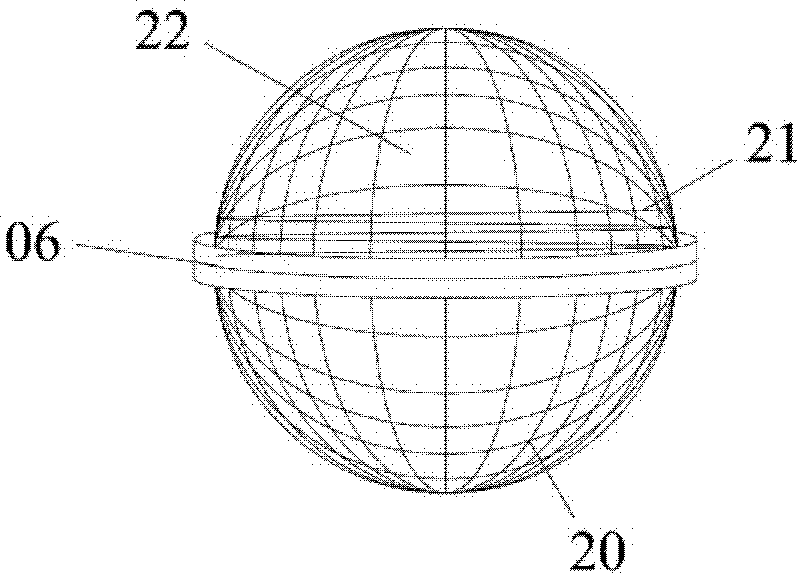
[0060] (2) Close the self-circulation loop 17 and the discharge 02; control the flow of the return pipe 16 at a certain flow rate, and spray it into the microbial agent loading area 18 through the material distribution pipe 08 to start the microbial agent 22 inside the microbial agent filling ball 06 Biomass-producing activity, as well as flushing the possible residual particulate organic matter inside the microbial agent filled ball 06. After more than 10 days of backflow spraying, the domestication and growth of methanogens were completed. For the present invention, before starting to start the bi...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Example 2 - Biogas Utilization of Batch Feed MSW
[0066] The processing raw material in this embodiment is municipal solid waste.
[0067] (1) Municipal solid waste should be pretreated by sorting, crushing and screening to remove large-sized components (greater than 2cm) and biodegradable inert components and impurities in the garbage, so as to obtain smaller-sized and more homogeneous rubbish (less than 2cm);
[0068] (2) Disposable pumping into the garbage filling area 05 to below the liquid level 10; close the discharge 02 and the self-circulation loop 17; municipal solid waste is hydrolyzed and acidified in the garbage filling area. In the present embodiment, the conditions for hydrolysis and acidification are: The pH value is 6-7.5, the temperature is 42°C, the residence time is 3 days, and the operating range of solid concentration is 25%-35%;
[0069] (3) In an intermittent or semi-continuous manner, control the return pipe 15 with a certain flow rate (the fl...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Example 3 - Biogas Utilization of Continuous Feed Fruit and Vegetable Garbage
[0073] The processing raw material of this embodiment is fruit and vegetable waste.
[0074] (1) Fruit and vegetable waste should be pretreated by sorting, crushing, and screening to remove large-size components (greater than 2 cm) and biodegradable inert components and impurities in the waste, so as to obtain smaller and more homogeneous waste. Garbage (less than 2cm);
[0075] (2) Disposable pump into the garbage filling area 05 to below the liquid level 10; close the discharge 02 and the self-circulation loop 17; the fruit and vegetable garbage is hydrolyzed and acidified in the garbage loading area. In the present embodiment, the condition for hydrolysis and acidification is: pH The value is 5.5-7, the temperature is 35°C, the residence time is 3 days, and the operating range of solid concentration is 17%-25%;
[0076] (3) In an intermittent or semi-continuous manner, control the retur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com