Thermal treatment method suitable for magnetism alloy with age-hardening property
A heat treatment method and aging hardening technology, applied in the field of metal heat treatment, can solve the problems of difficult to observe aging strengthening, reduction of solute supersaturation, reduction of volume fraction of strengthening phase, etc. Effect of Volume Precipitation Fraction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
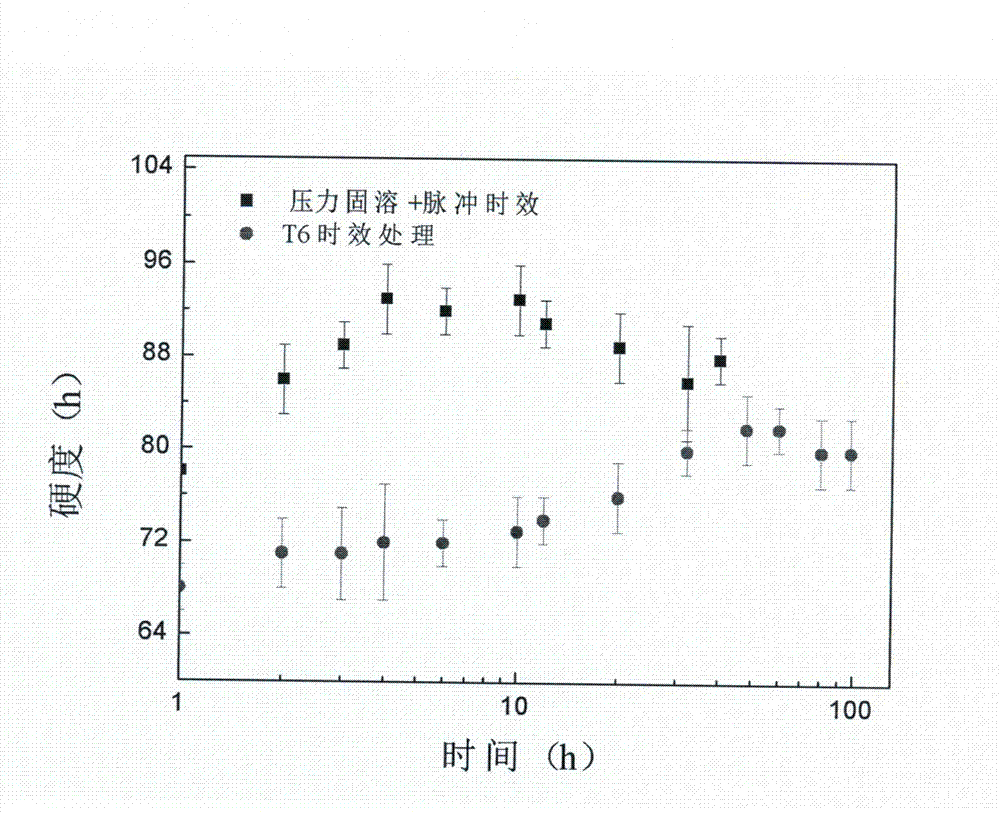
[0022] Take Mg-5Zn-0.6Zr-0.2Mn (wt.%, mass percentage) alloy, solid solution at 0.85Tm (520 ℃) in an isobaric external field of 0.5GPa, and the solution time is 2 hours. Remove the pressure after treatment. It is directly cooled with hot water at 60℃, and then aged at room temperature under an external stress of 30MPa and a pulsed electric field of 1kV / cm. When the aging time is 50,000 pulses and the pulse interval is 1 second, the peak hardness can be reached and the highest mechanical performance can be obtained. The Vickers hardness reaches 125 HV (load 50 g, load time 15s).
[0023] The above alloy is treated with traditional T6 (Solid Solution and Aging). The solution temperature is 520℃, the solution time is 8 hours, the aging temperature is 200 ℃, the aging time is 24 hours, and the maximum hardness after treatment is 95 HV (Load 50 g, load time 15s).
[0024] Such as figure 1 As shown, the hardness of the Mg-5Zn-0.6Zr-0.2Mn alloy treated with the low-temperature pulse in...
