Method for preparing porous carbon based nanomaterial through carbon dioxide conversion
A technology of nanomaterials and carbon dioxide, applied in the direction of carbon nanotubes, nanocarbons, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of poor controllability of carbon-based nanomaterials, and achieve the effect of simple and controllable preparation process, easy industrial production, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
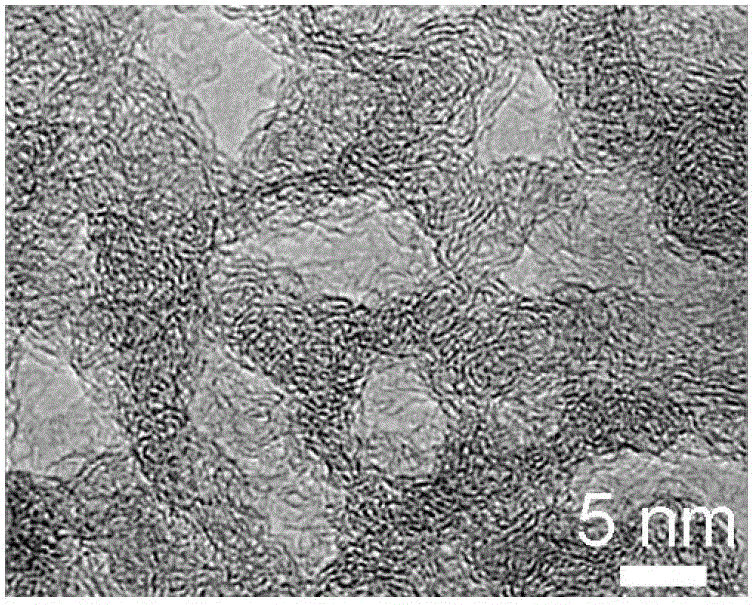
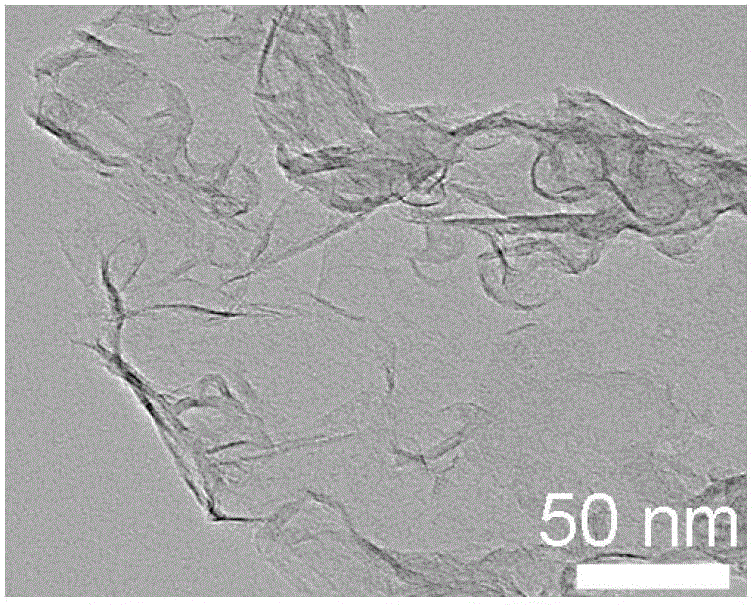
[0028] Place the magnesium metal powder in a high-temperature furnace, raise it to 600°C at a heating rate of 10° / min under an argon protective atmosphere, and then introduce CO 2 Atmosphere, CO 2 The ratio of flow rate to Ar gas is 1:1, CO is turned off after 30 minutes of reaction 2 Airflow, cooling to room temperature in an argon atmosphere, black powder is obtained. The resulting black powder is reacted with a hydrochloric acid solution with a concentration of 8 mol / L for 12 hours, then fully washed with deionized water to neutrality, and dried to obtain porous graphene. among them Figure 1a Shows that graphene has a sheet-like structure, Figure 1b It shows that graphene has a rich pore structure. Figure 2a Is an atomic force microscope photo of porous graphene, Figure 2b It is proved that the thickness of the graphene sheet is about 0.7nm. image 3 The middle curve (a) is the pore size distribution diagram of porous graphene, with an average pore size of 7.9 nm.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Put the metal magnesium powder in a high-temperature furnace, raise it to 500°C at a heating rate of 5° / min under an argon atmosphere, and then introduce CO 2 Atmosphere, CO 2 The ratio of flow rate to Ar gas is 4:1, and CO is turned off after 60 minutes of reaction 2 Airflow, cooling to room temperature in an argon atmosphere, black powder is obtained. The obtained black powder is reacted with a nitric acid solution with a concentration of 2mol / L for 24h, and then fully washed with deionized water to neutrality, and dried to obtain porous graphene.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Place the metallic magnesium strip in a high-temperature furnace, and raise it to 650°C at a heating rate of 8° / min under an argon atmosphere, and then introduce CO 2 Atmosphere, CO 2 The ratio of flow rate to Ar gas is 1:4, and CO is turned off after 5 minutes of reaction 2 Airflow, cooling to room temperature in an argon atmosphere, black powder is obtained. The obtained black powder is reacted with a sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 6 mol / L for 20 hours, and then fully washed with deionized water to neutrality, and dried to obtain porous graphene.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com