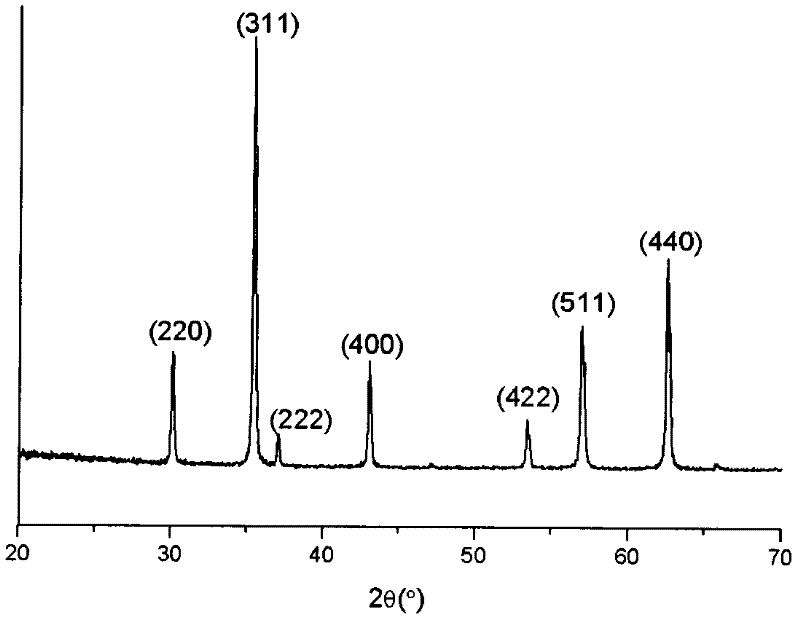
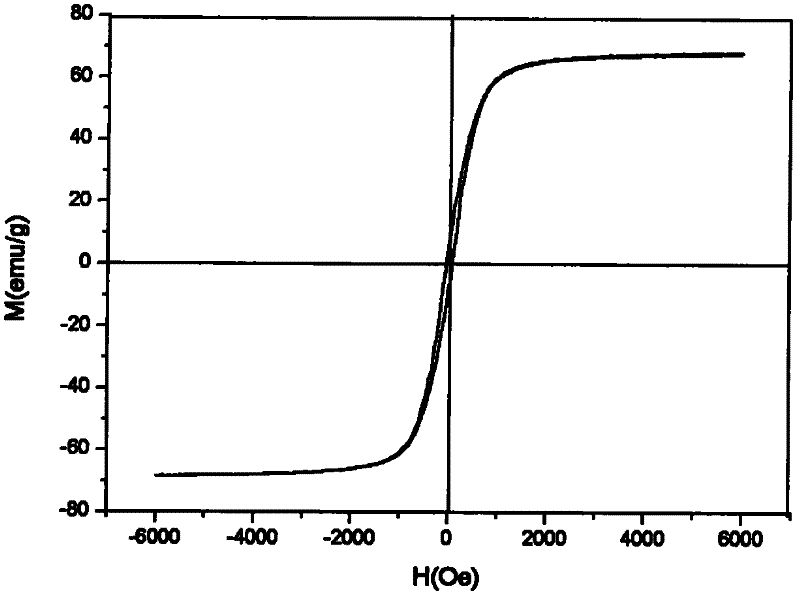
Simple method for synthesizing porous magnetic ferroferric oxide (Fe3O4) microspheres
A technology of magnetic microspheres and ferric iron, applied in the direction of iron oxide/hydroxide, iron oxide, etc., can solve the problems of high energy consumption and high equipment requirements, and achieve low production cost, simple equipment, and high production efficiency. high rate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
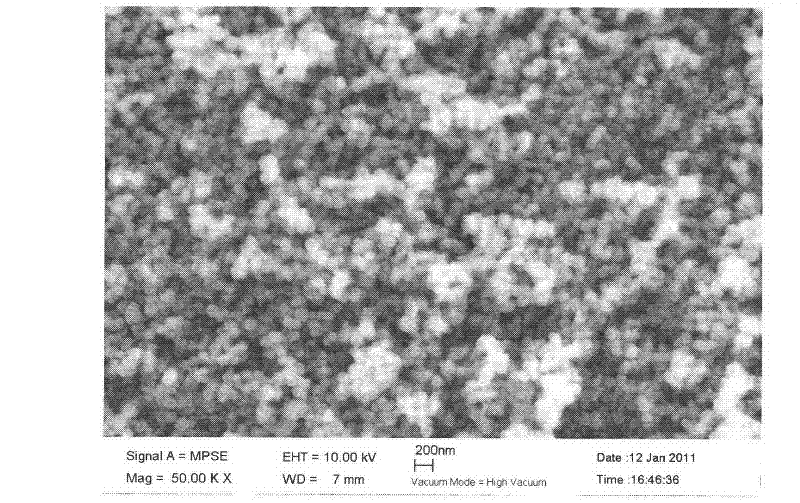
[0017] Add 3.5mmol of PVA (polymerization degree: 1700) and 35ml of secondary water into the three-necked bottle, heat to dissolve and cool down, add 40mmol of urea, seal, pump-fill with N 2 Four times to make the system completely free of oxygen, then add 5mmol FeCl 3 .6H 2 O and 2.5 mmol FeCl 2 .4H 2 O, after the solid is completely dissolved, in N 2 Heated to 85°C under protection, and reacted at this temperature for 48 hours to obtain a black precipitate, which was washed with water and absolute ethanol respectively, and dried under vacuum at 40-60°C overnight to obtain dry black Fe 3 o 4 The yield of solids was 95.8%. The product is about 100nm magnetic microspheres.
[0018] Under the same conditions, the amount of PVA was changed to 0.52mmol, 0.7mmol and 1.75mmol respectively to obtain magnetic microspheres with particle diameters of 280nm, 230nm and 150nm. That is, as the amount of PVA increases, the particle size of the magnetic microspheres becomes smaller.
Embodiment 2