Embodiment 2
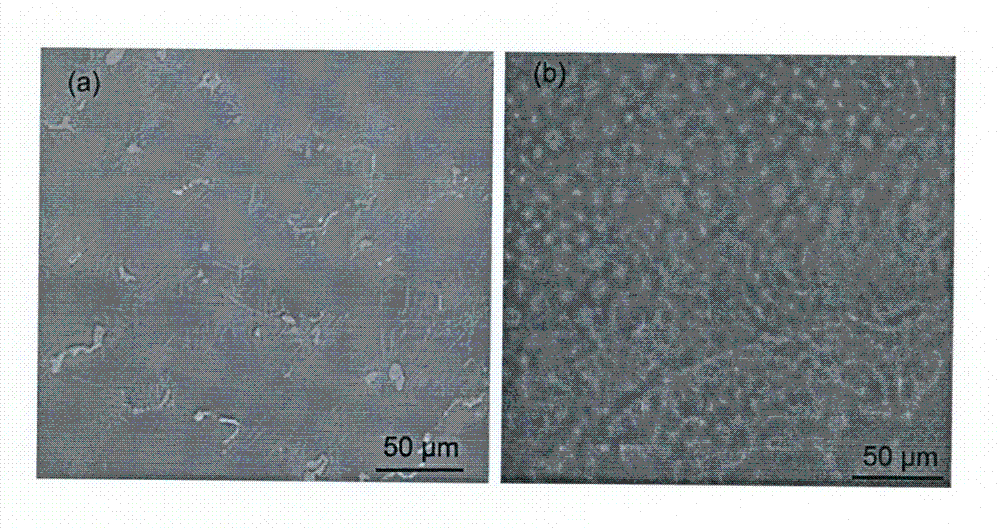
[0026] Take Mg-10Sn-0.6Zr-0.2Mn (wt.%, mass percentage) alloy, and solid solution at 0.7Tm (310 ℃) under an isobaric field of 1GPa. The solution time is 4 hours. After treatment, release the pressure and directly Cooled with hot water at 80℃, then aged at room temperature under an external stress of 50MPa and a pulsed electric field of 10 kV / cm. When the aging time is 10,000 pulses and the pulse interval is 1 second, the peak hardness can be reached and the highest mechanical performance can be obtained. The Vickers hardness is 93HV (load 50g, bearing time 15s).
[0027] The above alloys are treated with traditional T6 (Solid Solution and Aging). The solution temperature is 310℃, the solution time is 8 hours, the aging temperature is 180 ℃, the aging time is 48 hours, and the maximum hardness is 82 HV (load 50 g, bearing time 15s).
[0028] Such as figure 2 As shown, there are a large number of square particles in the Mg-10Sn-0.6Zr-0.2Mn alloy after T6 solution treatment. Due to...
Embodiment 3
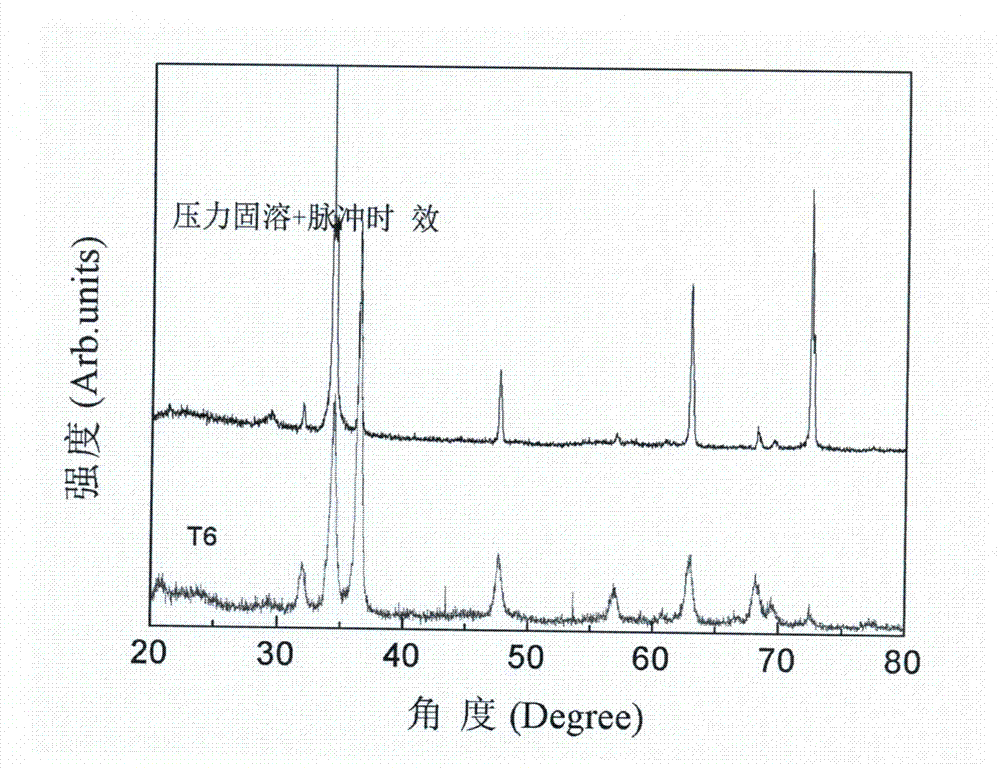
[0030] Take Mg-16Pb-2Sm-2Nd-0.6Zr-0.2Mn (wt.%, mass percentage) alloy and solid solution at 0.8Tm (525 ℃) under an equal pressure field of 0.75GPa. The solution time is 3 hours. After treatment Relieve the pressure, directly cool with 70℃ hot water, and then aging at room temperature under an external stress of 40MPa and a pulsed electric field of 8 kV / cm. When the aging time is 30,000 pulses and the pulse interval is 1 second, the peak hardness can be reached. The highest mechanical performance, the highest Vickers hardness is 118HV (load 50 g, load time 15s).
[0031] The above alloy is treated with traditional T6 (Solid Solution and Aging), the solution temperature is 525℃, the solution time is 24 hours, the aging temperature is 210 ℃, the aging time is 36 hours, and the maximum hardness is 96 HV (load 50 g, bearing time 15s).
[0032] Such as image 3 As shown, compared with the traditional T6 treatment method, the precipitated phase composition of the Mg-16Pb-2Sm-2Nd-0.6Zr-0....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com