Method for breeding, culturing and storing plant nematodes by using sweet potato calluses
A callus and nematode technology, applied in the field of using sweet potato callus to propagate, cultivate and preserve plant-parasitic nematodes, can solve the problems of low reproductive success rate and reproduction amount, inability to cultivate and preserve for a long time, and high water content in carrots, and achieve success High efficiency, simple operation, and easier to obtain effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Propagation and preservation of D. destructor on sweet potato callus
[0041] Specific steps are as follows:
[0042] (1) Preparation of sweet potato callus:
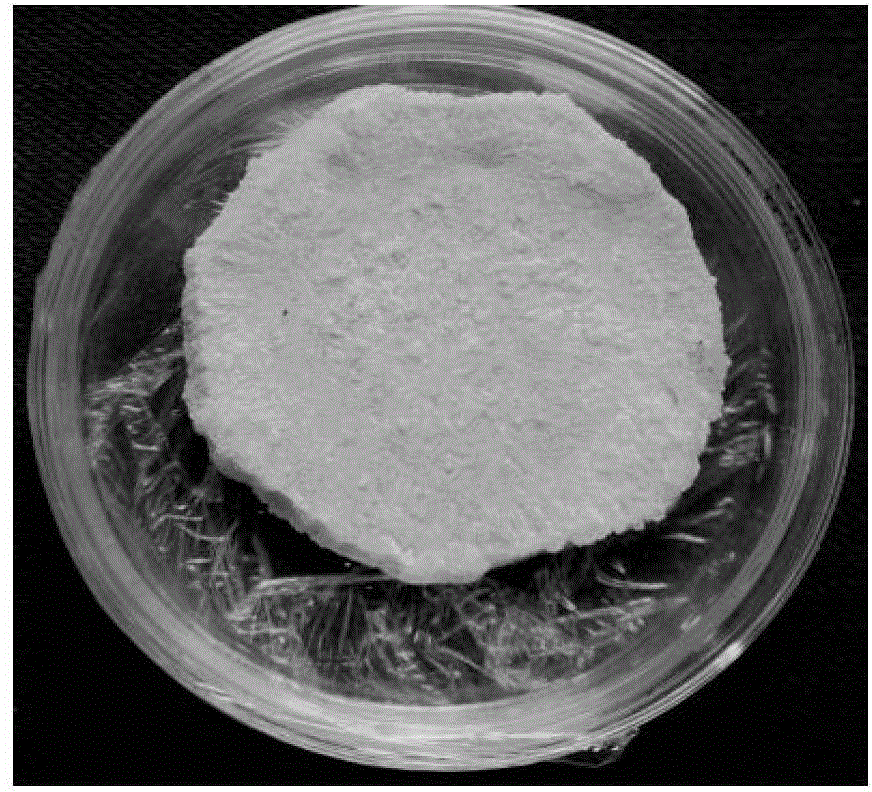
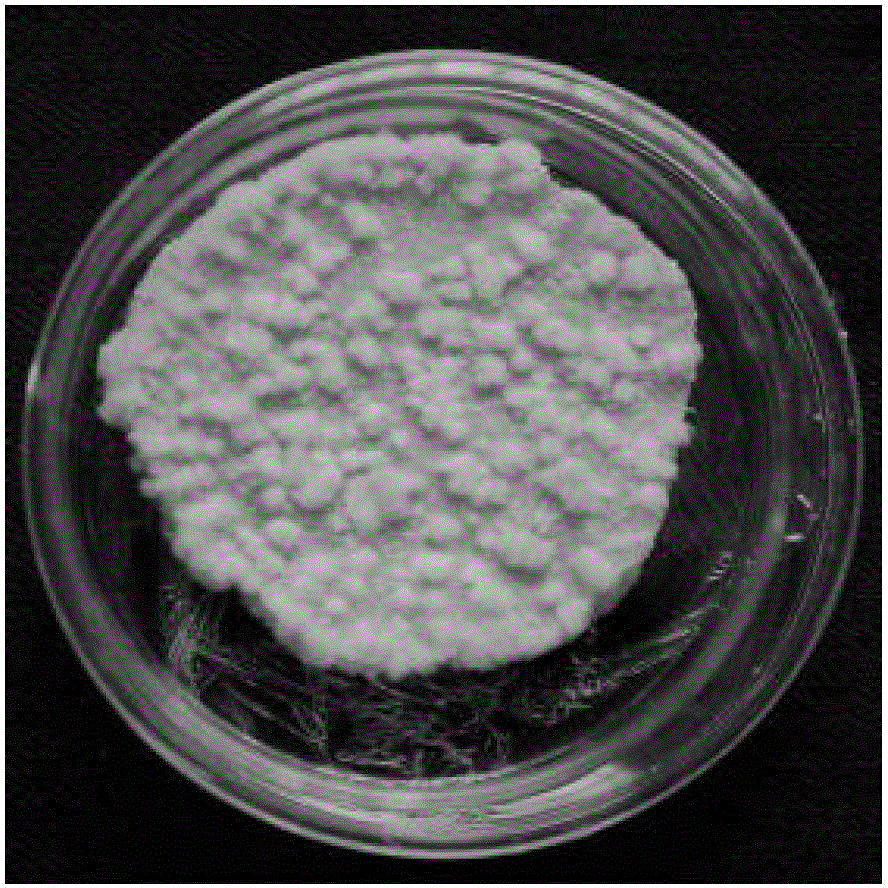
[0043] Select healthy, relatively slender and regular sweet potato pieces (Guangshu 128), wash and dry them; soak them in 70% alcohol by mass for 2 minutes, then burn off the alcohol on the surface in an ultra-clean workbench, and use sterilized shavings Peel off the skin of the sweet potato with a leather knife, then cut into thin slices of about 4mm, and put the thin slices into a sterile petri dish ( figure 1 ), sealed with plastic wrap, and cultured in the dark in a constant temperature incubator at 25°C until the callus grows for later use (generally, the callus will appear in 7 days, and the tubers will be covered with potato pieces in 10-15 days) ( figure 2 ).
