Method for preparing submillimeter hydryoxyapetite crystal with regular shape
A submillimeter-scale technology of calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc. Large size calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate crystals, fast crystal nucleation speed and other problems, to achieve the effects of regular crystal shape, low toxicity and simple installation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Step 1. Prepare 25 grams of aqueous solution containing 0.16 moles per liter of L-glutamic acid, 0.043 moles per liter of disodium hydrogen phosphate and 0.070 moles per liter of sodium hydroxide, stir at room temperature to make it completely dissolve, add 20 grams of ice, and then Add L-arginine, urea and calcium nitrate successively so that their concentrations are respectively 0.026 moles per liter, 0.056 moles per liter and 0.026 moles per liter;
[0021] Step 2. Add the uniformly stirred mixed solution into a 50 ml stoppered colorimetric tube, react at 37oC for 24 hours and then cool to room temperature;
[0022] Step 3. The product obtained by the reaction in step 2 is filtered, washed and dried to prepare calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate crystals.
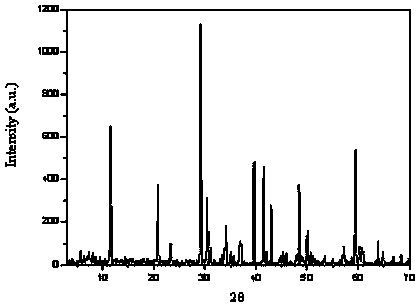
[0023] The product was identified as calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate through X-ray powder diffraction (see figure 1 ). SEM scanning electron microscope inspection product morphology (see figure 2 ).
Embodiment 2
[0025] Step 1. Prepare 25 grams of aqueous solution containing 0.16 moles per liter of L-glutamic acid, 0.043 moles per liter of disodium hydrogen phosphate and 0.070 moles per liter of sodium hydroxide, stir at room temperature to make it completely dissolve, add 20 grams of ice, and then Add L-arginine, urea and calcium nitrate successively so that their concentrations are respectively 0.026 moles per liter, 0.056 moles per liter and 0.026 moles per liter;
[0026] Step 2. Add the uniformly stirred mixed solution into a 50 ml stoppered colorimetric tube, react at 37oC for 6 hours and then cool to room temperature;
[0027] Step 3. The product obtained by the reaction in step 2 is filtered, washed and dried to prepare calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate crystals.
[0028] SEM scanning electron microscope inspection product morphology (see image 3 ).
Embodiment 3
[0030] Step 1. Prepare 25 grams of aqueous solution containing 0.16 moles per liter of L-glutamic acid, 0.043 moles per liter of disodium hydrogen phosphate and 0.070 moles per liter of sodium hydroxide, stir at room temperature to make it completely dissolve, add 20 grams of ice, and then Add L-arginine, urea and calcium nitrate successively to make the concentration respectively 0.038 mole per liter, 0.056 mole per liter and 0.026 mole per liter;
[0031] Step 2. Add the uniformly stirred mixed solution into a 50 ml stoppered colorimetric tube, react at 37oC for 24 hours and then cool to room temperature;
[0032] Step 3. The product obtained by the reaction in step 2 is filtered, washed and dried to prepare calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate crystals.
[0033] SEM scanning electron microscope inspection product morphology (see Figure 4 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com