Lactobacillus plantarum used for silage alfalfa and use method thereof
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum and alfalfa, applied in the field of lactic acid bacteria for silage, can solve the problems of high buffer energy, high moisture content of alfalfa, low sugar content, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] A strain of Lactobacillus plantarum, said Lactobacillus plantarum (L.plantarum Ps-9) is a lactic acid bacterium with good acid resistance, strong growth ability and fast acid production speed screened out from 100 strains of Lactobacillus plantarum; It has been preserved in the General Microorganism Culture Collection Center of China Microbiology Culture Collection Management Committee, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.5489.
[0020] Application of the plantaractobacillus in alfalfa silage.
[0021] For the activation and cultivation of Lactobacillus plantarum, inoculate the cryopreserved L. plantarum Ps-9 in the MRS liquid medium, culture it at 37°C for 18-22 hours, and subculture it for 2-3 times to obtain the activated L. plantarum Ps-9 strain; the composition of the MRS liquid medium is as follows: 10g peptone, 5g beef extract, 4g yeast extract powder, 20g glucose, 2g dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 5g sodium acetate, 2g trisodium citrate, 1mL spit Temperatu...
Embodiment 2
[0035] The method for using Lactobacillus plantarum in alfalfa silage comprises the following steps:
[0036] The alfalfa raw material is naturally dried to a moisture content of 45%-55% for semi-dry silage. Take 1×10 5 The inoculation amount of cfu / g was inoculated into alfalfa raw materials, and the same volume of sterilized distilled water was added as a control group. After being vacuum-packed by a vacuum packaging machine, it was placed in a storage room for fermentation. After 30 days of fermentation, that is, after the fermentation is mature, a part of the silage is taken out for microbial composition and fermentation quality analysis.
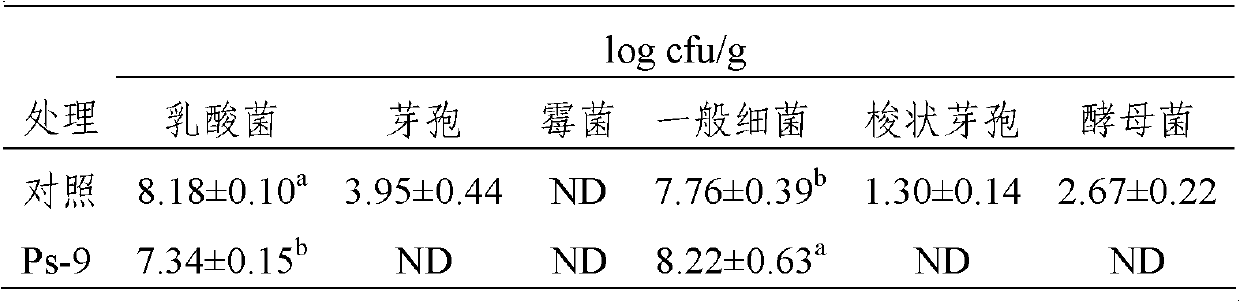
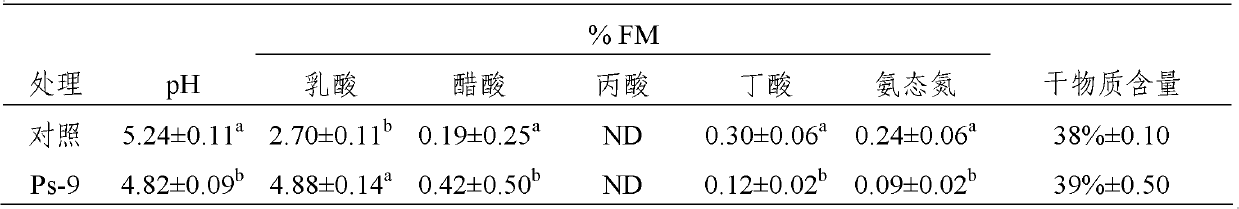
[0037]Microbial composition analysis included counts of lactic acid bacteria, yeast, bacillus, mold, common bacteria and E. coli. Weigh 10g of fermented mature silage, add 90ml of sterilized water, shake fully, and then use sterilized water to dilute the sample by ten-fold dilution method, and select 100μL of appropriate diluent to ap...
Embodiment 3
[0047] The method for using Lactobacillus plantarum in alfalfa silage comprises the following steps:
[0048] Dry the raw material of alfalfa naturally until the water content is 45%-55% for semi-dry silage, add 3.0% and 5.0% molasses respectively, and mix the strain Ps-9 with 1×10 5 The inoculation amount of cfu / g was inoculated into alfalfa, and the same volume of sterilized distilled water was added as a control group. After being vacuum-packed by a vacuum packaging machine, it was placed in a storage room for fermentation. After 30 days of fermentation, that is, after the fermentation is mature, part of the silage is taken out for microbial composition and fermentation quality analysis.
[0049] Table 5 Effect of adding molasses on microbial composition of alfalfa semi-dry silage
[0050]
[0051] Note: different letters in the same column indicate significant difference (P<0.05); ND: not detected
[0052] From the analysis of microbial composition in Table 5, it can ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com