Method for preparing hydrophilic macromolecule microporous composite membrane
A hydrophilic polymer and composite membrane technology, applied in the field of membrane separation, can solve the problems of poor pollution resistance and low membrane flux, and achieve the effect of improving processing capacity and efficiency and superior pollution resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] 1. Preparation of casting solution: Add 100g of polyvinyl formal (56% degree of acetalization) into 520g of 15% hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, heat to 80°C to dissolve it, and let it stand for defoaming.
[0019] 2. Scraping film: use a scraper to scrape and coat the casting solution on the polyester non-woven fabric.
[0020] 3. Solidification: The above-mentioned casting solution is immersed in an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution at 40°C and pH=9, and solidifies into a microporous membrane through phase separation.
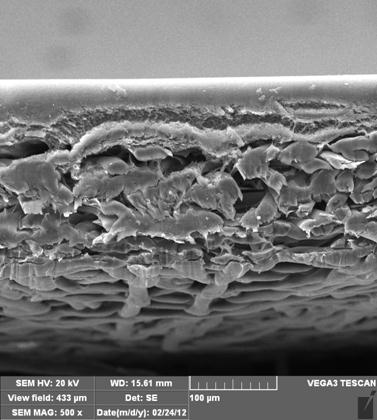
[0021] After the sample was dried, the structure and morphology were observed with a scanning electron microscope, and the results are shown in the attached figure 1 , attached figure 2 , the surface film thickness is about 20 μm, and the average membrane pore size is 0.2 μm.
[0022] Under the pressure of 1.5 meters of water column, the flux of clear water is measured as 28m 3 / m 2 d.
Embodiment 2
[0024] 1. Preparation of casting solution: Add 100g of polyvinyl formal (60% degree of acetalization) into 520g of 16% hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, heat to 80°C to dissolve, and let stand for defoaming.
[0025] 2. Scraping film: use a scraper to scrape and coat the casting solution on the polyester non-woven fabric.
[0026] 3. Solidification: The above-mentioned casting solution is immersed in an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution at 25°C and pH=10, and is solidified into a microporous membrane through phase separation.
[0027] After the sample was dried, the structure and morphology were observed with a scanning electron microscope, and the results are shown in the attached image 3 , attached Figure 4 , the surface film thickness is about 10μm, and the average membrane pore size is 0.45μm.
[0028] Under the pressure of 1.5 meters of water column, the clear water flux is 36m 3 / m 2 d.
Embodiment 3
[0030] 1. Preparation of casting solution: Add 100g of polyvinyl formal (60% degree of acetalization) into 700g of 12% sulfuric acid aqueous solution, heat to 85°C to dissolve it, and let it stand for defoaming.
[0031] 2. Scraping film: use a scraper to scrape and coat the casting solution on the polyester non-woven fabric.
[0032] 3. Solidification: The above-mentioned casting solution is immersed in an aqueous potassium hydroxide solution at 45°C and pH=10.5, and solidifies into a microporous membrane through phase separation.
[0033] Under the pressure of 1.5 meters of water column, the clear water flux is 32m 3 / m 2 d.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average membrane pore diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com