Multiple nutrient macromolecule slow release carbon-base fertilizer and preparation method thereof
A polymer and multi-nutrient technology, applied in fertilization equipment, fertilizer mixture, application, etc., can solve the environmental pollution of eutrophication of water body, reduce the effective utilization rate of fertilizer, groundwater pollution and other problems, and meet the requirements of reducing pressure resistance performance , Improve the effective utilization rate and reduce the production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Preparation of polycarbonyl urea with m=1
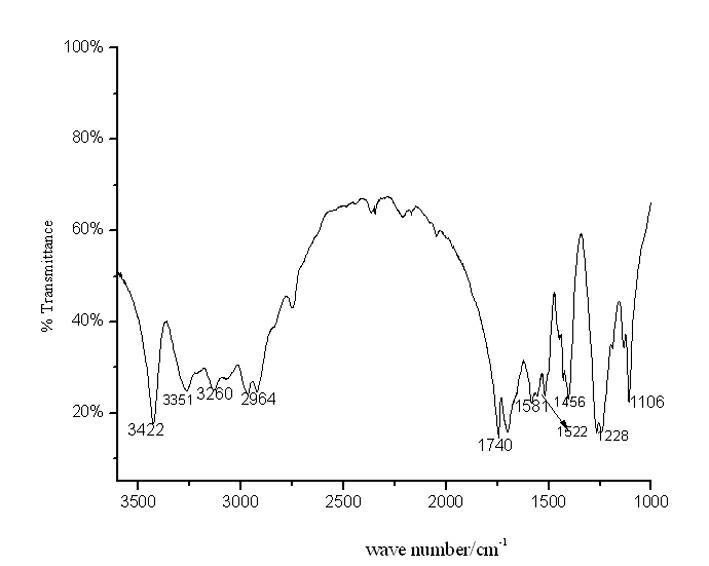
[0035] In a 1L autoclave, add 216g (3.6mol) of urea, 162g (1.8mol) of dimethyl carbonate, and 1.0g of potassium oxalate. -1 After stirring for 30 minutes at a high speed, heat up and react at 125°C for 6 hours, stop heating and continue stirring, and let it cool naturally to room temperature before discharging. After discharging, transfer the reaction mixture to a distillation pot for distillation, first recover the by-product methanol, then raise the temperature to 150°C, and heat for 1.0 h to adjust the molecular weight of polycarbonyl urea molecules, and obtain solid polycarbonyl urea after cooling. Urea 250g. The yield was 95%, the carbon content was 24.7%, and the nitrogen content was 38.4%. The infrared spectrum of the product is attached figure 1 As shown, the data attribute is as follows: N-H (3422, 3351, 3260 cm -1 ), C=O (1740 cm -1 ).
Embodiment 2
[0037] Preparation of polycarbonyl urea with m=3
[0038] In a 1L autoclave, add 216g (3.6mol) of urea, 243g (2.7mol) of dimethyl carbonate, and 0.43g of potassium carbonate.-1 After stirring for 30 minutes at a high speed, heat up and react at 145° C. for 7 h, stop heating and continue stirring, and let it cool naturally to room temperature before discharging. After discharging, transfer the reaction mixture to a distillation pot for distillation, first recover the by-product methanol, then raise the temperature to 160°C, and heat for 1.0 h to adjust the molecular weight of the polycarbonyl urea molecules, and obtain a viscous liquid after cooling Polycarbonylurea 266g. The yield is 93%, the viscosity is 405 Pa·s (measured at 25°C by using a NDJ-8S rotational viscometer), the carbon content is 26.4%, and the nitrogen content is 35.2%.
Embodiment 3
[0040] Preparation of polycarbonyl urea with m=4
[0041] In a 1L autoclave, add 216g (3.6mol) of urea, 259g (2.88mol) of dimethyl carbonate, and 0.6g of potassium formate. -1 After stirring for 30 minutes at a high speed, heat up and react at 130° C. for 10 h, stop heating and continue stirring, cool to room temperature naturally, and then discharge. After discharging, transfer the reaction mixture to a distillation pot for distillation, first recover the by-product methanol, then raise the temperature to 155°C, and heat for 1.5 h to adjust the molecular weight of the polycarbonyl urea molecules, and obtain a viscous liquid after cooling Polycarbonyl urea 253g, yield 87%, viscosity 410Pa·s (measured by NDJ-8S rotational viscometer at 25°C), carbon content 26.7%, nitrogen content 34.7%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com