Gene engineering bacteria high-efficiently expressing recombined human glucagon-like peptide-1 (1-37) and construction method and application thereof
A technology of glucagon and genetically engineered bacteria, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, medical preparations containing active ingredients, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of high synthesis cost, expensive price, and difficult purification, and achieve production The effect of low cost, low cost, and simple purification steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
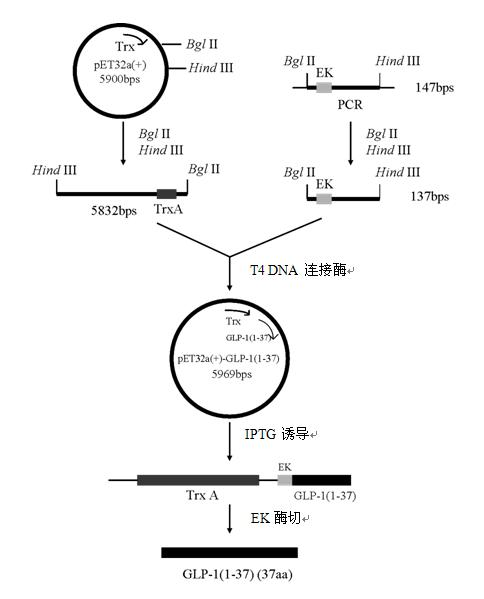
[0048] Example 1 Construction of a genetically engineered bacterium that highly expresses human glucagon-like peptide-1 (1-37)
[0049] Step 1 Amplification of GLP-1(1-37) DNA sequence
[0050] Entrust a professional biotechnology company to chemically synthesize the following base sequences: P1—upstream primer, introduce GLP-1 (1-6) gene sequence, P2—upstream primer, introduce Bgl II restriction site and enterokinase EK site, P3-downstream primer, introduced Hind III restriction site and stop codon TAA.
[0051] P1 (39bp):
[0052] 5'- CATGATGAATTTGAACGC CATGCCGAAGGCACCTTTACC-3'
[0053] GLP-1(1-6) gene sequence
[0054] P2 (43bp):
[0055] 5'-GG AGATCT G GACGACGACGACAAG CATGATGAATTTGAACGCC-3'
[0056] Bgl II restriction site Enterokinase EK site
[0057] P3 (32bp):
[0058] 5'-GG AAGCTT G TTA GCCTCTGCCTTTCACCAGCC-3'
[0059] Hind III restriction site stop codon
[0060] Using the plasmid pET32a(+)-GLP-1(7-37) as a template, adding primers P1 ...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Example 2 Production of human glucagon-like peptide-1 (1-37) by a genetically engineered bacterium that highly expresses human glucagon-like peptide-1 (1-37)
[0069] The affinity chromatography medium described below in this example is NTA-0 resin, purchased from Novagen Company, and the following enterokinase EK, purchased from NEB Company.
[0070] The first step liquid culture
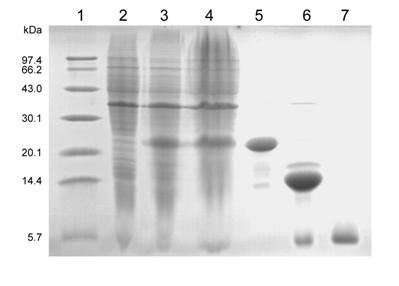
[0071] The genetically engineered bacteria constructed in Example 1 were inoculated into 20 mL of LB medium containing 100 μg / mL Amp, cultivated overnight at 37°C and 210 r / min, and the bacterial liquid was inoculated into 200 mL of LB medium containing 100 μg / mL LB culture medium of mL Amp, cultivated until the OD600 of the bacterial liquid was 0.6-0.8, and took 1 mL of the bacterial liquid as a reserved sample before induction (see attached figure 2 2), add IPTG with a final concentration of 0.6-1.0mM to the remaining bacterial solution for induction for 4 hours, and take a 1mL sample of...
Embodiment 3
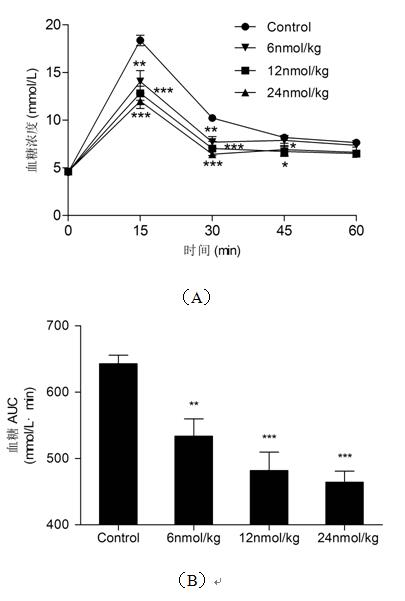
[0077] Example 3 Hypoglycemic effect of intraperitoneal administration of human glucagon-like peptide-1 (1-37)
[0078] Experimental materials and methods:
[0079] Female healthy Kunming mice (clean grade, Shanghai Slack Experimental Animal Co., Ltd.);
[0080] 40% glucose solution, 0.9% NaCl solution, human glucagon-like peptide-1 (1-37);
[0081] Blood glucose tester, blood glucose test strip (Shanghai Xinli Medical Instrument Co., Ltd.);
[0082] Disposable 1mL sterile syringe (Shanghai Kindly Enterprise Development Group Co., Ltd.);
[0083] Female healthy Kunming mice were fasted for 16 h and divided into 4 groups (n=8). 1, normal saline control group; 2-4, human glucagon-like peptide-1 (1-37) administration group, the administration doses were 6 nmol / kg, 12 nmol / kg, 24 nmol / kg respectively. The administration group was injected with 250 μL of 40% glucose solution and different doses of human glucagon-like peptide-1 (1-37), and this time was recorded as time zero. A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com