Nanometer composite wave absorbing powder having low density and porous structure, and its preparation method
A nano-composite, porous structure technology, applied in the field of absorbing materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Preparation of low-density nanoferrite A: Weigh 27.3g of citric acid, dissolve it in 200g of deionized water to form a citric acid aqueous solution, weigh 48.48g of iron nitrate nonahydrate, 2.9g of nickel nitrate hexahydrate, and dissolve them in the aqueous citric acid solution Stir to dissolve, mix the two solutions evenly under rapid stirring, then weigh 5.7g of sodium lauryl sulfate, add to the above solution and stir to dissolve, after dissolving, add ammonia water dropwise under rapid stirring conditions to adjust the pH value to 8, at 90°C Stir to evaporate the water until a gel with a moisture content of <10% is formed. Dry the gel in a drying oven at 120°C for 24 hours to obtain a dry gel, ignite it with alcohol, grind the dry gel with a mortar after self-propagating combustion, calcinate at 1100°C in a muffle furnace for 4 hours, and grind it finely to obtain a low-density gel. Nanoferrite A.
Embodiment 2
[0054] Preparation of tin-doped indium oxide precursor: Weigh 5.28g of indium chloride tetrahydrate and 0.7g of tin chloride pentahydrate and dissolve them in deionized aqueous solution and mix them evenly. Add ammonia water dropwise under rapid stirring conditions to adjust the pH value to 8.5. The temperature was kept at 50° C. for two hours to obtain a tin-doped indium oxide precursor. Finally, the mass of the precursor was weighed, and the theoretical value of the obtained tin-doped indium oxide was calculated, and the mass ratio of the two was obtained as the theoretical value of tin-doped indium oxide:precursor=1:2.1. Take part of the precursor and wash it with ethanol, filter to obtain the precipitate, dry it in a drying oven at 120°C for 24 hours, and grind it with a mortar to obtain a xerogel, calcinate it at 600°C for 2 hours, cool it, and grind it finely to obtain a tin-doped indium oxide precursor.
Embodiment 3
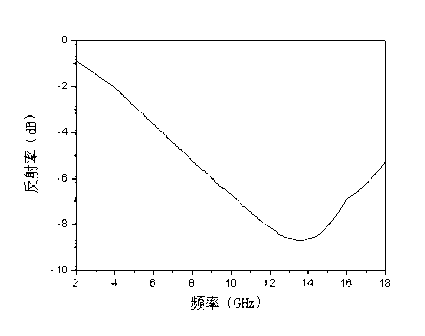
[0056] Weigh 4.2 g of the tin-doped indium oxide precursor obtained in Example 2, add 2 g of the low-density nano-ferrite A in Example 1, stir evenly at high speed, wash with ethanol, filter to obtain the precipitate, and dry in a drying oven at 120°C for 24 hours , the dried product was ground with a mortar, calcined at 600°C for 2h, cooled, and ground to obtain a nanocomposite powder A with compatible absorption of low-density radar waves and infrared waves.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com