Process for recovering magnesium sulfate monohydrate from boron extraction mother liquor
A technology of magnesium sulfate and boron mother, applied in directions such as magnesium sulfate, can solve the problems of high equipment requirements, unfavorable technology promotion and utilization, large energy consumption, etc., and achieves low equipment requirements, high economic value, and low operating temperature. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
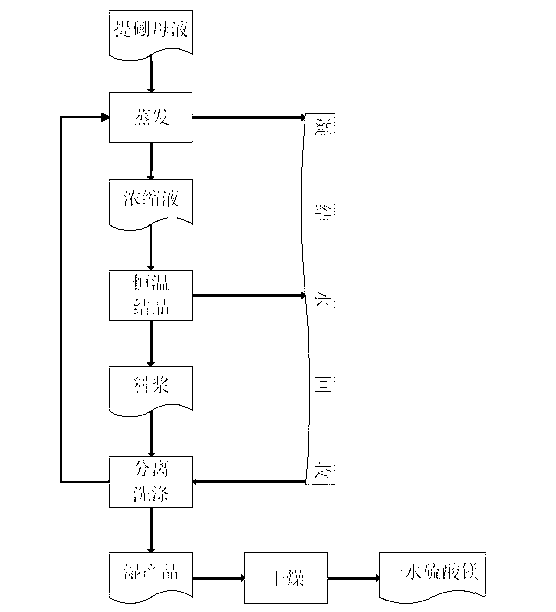
[0023] Example 1 Such as image 3 Shown, a kind of technique that reclaims magnesium sulfate monohydrate from boron extracting mother liquor comprises the following steps:
[0024] (1) Under normal pressure conditions, put 3.87t of the boron extracting mother liquor with an initial composition of magnesium sulfate concentration of 20.4% and boric acid concentration of 0.2% into the evaporation reactor. When heated to 95°C, the boron extracting mother liquor starts to boil and keep the temperature unchanged; When the concentration of boron extraction mother liquor reaches 1.410g / mL or 42 ? When Be', slowly raise the temperature to 104°C at a rate of 0.05°C / min; ? When Be', 2.45t concentrated liquid and 2.05t condensed water A are obtained respectively.
[0025] (2) Move the concentrated solution to the crystallizer, and carry out constant temperature evaporation and crystallization at a temperature of 120°C. When the solid-to-liquid ratio is 2g:1L, 1.47t of slurry and ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2 Such as image 3 Shown, a kind of technique that reclaims magnesium sulfate monohydrate from boron extracting mother liquor comprises the following steps:
[0030] (1) Under normal pressure, put 3.93t of the boron-extracting mother liquor with an initial composition of magnesium sulfate concentration of 18% and boric acid concentration of 4% into the evaporation reactor, and when heated to 95°C, the boron-extracting mother liquor begins to boil and keep the temperature constant; When the concentration of boron extraction mother liquor reaches 1.397g / mL or 41 ? When Be', slowly raise the temperature to 102°C at a rate of 0.05°C / min; ? When Be', 5.08t of concentrated liquid and 2.19t of condensed water A were obtained respectively.
[0031] (2) Move the concentrated solution to the crystallizer, and carry out constant temperature evaporation and crystallization at a temperature of 110°C. When the solid-liquid ratio is 0.5 g: 1L, 4.05t of slurry and 1.03...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3 Such as image 3 Shown, a kind of technique that reclaims magnesium sulfate monohydrate from boron extracting mother liquor comprises the following steps:
[0036] ⑴Under normal pressure, put 3.78t of the boron-extracting mother liquor with an initial composition of magnesium sulfate concentration of 24% and boric acid concentration of 0% into the evaporation reactor, and when heated to 94°C, the boron-extracting mother liquor begins to boil and keep the temperature constant; When the concentration of boron extraction mother liquor reaches 1.410g / mL or 42 ? When Be', slowly raise the temperature to 105°C at a rate of 0.1°C / min; ? When Be', 2.60t concentrated liquid and 1.83t condensed water A are obtained respectively.
[0037] (2) Move the concentrated solution to the crystallizer, and carry out constant temperature evaporation and crystallization at a temperature of 120°C. When the solid-to-liquid ratio is 2g:1L, 1.56t of slurry and 1.04t of condens...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com