Method for preparing nickel-cobalt-manganese alloy powder
A technology of alloy powder and nickel-cobalt-manganese, which is applied in the field of metal powder material preparation, can solve problems such as the difficulty in ensuring effective and uniform mixing of nickel, cobalt, and manganese, and the influence of product consistency, and achieve controllable and adjustable particle size and technological excellence. The effect of good matching and uniform composition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] The elemental metals nickel, cobalt, and manganese are mixed in a molar ratio of 1:1:1. The mixture is heated and melted in an induction furnace under the protection of nitrogen until it is completely melted into a metal liquid. The pressure is 3MPa. Nitrogen sprays the molten and mixed metal liquid into a metal droplet shape, and then cools the metal droplet to solidify it into metal powder particles to obtain nickel-cobalt-manganese alloy powder.
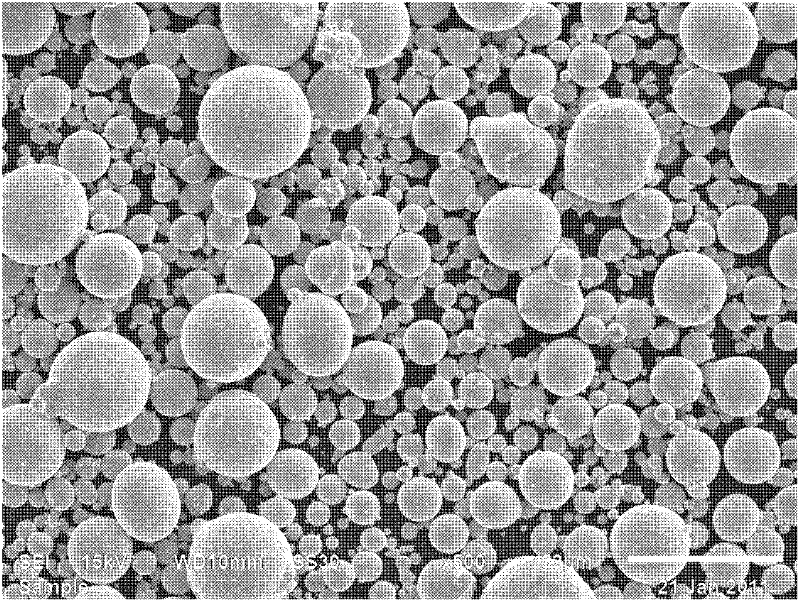
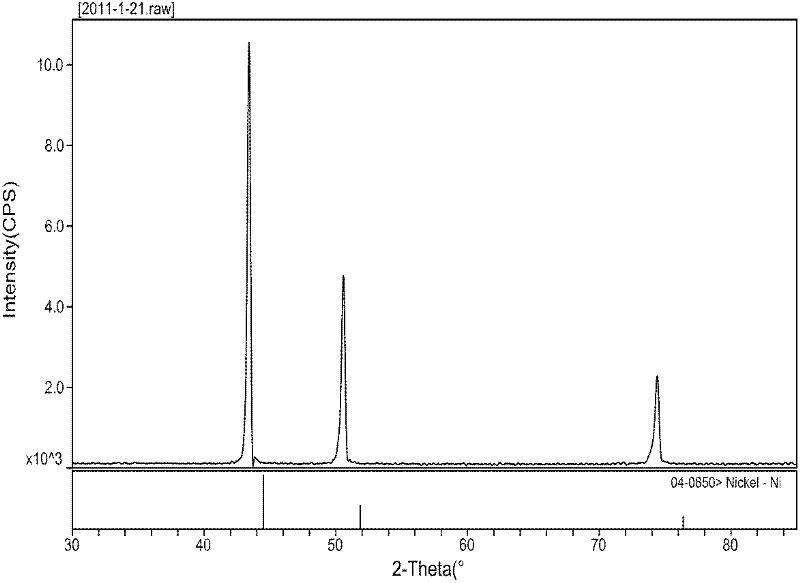
[0021] The SEM of the above alloy powder is like figure 1 As shown, it can be seen that the alloy powder has reached an atomic level of uniform mixing in composition, and the powder particles are regular spherical; its X-ray diffraction pattern is as figure 2 As shown, it can be seen from the figure that the diffraction pattern of the alloy powder is more consistent with the standard diffraction pattern of elemental nickel, but the diffraction peak of the alloy powder is slightly shifted to a low angle, and no other miscellaneo...
Embodiment 2
[0023] The metallic nickel, cobalt, and manganese are mixed in a molar ratio of 1:1:1, and the mixture is heated and melted to a molten liquid in a vacuum induction furnace. Afterwards, a high-pressure water flow with a water pressure of 40 MPa is used to spray the molten metal liquid into small metal droplets, and then the droplets are cooled to solidify them into powder particles to obtain nickel-cobalt-manganese alloy powder. From image 3 It can be seen from the SEM photograph of the alloy powder that the composition of the alloy powder is uniformly mixed at the atomic level, and the powder particles are irregular in shape. After measurement, the alloy powder particle size D50 reaches 30μm, and the bulk density reaches 3.5g / cm 3 , The tap density reaches 4g / cm 3 .
Embodiment 3
[0025] The metallic nickel, cobalt, and manganese are mixed according to a molar ratio of 5:2:3, and the mixture is heated and melted into a molten liquid in a vacuum induction furnace. Afterwards, a 4MPa high-pressure argon gas stream is used to spray the molten metal liquid into small metal droplets, and then the droplets are cooled to solidify them into powder particles to obtain nickel-cobalt-manganese alloy powder. The alloy powder is uniformly mixed in composition at the atomic level, the powder particles are regular spherical, the particle size D50 reaches 45μm, and the loose density reaches 4.98g / cm 3 , The tap density reaches 5.32g / cm 3 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com