Chinese isolated strain of bovine enterovirus, and construction and application of infectious cDNA clone thereof
A technology of enteroviruses and isolates, applied in the field of bovine enteroviruses, to achieve the effect of easy preservation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Isolation and identification of bovine enterovirus Chinese isolate BHM26
[0041] 1 Experimental method
[0042] 1.1 Disease material treatment
[0043] Freshly collected feces samples were made into a 1:10 (W / V) feces suspension with PBS, vortexed, freeze-thawed three times, 3000r / min, and centrifuged at 4°C for 10min. After sterilizing by filtration with a pore filter, store in a -70°C refrigerator for later use.
[0044] 1.2 Virus isolation and culture
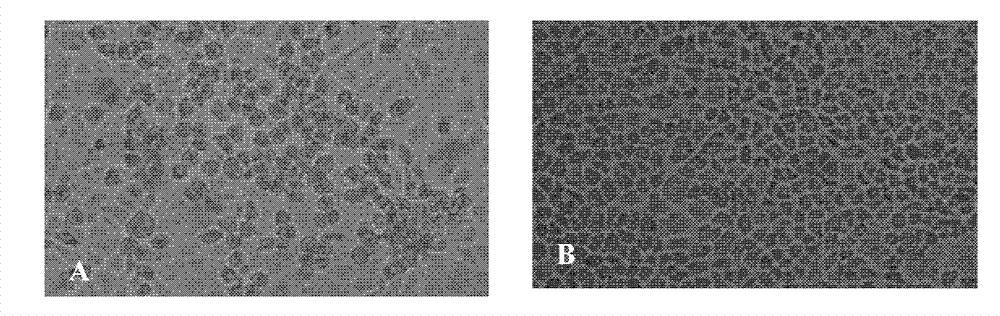
[0045] Wash the MA104 cells that have grown into a monolayer three times with PBS, inoculate the treated fecal samples into the MA104 monolayer cells, absorb at 37°C for 1 h, add serum-free DMEM, and inoculate in 5% CO 2 Culture at 37°C under conditions, and observe the cytopathic changes every day
[0046] (CPE). If there is still no CPE after 1 week of cell culture, or if the cells show 50%-80% CPE after inoculation, the cell culture is repeatedly frozen and thawed 3 times, and harvested. In the sam...
Embodiment 2、2
[0103] Construction and identification of embodiment 2, type 2 bovine intestinal rescue virus
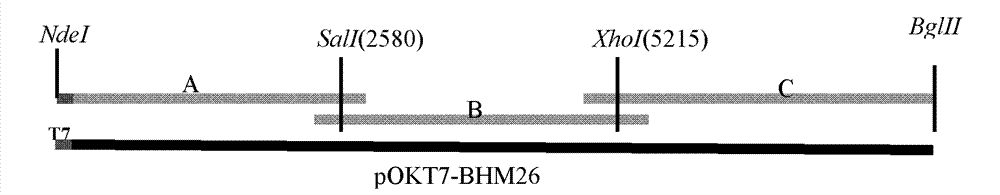
[0104] 1. Construction of full-length infectious cDNA clones
[0105] Genomic RNA of bovine enterovirus was extracted from the cell culture of bovine enterovirus BHM26 strain by Trizol method. Then oligo(dT)-15 was used for reverse transcription, and the reverse transcription product was used as a template, and the primers in Table 2 were used to amplify the three overlapping fragments A, B and C covering the full length of the genome. By PCR amplification, a T7 RNA polymerase promoter sequence was introduced at the 5' end of the viral genome, and a Bgl II restriction enzyme site was introduced at the 3' end of the viral genome. Using site-directed mutagenesis, C is mutated to T at the 4074nt position of the viral genome, so that CAGCTG (PvuII) at this position becomes TAGCTG, and the PvuII restriction site is eliminated as a molecular marker. The three fragments were sequentially...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com