[0044] (2) Isolation of D. destructor
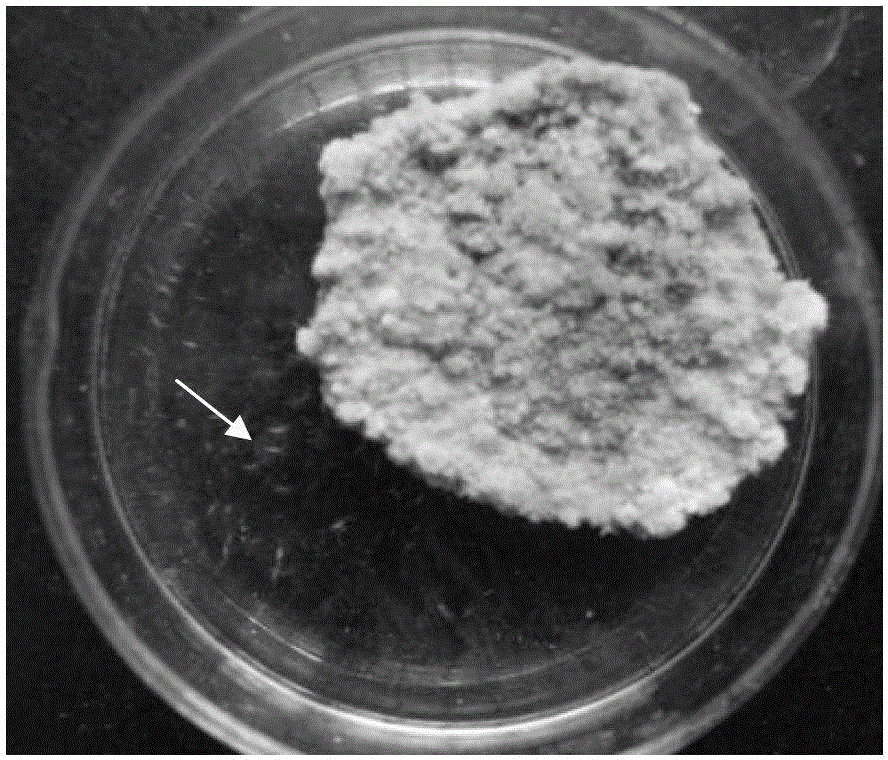
[0045] Cut the symptomatic sweet potato pieces, cut out some symptomatic sweet potato tissu...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Implementation 2 Propagation and preservation of D. tsienmus on sweet potato callus
[0053] Specific steps are as follows:
[0054] (1) See Example 1 for the preparation of sweet potato callus.
[0055] (2) Isolation of D. tesselis
[0056] The symptomatic diseased root is cut into pieces with scissors, and separated from the matrix around the diseased root using the Behmann funnel method. The method is the same as in Example 1.
[0057] (3) Disinfection, inoculation and cultivation of D.
[0058] 25 female worms were picked, and the petri dish was placed in an incubator at 18° C. for cultivation after inoculation, and other disinfection and inoculation methods were the same as in Example 1.
[0059] (4) The collection and counting of the nematodes after being cultured on the sweet potato callus for a certain period of time can be seen in Example 1 for specific methods.
[0060] After inoculating 25 D. trunchelis on the sweet potato callus and culturing for 50 days...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3 Propagation and preservation of banana borer nematode on sweet potato callus
[0063] Specific steps are as follows:
[0064] (1) See Example 1 for the preparation of sweet potato callus.
[0065] (2) Isolation of banana perforator nematode
[0066] Symptomatic diseased root tissue is shredded with scissors, and separated from the matrix around the diseased root using the Behmann funnel method, the method is the same as in Example 1.
[0067] (3) Banana perforator nematode disinfection, inoculation and culture
[0068] Pick 25 female worms, and other disinfection and inoculation methods are the same as in Example 1.
[0069] (4) The collection and counting of nematodes after being cultured on the sweet potato callus for a certain period of time refer to Example 1 for specific methods.
[0070] After 25 nematodes were inoculated on the sweet potato callus and cultured for 50 days, the average number of worms reproduced was 21836±1459.2, the average number o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com