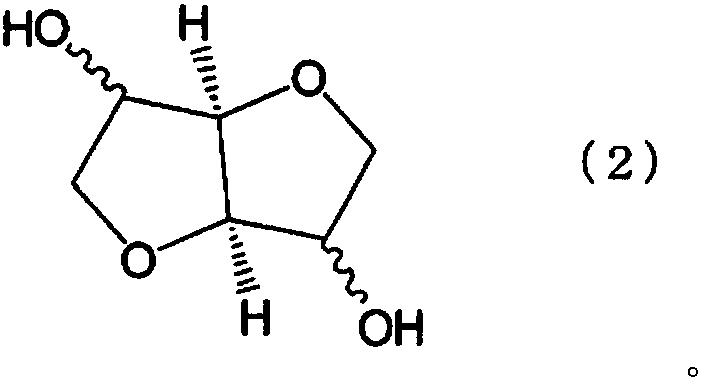
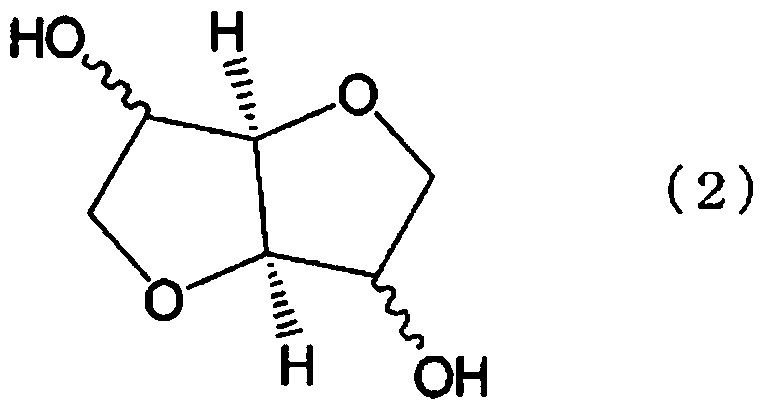
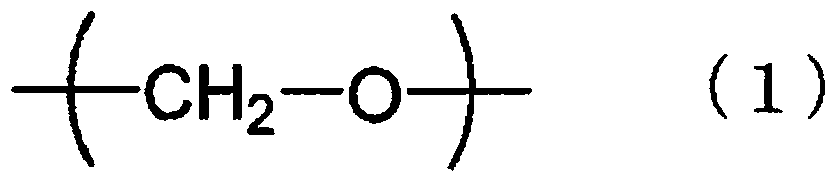Manufacturing method of polycarbonate resin
A technology of polycarbonate resin and manufacturing method, which is applied in the direction of instruments, optical components, optics, etc., can solve the problems of poor thermal stability of raw materials, decline of polycarbonate resin commodity value, poor thermal stability of dihydroxy compounds, etc., and achieve excellent transparency sex, excellent hue effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0198] Isosorbide (ISB) in a solid state and tetramethylammonium hydroxide pentahydrate ( TMAH), disodium hydrogen phosphite pentahydrate of 1 weight ppm, heated with a heat medium. Stirring was started when melting started and stirring was possible, the entire amount was uniformly melted, and the inner temperature was brought to 80°C. After 12 hours from the start of melting, the ISB in the molten state was sampled in a porcelain plate, water-cooled to solidify, then heat-sealed in an aluminum laminated bag under nitrogen gas, and stored in a refrigerator.
[0199] The obtained samples were subjected to various analyzes according to the methods described above. The nitrogen atom content of ISB was 3.7 wtppm, and the sodium atom content was 0.2 wtppm. The amount of formic acid contained in ISB was 1.3 ppm by weight, furfural was 13 ppb by weight, pH was 7.7, and solution YI was 0.55.
[0200] The ISB thus obtained was placed in a container equipped with a stirring blade und...
Embodiment 2
[0206] When melting ISB, only 50 weight ppm of TMAH was added with respect to ISB, and disodium hydrogen phosphite pentahydrate was not added, It carried out similarly to Example 1.
[0207] The ISB after melting at 80°C for 12 hours had a nitrogen atom content of 3.8 wtppm and a sodium atom content of less than 0.1 wtppm. The amount of formic acid contained in ISB was 1.2 ppm by weight, furfural was 12 ppb by weight, the pH was 7.4, and the solution YI was 0.51, showing the same level of storage stability as in Example 1.
[0208] After 129 minutes from the start of the reaction in the second polymerization reactor (second tank), the given stirring power was reached. The reduced viscosity of the obtained polycarbonate resin was 0.464 dL / g, the particle YI was 11.3, and the hue was slightly improved compared with Example 1. The results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0210] When melting ISB, only 100 weight ppm of TMAH was added with respect to ISB, and disodium hydrogen phosphite pentahydrate was not added, It carried out similarly to Example 1.
[0211] The ISB after melting at 80°C for 12 hours had a nitrogen atom content of 7.6 wtppm and a sodium atom content of less than 0.1 wtppm. In addition, the amount of formic acid contained in ISB was 1.2 ppm by weight, furfural was 15 ppb by weight, pH was 7.6, and solution YI was 0.54, showing the same level of storage stability as in Example 1.
[0212] After 108 minutes from the start of the reaction in the second polymerization reactor (second tank), the given stirring power was reached. The reduced viscosity of the obtained polycarbonate resin was 0.474 dL / g, the particle YI was 13.4, and the hue was about the same as that of Example 1. The results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com