[0020] Add 1.75mmol (calculated as repeating units, the same below) of PVA (polymerization degree: 1700) and 35ml of secondary water into the three-neck flask, heat to dissolve and then cool, add 40mmol of urea, seal, pump-fill with N 2 Four times to make the system completely free of oxygen, then add 5mmol FeCl 3 .6H 2 O, 2.5mmol FeCl 2 .4H 2 O and 3.5mmol acetic acid, after the solid is completely dissolved, in N 2 Heated to 85°C under protection, and reacted at this temperature for 48 hours to obtain a black precipitate, which was washed with water and absolute ethanol respectively, and dried under vacuum at 40-60°C overnight to obtain dry black Fe 3 o 4 The yield of solids was 97.2%. The product is loose and porous magnetic microspheres with a diameter of about 250 nm.
[0021] Under the same conditions, the amount of acetic acid was changed to 1.75mmol and 7mmol to obtain magnetic microspheres with a particle size of 210nm and 300nm, respectively, that is, the parti...
Embodiment 3
[0023] Add 1.75mmol of PVA (polymerization degree is 1700), 35ml of secondary water into the three-necked bottle, heat to dissolve and cool, add 40mmol of urea, seal, pump-fill with N 2 Four times to make the system completely free of oxygen, then add 5mmol FeCl 3 .6H 2 O, 2.5mmol FeCl 2 .4H 2 O and 3.5mmol acetic acid, after the solid is completely dissolved, in N 2 Heated to 80°C under protection, and reacted at this temperature for 72 hours to obtain a black precipitate, which was washed with water and absolute ethanol respectively, and dried in vacuum at 40-60°C overnight to obtain dry black Fe 3 o 4 The yield of solids was 93.4%. The product is loose and porous magnetic microspheres with a diameter of about 250 nm.
[0024] Compared with Example 2, it can be seen that the lower the reaction temperature, the slower the decomposition of urea, and the formed Fe 3 o 4 The larger the particle size of the magnetic microspheres.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com