Recycling treatment method for zinc-containing ironmaking and steelmaking intermediate slag
A technology of iron and steel smelting and processing methods, applied in the field of resource processing, which can solve the problems of low equipment production capacity, high processing cost, and low compressive strength of pellets, and achieve the effect of reduced product energy consumption and high product energy cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] Follow these steps:
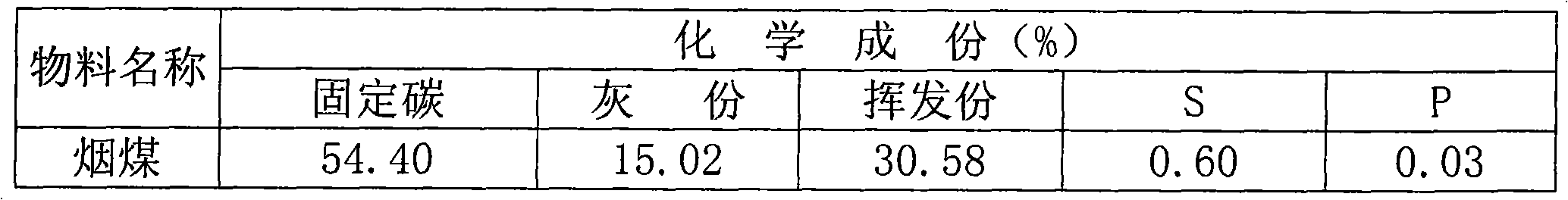
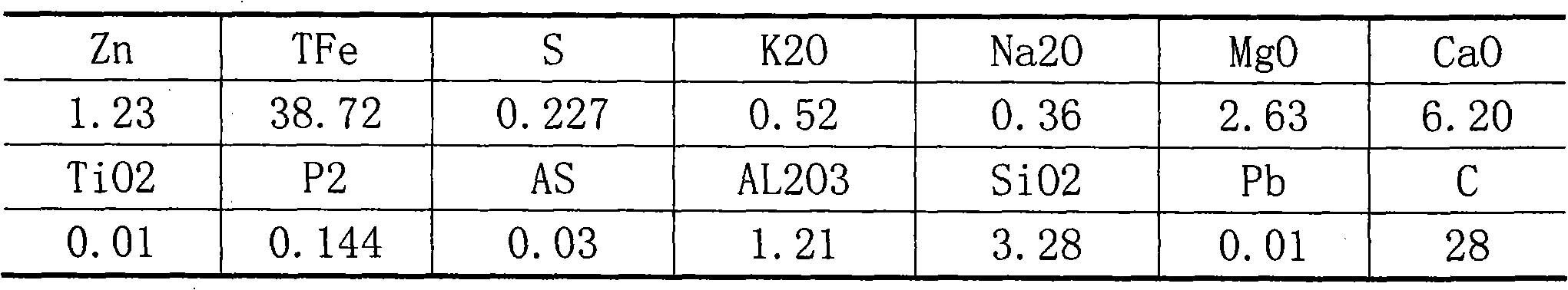
[0070] 1. Use the following raw materials by weight: 40-60% of gravity dust removal, 40-60% of converter sludge, 10%-40% of electric furnace dust, after mixing, dry and ball mill to about 120-160 mesh, and measure the dry material by screw The scale and atomized water microcomputer control system enter the pre-adding water into the ball forming twin-shaft mixer, and the pre-wet material enters the disc ball forming machine to form 12-16mm carbon-containing pellets.
[0071] 2. Adopt the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40-80% of bituminous coal, 10-50% of coal gangue, and 0-10% of lime, mix and grind to 160-200 mesh through ball milling, and then make 160-200 mesh fine powder to obtain packaged Shell powder, the mass percentage of fixed carbon content in the cladding powder is 20-60%, and the mass percentage of volatile component content is 20-40%.
[0072] 3. Put the carbon-containing pellets and shell powder into the second disc formi...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Follow these steps:
[0084] 1. Use the following raw materials by weight: 40-60% of gravity dust removal, 40-60% of converter sludge, 10%-40% of electric furnace dust, after mixing, dry and ball mill to about 120-160 mesh, and measure the dry material by screw The scale and atomized water microcomputer control system enter the pre-adding water into the ball forming twin-shaft mixer, and the pre-wet material enters the disc ball forming machine to form 12-16mm carbon-containing pellets.
[0085] 2. Adopt the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40-80% of bituminous coal, 10-50% of coal gangue, and 0-10% of lime, mix and grind to 160-200 mesh through ball milling, and then make 160-200 mesh fine powder to obtain packaged Shell powder, the mass percentage of fixed carbon content in the cladding powder is 20-60%, and the mass percentage of volatile component content is 20-40%.
[0086] 3. Put the carbon-containing pellets and shell powder into the second disc formi...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Follow these steps:
[0098] 1. Use the following raw materials by weight: 40-60% of gravity dust removal, 40-60% of converter sludge, 10%-40% of electric furnace dust, after mixing, dry and ball mill to about 120-160 mesh, and measure the dry material by screw The scale and atomized water microcomputer control system enter the pre-adding water into the ball forming twin-shaft mixer, and the pre-wet material enters the disc ball forming machine to form 12-16mm carbon-containing pellets.
[0099] 2. Adopt the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40-80% of bituminous coal, 10-50% of coal gangue, and 0-10% of lime, mix and grind to 160-200 mesh through ball milling, and then make 160-200 mesh fine powder to obtain packaged Shell powder, the mass percentage of fixed carbon content in the cladding powder is 20-60%, and the mass percentage of volatile component content is 20-40%.
[0100] 3. Put the carbon-containing pellets and shell powder into the second disc formi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com