Simple identification method for leather fiber structure
A leather fiber, simple technology, applied in the field of identification of leather materials, can solve the problems of difficulty in extracting cross-sectional characteristic parameters, complicated production process, compression of embedding agent embedding treatment, etc., to improve the accuracy of leather identification and simple sample preparation method , the effect of improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] The following descriptions are only preferred embodiments of the present invention, and therefore do not limit the protection scope of the present invention.
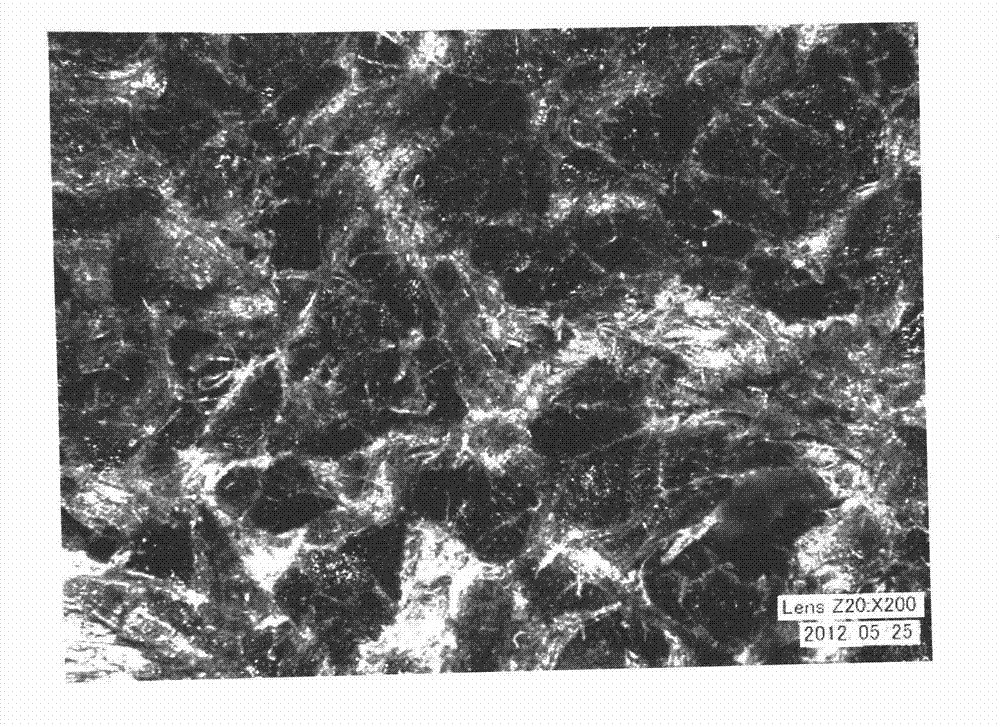
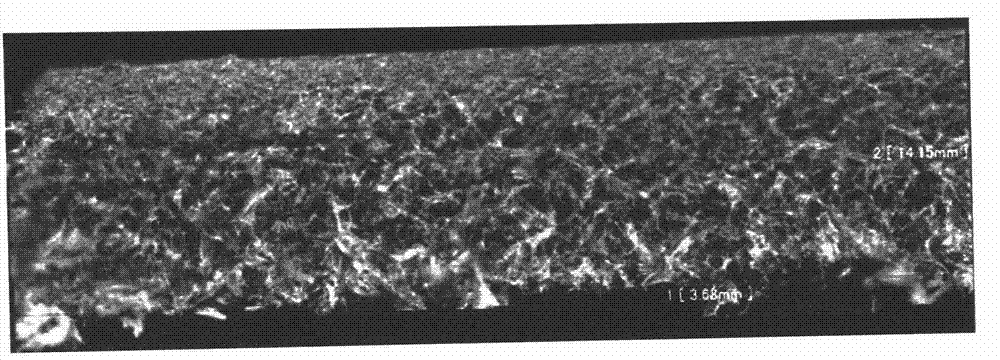
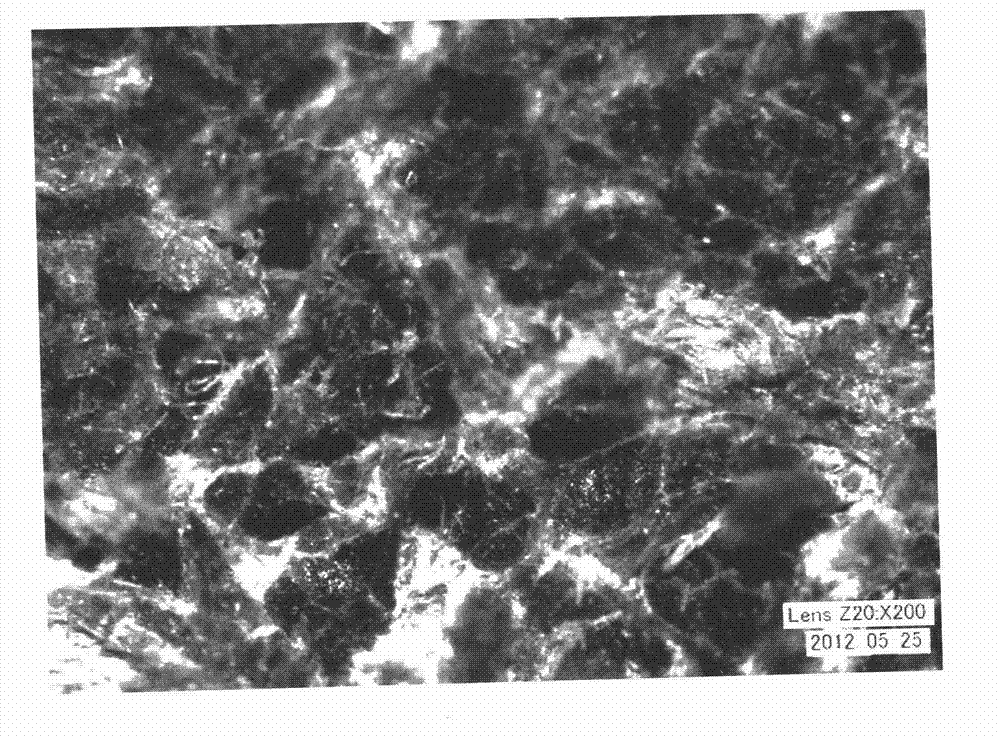
[0026] Examples, see Figure 1 to Figure 5 Shown:
[0027] A kind of simple and easy identification method of leather fiber structure, comprises the steps:
[0028] (1) pave the bovine finished leather as it is, and carry out a 48-hour preconditioning under standard atmospheric conditions;
[0029] (2) On the sample preparation table, clamp both ends of the pre-adjusted original leather with a clamp, and make it naturally straighten under low tension, and then quickly cut off the original leather with a cutting machine, and the pre-adjusted The final leather sample is made into a cross-section sample, and is left to stand for 1 to 3 hours under standard atmospheric conditions until the deformation of the incision of the cross-section sample recovers;
[0030] (3) Fix the section of the cross-section sample aft...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com